本文目录
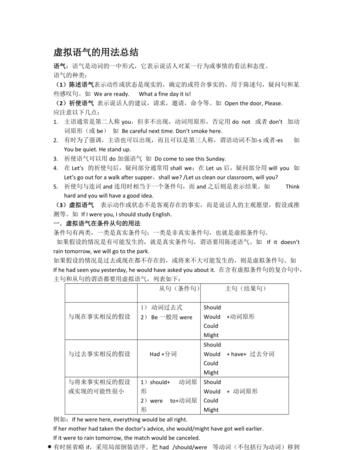
我的虚拟语气
虚拟语气
一、概念
[Subjunctive Mood]
中文译作"虚拟语气"。它是一种动词形式,表示说话人的某种假设、愿望、怀疑、猜测、建议等含义。
二、语法结构
1.if结构(非真实条件句——表示的是假设的或实际可能性不大的情况)
与..事实相反 If从句 主句
过去 Had done Would* have done
现在 Were/did Would* do
将来 Should do/were/were to do Would* do
例句:If there hadn’t been much rain in spring, we would have had a good harvest now. [过去]
If he smoked less, his cough might be well soon. [现在]
If the lecturer should be late, you would have to make a speech first. [将来]
备注:
(1)上表中’*’,would都可转换为should、could、might。
(2) 如果为时间错综句的话,左右两栏可互相搭配,排列组合。
例句:
He would still be alive today if he hadn’t taken that drug.
[与现在事实相反] [与过去事实相反]
(3) if可转换为其他形式
例句:Without your advice, our meeting wouldn’t have been so successfully. [过去]
(=>可转换为:If there hadn’t been your advice, we …)
Your notes are almost illegible (难以辨认的). Notes typed out would be a lot easier to read. [将来]
(=> 可转换为:If the notes had been typed out, it would be a lot easier to read.)
I should have gone to see Dr. Smith and he might have cured me of the disease.[过去]
(=> 可转换为:If he have gone to see Dr. Smith, he ..)
2、wish结构
与..事实相反
过去 Had done
现在 Were/did
将来 Would
备注:可转换为其他形式。
例句:He talks as if (好像) he had done all the work himself. [过去]
I wish I were a bird.
I wish he handn' done that.
I wish I would be rich in the future.
3、should结构
从句中用“should + 动词原形”构成。而且should可以省去。用于此结构的动词有:advise, direct, agree, ask, demand, decide, desire, insist, order, prefer, propose, request, suggest,intend等。
例句:The teacher suggest he (should) read English aloud.
注意:当insist表示“坚持认为”、suggest表示“表明,显示”时,不用虚拟语气。
例句:The look on his face suggested that he was quite satisfied with what I had done for him.
He insisted that he was honest.
4、would rather +从句
在这种结构中,从句的谓语动词用过去形式表示虚拟。
例句:I would rather you did this instead of me.
5、主语从句中的虚拟语气
1)It be + 形容词 + that ...(should)...
用于该句型的形容词是:necessary, good, important, right, wrong, better, natural, proper, funny,
strange, surprising .
一些名词也可以用于 在该结构中。如:a pity, no wonder....
2)It be + 过去分词 + that ...(should)....
用于该结构中的过去分词是表示“建议、请求、命令”等词的过去分词。如:desired, suggested, requested,
ordered, proposed等。
3)It is time(about time, high time)that ...(过去式动词形式或should+动词原形)....
It is high time I went home now. = It is high time I should go home now.
6、表语从句、同位语从句中的虚拟语气
在suggestion, proposal, order, plan, idea, advice, decision等需要有内涵的名词后面的表语从句、同
位语从句中,要使用虚拟语气。其谓语动词应用:should+原形动词。另外连接从句的that不能省
略。
例:My suggestion is that we should go there at once.
What do you think of his proposal that we should put on a play at the English evening?
三、使用范围及判断
1、虚拟语气表示一种不能实现的假设。该语法主要用于if条件状语从句。也可用于主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句等。
2、if条件状语从句中虚拟语气的判断
判断是真实条件句还是非真实条件句。只有在非真实条件句中才使用虚拟语气。通过句子意思,看假设的条件是否能够实现,能够实现是真实条件句,不能使用虚拟语气;假设的条件不能实现则是非真实条件句,要用虚拟语气。
判断这个假设是与哪个事实相反。通常有三种情况:①与过去事实相反。②与现在事实相反。③与将来事实可能相反。
3、“后退一步法”
后退一步法是指在准确地判断了该句与哪一事实相反后,按虚拟语气的后退一步法处理从句谓语动词的时态。即:在非 真实条件状语从句中,谓语动词按正常情况“后退一步”。也就是:
1)与过去事实相反,在从句中用过去完成时形式表示。
2)与现在事实相反,在从句中用过去一般时形式表示。
3)与将来事实可能相反,在从句中用过去将来时形式表示。
主句中则用情态动词would, should, could 等加一个与从句一致的动词形式。
例:If I had come her yesterday, I would have seen him.
If I were a teacher, I would be strict with my students.
If it should snow tomorrow, they couldn’t go out.
四、注意事项
1.if条件句中如有were, should, had,可以省去if,并使用倒装语序。
2、在现代英语中if条件状与从句中的谓语动词如果是be其过去形式一般用were。
3、wish 后面宾语从句中的虚拟语气,按“后退一步法”处理从句的谓语动词。注意:与哪个事实相反,不能以主句的时态为判断依据,而是根据从句的意义判断。
我学不会英语怎么办
条件是否能够实现,能够实现是真实条件句,不能使用虚拟语气;假设的条件不能实现则是非真实条件句,要用虚拟语气。
判断这个假设是与哪个事实相反。通常有三种情况:①与过去事实相反。②与现在事实相反。③与将来事实可能相反。
3、“后退一步法”
后退一步法是指在准确地判断了该句与哪一事实相反后,按虚拟语气的后退一步法处理从句谓语动词的时态。即:在非真实条件状语从句中,谓语动词按正常情况“后退一步”。也就是:
①与过去事实相反,在从句中用过去完成时形式表示。
②与现在事实相反,在从句中用过去一般时形式表示。
③与将来事实可能相反,在从句中用过去将来时形式表示。
主句中则用情态动词would, should, could 等加一个与从句一致的动词形式。例:
⑴、If I had come her yesterday, I would have seen him.
⑵、If I were a teacher, I would be strict with my students.
⑶、If it should snow tomorrow, they couldn't go out.
4、注意事项
①if条件句中如有were, should, had,可以省去if,并使用倒装语序。
②在现代英语中if条件状与从句中的谓语动词如果是be其过去形式一般用were。
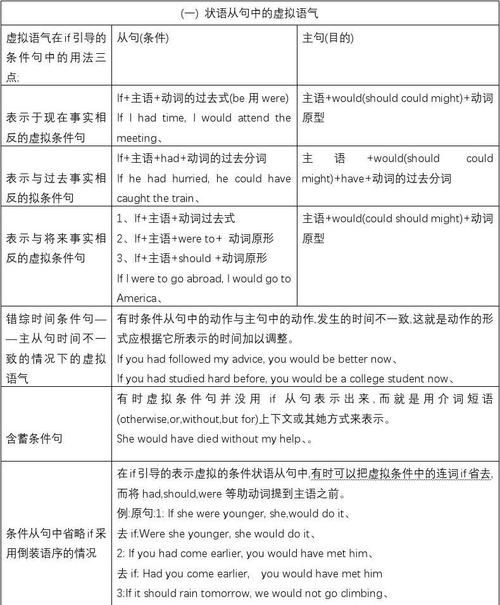
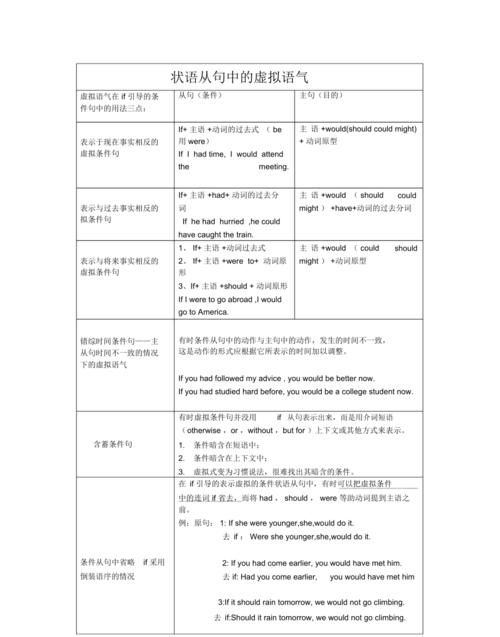
二、虚拟语气在if 引导的条件句中的用法:
(一)、表示与现在事实相反的情况。其句子结构为:
从句:if + 主语+ 动词的过去式(be 用were) + ……
主句:主语+ would (should, could , might) + 动词原形+ ……
例:
1.If I were you, I would go with him.
2.If the weather were fine, I would go there.
如果天气好,我去那儿。(事实天气不好)
3.If I were you, I would read it again.
如果我是你的话,我再读一遍。(事实上我不是你)
4.If time permitted, I would write it again.
如果时间允许的话,我再写一遍。(事实上时间不允许)
5.If it weren’t snowing, we wouldn’t stay in the house.
要是现在不下雪的话,我们就不会待在屋里。(事实上现在下雪)
6.What would I do if I were in your place?
要是我处于你地位我会怎么办?(事实上我不在你的位置上)
7.If he hurried, he could catch the first bus.
他要是快点能够赶上头班公共汽车。(可是他不着急)
8.If it weren’t for your help, we would get into trouble.
如果没有你们的帮助,我们就会陷入困境。(而事实上得到了你们的帮助)
9.If we had the manpower, we could open up even more land.
如果有人力,我们还能开更多的荒地.
10. If I were you, I would go with him.
(从句If I were you, 主句I would go with him.)
11. If I were you, I should buy it.
(从句用过去式动词were,主句用动词原形buy)
12. If I had time, I would study French.
(如果有时间,我会学习法文。)(从句用过去式动词had,主句用动词原形study)
13. If she knew English, she would not ask me for help.
(如果她懂英文,她就不必要我帮了。)(从句用过去式动词knew, 主句用动词原形ask)
注意:如果动作在进行中,主句要用:"主语+ would be + 进行式动词+ ……"
14. If they were here, he would be speaking to them now.
(从句用过去式动词were, 主句用would be speaking)
(二)、表示与过去事实相反的虚拟条件句。其句子结构为:
从句:If + 主语+ had +过去完成式动词+ ……
主句:主语+ would (should, could, might) + have +过去完成式动词+……
例如:
⑴、If you had taken my advice, you would not have made such a mistake.如果你听了我的劝告,就不会犯这样的错误。(事实上你没有听我的劝告)
⑵、I shouldn’t have been able to write such good novels if I hadn’t lived among the peasants for five years.如果我不是和农民生活了五年,就不可能写出这样好的小说。(事实上我和农民生活了五年)
⑶、If you hadn’t invited me, I shouldn’t have come to the party.如果你不邀请我,我就不会来参加你的舞会。(事实上你邀请了我)
⑷、If it hadn’t been for your help, I shouldn’t have finished this work on time. 要是没有你们的帮忙,我就不会按时完成了这项工作。(事实上你们帮助了我)
⑸、If he hadn’t broken the law, he wouldn’t have been put in prison.如果他不违法的话,就不会被打入监狱。(事实上他违法了)
⑹、If I hadn’t been ill yesterday, I might have come to school.昨天要是不生病,我是可能来上学的。(事实上我生病了)
⑺、If I had been your headmaster, I should have dismissed you from school. 我要是你们校长的话,就把你开除学籍了。(事实上我不是)
⑻、 If you had studied harder last term, you could have passed exam.(从句动词用had studied, 主句动词用have passed)如果你在上个学期用功一些,你就会在考试中过关了。
⑼、 If you had taken my advice, you wouldn't have failed in the exam.(从句动词用had taken, 主句动词用have failed)如果你当时听从我的劝告的话,你就不会在考试中失败了。
⑽、 If you had got up earlier, you could have caught the train.(从句动词用had got up, 主句动词用have caught)如果你起身得早一点,你就会赶得上火车了。
⑾、 If it had snowed, I would have skied in the park.(从句动词用had snowed, 主句动词用have skied)如果下雪的话,我就可在公园里滑雪了。
注意:如果动作在进行中,主句要用:"主语+ would + have + 完成进行式动词 +……
⑿、 If they had been here, he would have been speaking to them.(从句动词用had been, 主句动词用have been speaking)
(三)、表示与将来事实相反的虚拟条件句(对将来的事实实现的可能性不大)。其句子结构为:
从句:If + 主语+ should (或were) + 动词原形+……
主句:主语+ would (could, should, might) + 动词原形+……
例如:
⑴、If I were to work at this problem, I would do it in another way.要是我来解这道难题,我会用另外一种方法的。
⑵、If you were to do such a thing again, you would be punished. 如果你再做这样的事情,就会受到惩罚。
⑶、If I should work harder, I could make much more progress.假如我更努力学习的话,我会取得更大的进步。(事实上我不可能努力学习)
⑷、If it should rain tomorrow, I would stay at home.如果明天下雨的话,我将待在家里。(根据天气情况,明天不可能下雨)
⑸、If he should come, I could ask him for some advice.万一他来了,我就能够向他请教。(事实上他来的可能性很小)
⑹、If he came tomorrow, I would do it with him.如果明天他来的话,我将和他一起做此事。(事实上他来的可能性很小)
⑺、 If it should rain, the crops would be saved.(从句动词用should rain,主句动词用be)如果天下雨,庄稼可能就收获了。
⑻、 If he were to go fomorrow, he might tell you.(从句动词用were to, 主句动词用tell)如果明天他走的话,他可能会告诉你。
⑼、 If he were here, I would give him the books.(从句动词用were, 主句动词用give)如果他在这儿,我可能会把书给他。
注意:如果动作在进行中,从句(不是主句喔)要用:"If + 主语+ 过去进行式动词 +……"
⑽、 If she were staying here now, I would let her ride my horse.(从句动词用were staying, 主句动词用let)如果她现在留在这儿,我可能会让她骑我的马。
三、混合条件句----主从句时间不一致情况下的虚拟语气
有时条件从句中的动作和结果与主句中的动作,发生的时间不一致,这时动作的形式应根据它所表示的时间加以调整。如:
1. 从句表示过去,主句表示将来:
⑴、If they had started the early morning yesterday, they would be here now.
⑵、If we hadn' t made adequate preparations, we shouldn' t dare to do the experiment next week。
2. 从句表示将来,主句表示过去:
⑴、If I were not to make a preparation for my experiment this afternoon, Iwould have gone to see the film with you last night.
3.从句表示过去,主句表示将来:
⑴、If we hadn't made adequate preparations, we shouldn't dare to do theexperiment next week.
4.从句表示将来,主句表示现在:
⑴、If we shouldn't have an exam this afternoon, I would go shopping now.
5.从句表示过去,主句表示现在。
⑴、If they had stared the early morning yesterday, they would be here now.
⑵、If you had followed my advice, you would be able to finish the work now.
如果你当时听了我的话,现在就能完成这份工作了。(从句说明过去,主句说明现在。)
6.从句表示现在,主句表示过去
⑴、If I were you, I would have gone to her birthday party.如果我是你,我就去参加她的生日晚会了。(从句说明现在,主句说明过去。)
7.从句表示过去,主句表示过去和现在
⑴、If you hadn’t lent me some money, I couldn’t have bought the new house and most likely I would be still living in the dangerous house now.
假若你不借钱给我,我不可能买下这幢新房,很可能现在还住在危房里。(从句说明过去,主句说明过去和现在。)
四、含蓄条件句
非真实条件句中的条件从句有时不表出来,只暗含在上下文中,这种句子叫做含蓄条件句。含蓄条件句大体有三种情况;
1. 条件暗含在短语中。如:
(1)、What would I have done without you? 如没有你,我会怎么办呢?(条件暗含在分词短语without you中)
(2) 、It would be easier to do it this way. 这样做会比较容易。(条件暗含在不定式短语to do it this way中)
(3) 、This same thing, happening in wartime, would lead to a disaster. 同样的事,如发生在战时,就会酿成大祸。(条件暗含在分词短语happening in wartime中)
(4)、 But for your help we couldn’t have succeeded in the experiment. 如果没有你的帮助,我们的实验是不会成功。(暗含条件是but for your help)
(5)、 He must have the strength of a hippopotamus, or he never could have vanquished that great beast. 他一定是力大如河马,否则他绝不会击败那只庞大的野兽。(暗含条件是连词or)
(6)、 Alone, he would have been terrified. 如是单独一人,他是会感到害怕的。(暗含条件是alone)
2. 条件暗含在上下文中。如:
(7)、 You might stay her forever. 你可以永远待在这儿。(可能暗含if you wanted to)
(8) 、We would have succeeded. 我们本来是会成功的。(可能暗含if we had kept trying)
(9) 、Your reputation would be ruined. 你的名誉会败坏的。(可能暗含if you should accept it)
(10) 、I would appreciate a little of your time. 谢谢你给我一点时间吧。(可能暗含if you were so kind as to give me a little of your time)
3. 在不少情况下,虚拟式已变成习惯说法,很难找出其暗含的条件。如:
(11) 、You wouldn’t know. 你不会知道。
(12) 、I would like to come. 我愿意来。
(13) 、I wouldn’t have dreamed of it. 这是我做梦也不会想到的。
(14) 、He told the story in such minute detail that he might himself have been an eye-witness. 他将那事讲的非常仔细,简直就象他亲眼看见一样。
五、条件从句中省略if 采用倒装语序的情况
1、在if引导的表示虚拟的条件状语从句中,有时可以把含有助动词、情态动词、be或have的虚拟条件句中的连词if 省去,而将had , should, were 等词提到主语之前,即用倒装结构。
例如:
1). 原句:If she were younger, she would do it.
去If:Were she younger, she would do it. (把动词were移到主语she的前面)
2). 原句:If he had tried it, he could have done it.
去If:Had he tried it, he could have done it.(把had移到主语he的前面)
3).Had he worked harder, he would have got through the exams.
4).Were he to leave today, he would get there by Friday.
5).Were I in your place, I wouldn’t do that.
6).Had I seen the film, I would have discussed it with them last night.
假如我看了那部电影,昨晚我就可以和他们一起讨论了。
7).Were I a bird, I could fly freely.
假如我是一只小鸟,我就能自由翱翔。
8).Should it rain next week the farmers would have a good harvest.
要是下周能下雨的话,农民们就能有个好收成了。
2、如果虚拟条件句中有were, had或should时,把它们放在if的位置上;但是如果条件句中没有were, had或should不能用倒装。例如:
⑴、Should it rain tomorrow, what should we do? 要是明天下雨的话,我们怎么办呢?
⑵、Were I you, I would have asked him for some advice.要是我是你的话,我就向他请教了。
⑶、Were he to do this work by himself, he would get a lot of money.如果他自己能够做此工作,他就会得到一些钱。
3、在“开放式条件句”(open conditional clause)和让步状语从句中should是被省略了的。在这种情况下,如果if省略,动词be与主语的位置要倒装。如:
⑴、If any person be guilty of a crime, the court shall have the right to appeal. (任何人犯罪,法院有权起诉。)
Be any person guilty of a crime, the court shall have the right to appeal.
⑵、Whether she be right or wrong, she will have my unanswering support. (不管她是对还是错,我都会支持她的。)
Be she right or wrong, she will have my unanswering support.
⑶、____ ,I will take her as my wife.
〔A〕Were she rich or poor
〔B〕Being rich or poor
〔C〕Be she poor or rich
〔D〕Whether is she poor or rich
4、注意:有时虚拟条件句并没来if 从句表示出来,而是用介词短语(otherwise, or, without, but for)、上下文或其它方式来表示。
⑴、We didn't know his telephone number; otherwise we would have telephoned him.
⑵、Without you help, I wouldn’t have achieved so much.
⑶、But for your help, I would not have succeeded.
六、有时虚拟条件句的从句或主句都可以省略其中一个:
1. I could help you. (只有主句)
2. If I had time. (只有从句)
3. She should have come to the meeting. (只有主句)
4. If he had much more money. (只有从句)
第二节:其他形式的条件句中的虚拟语气
一、用“without/but for/in the absence of ”表示“要不是”,“如果没有”(相当于if it were not
for…)表示条件时,句中一般用虚拟语气。(也可用陈述语气)
Without your help, I couldn' t finish my work on time.
In the absence of water and air, nothing could live.
二、由“providing (that)/ provided (that)/on condition that/ in order
that”引导的条件从句或目的从句,根据情况,可用虚拟语气。(有时也可用陈述语气)
They are willing surrender provided they are given free passage.
三、用without / but for / in the absence of 表示"要不是"、"如果没有",表示条件虚拟句:
(1). Without air, nothing could live.要是没有空气,什么也不能生存。
(2). But for your assistance, we could not accomplish it.要不是你的帮忙,我们是难有成就的。
(3). In the absence of water and air, nothing could live.如果没有水和空气,什么也不能生存。
第五部分:其他几种情况下的虚拟语气
第一节:虚拟语气在as if / as though 引导的方式状语从句中的应用
虚拟语气在as if / as though 引导的方式状语从句中,谓语动词形式与wish后的宾语从句基本相同
1.表示与现在事实相反或对现在情况有怀疑,谓语动词用过去式。例如:
(1) .He felt as if he alone were responsible for what had happened.他感到仿佛唯独他要对发生的一切负责。
(2). He acts as if he were / was a TV expert.他做起事来好象是个电视专家。
(3).Alan talked about Rome as if he were a Roman.艾伦谈起罗马来好像他是个罗马人一样。
(4).John pretends as if he didn' t know the thing at all, but in fact he knows it very well.(用过去式表示与现在事实相反的假设)
(5). He pretends as if he didn't know the thing at all, but in fact he knows it very well.(用过去式表示与现在事实相反的假设)他假装好象完全不懂那事,其实他对那事非常了解。
2. 表示过去想象中的动作或情况,谓语动词用过去完成式。如:
(1).The tree looked as if it ______ for a long time.
A. hasn't watered B. didn't water
C. hadn't bee watered D. wasn't watered
那棵树看上去好象很久没人给浇水了。(答案是c)
(2).The old man looked at the picture, he felt as though he had gone back to time 20 years ago.(用过去完成式表示与过去相反的事实)
(3). The old man looked at the picture, he felt as though he had gone back to time 20 years ago.(用过去完成式表示与过去相反的事实)那老人看着照片,他觉得仿佛回到20年前的时光。
3.表示与将来事实相反:
(1).They talked and talked as if they would never meet again (would+动词原形,表示与将来事实相反)
(2). They talked and talked as if they would never meet again.(would + 原形动词meet,表示与将来事实相反)他们谈了又谈,仿佛他们不会再相见的样子。
注: 在as if / as though 句中, 如果有可能成为事实, 用陈述语气.
He looks as if he is going to be ill.
第二节:虚拟语气用在lest,for fear that及in case引导的目的状语从句中
在由lest等引导的目的状语从句中需用虚拟语气,表示“以防,以免”等意思,其谓语动词多由should +动词原形构成,should也可省略。
例如:
⑴、He was punished lest he should make the same mistake again.他被处以惩罚以免他再犯。
⑵、The mad man was put in the soft-padded cell lest he _____ himself.
a. injure b. injured c. had injure d. would injure
这个疯子被关进墙上装有衬垫的病房,以免伤了他自己。(答案是a)
第三节:介词短语表示虚拟
有时假设的情况并不以条件从句表示出来,而是通过一个介词短语来表示,或通过上下文或其他方式表示出来。如but for, but that…, in case of, otherwise, supposing, under more favourable condition, without 等表示让步假设。
1).He worked very hard; otherwise he might have failed. (他刻苦工作,不然他就失败了。)
2).We could have done better under more favorable conditions.(假设我们有更有利条件,我们还会做得更好。)
3). But for his help,I .
〔A〕should not have succeeded
〔B〕had not succeeded
〔C〕did not succeed
〔D〕have not succeeded
4). But that he came to help me, I .
〔A〕could not have succeeded
〔B〕did not succeed
〔C〕could not succeed
〔D〕can’t but succeed
第四节:虚拟语气用在It is(about /high)time +that定语从句中
在It is(about/high)time +that定语从句中需用虚拟语气,表示“该做……的时候了”,其动词形式用一般过去时或should +动词原形。
(1).It's already 5 o'clock now.Don't you think it's about time we went home?现在已经5点钟了,你不认为我们应该回家了吗?
(2).It is about time you were in bed.
(3).It is high time we left.
(4).It is the first time I came here.
注:
1、在this is the first time /second time that...句型中,从句中谓语动词用陈述语气完成时态。
例如:
Is this the first time that you have visited Hongkong?这是你第一次参观香港吗?
2、It's time to do something有别于It's time that...
第五节:在if only 引起的感叹句中需用虚拟语气
谓语动词用过去式或过去完成式(谓语动词与wish宾语从句的虚拟形式相同).
⑴、If only he didn’t drive so fast! (现在)
⑵、If only she had asked someone’s advice.(过去)
⑶、If only the rain would stop.(将来)
例题解析:
⑷、Look at the terrible situation I am in! if only I ____ your advice.
A. follow B. had followed C. would follow D. have followed
if only 引出感叹句,意思是“要是……多好”,表示说话人的一种愿望,希望发生(事实上不可能发生)与过去事实相反的情况。本句的全句意思是:“看我现在的处境多糟糕!要是我听从你的劝告多好”。事实上,句中的“我”没有听从劝告,所以处境很糟糕。
题中空格处应当用虚拟语气,答案是B。
虚拟语气语法总结笔记
多数中国人对虚拟语气的理解是:虚拟语气表示说话人的愿望,是假设的,虚构的,与事实相反的,或者是不太可能的。这种理解固然是对的,但并不全面。在英语中,虚拟语气是个广义的概念,包括好几种句型和结构。假设,意愿等只是虚拟语气的两个方面。
英汉两种语言表达虚拟语气的方式差异:
而在英语中,虚拟语气是通过句子中谓语动词的特殊形式来表示的。这又一次证明动词在英语中的核心地位,又一次证明要学好英语语法,就要学好英语动词。由于虚拟语气是通过句子中谓语动词的特殊形式来表示的,因此,掌握虚拟语气中所使用的各种谓语动词形式变化是掌握虚拟语气的关键,这也是虚拟语气的难点。虚拟语气本身也是英语语法的一个难点。
学习虚拟语气的方法是分别弄通虚拟语气的各种句型和结构,各个击破。下面对虚拟语气在各种句式中的用法分别介绍。
(一)虚拟语气用于表示假设的条件状语从句,状语从句相当于汉语的“假如…” “要是…”等。
请看一个句子:
If she invites me tomorrow, I shall go to the party. 如果她明天邀请我参加聚会,我就去。
这是个带条件从句的主从复合句,是直接的陈述语气,主句谓语动词用将来时,从句谓语动词用现在时代替将来时,表示能实现的动作。这句话说明说话人认为邀请的可能性较大。此句的条件是“只要她邀请我”,“去”这一动作就能实现。
请把这句话与下面虚拟语气的带条件从句的主从复合句进行比较:
1) If she invited me, I should go to the party. 假如她邀请我参加聚会,我就去。(说话人认为邀请的可能性较小或不可能。)
这句话主句谓语动词用过去将来时,从句谓语动词用一般过去时,其含义是:
She will probably not invite me, so I shall not go to the party. 她很可能不会邀请我参加聚会,所以我不会去。
2) If she had invited me yesterday, I should have gone to the party. 假如她昨天邀请我参加聚会,我就去了。
这句话主句谓语动词用“should + have + 过去分词”形式,从句用过去完成时,对过去发生的事情进行虚拟假设,表示与过去事实相反的情况,其含义是:
She didn’t invite me yesterday, so I didn’t go to the party. 她昨天没有邀请我参加聚会,因此我没有去。
3) If she should invite me tomorrow, I should go to the party. 如果她明天邀请我参加聚会,我会去的。
这句话主句谓语动词用过去将来时,从句谓语动词也用过去将来时,表示的意思是,“邀请我”的可能性较小,对将来要发生的情况表示怀疑。其含义是:
It is unlikely that she will invite me tomorrow, so I shall not go to the party. 明天她不可能会邀请我,因此我不会去。
从以上例句可以看出:虚拟语气的条件句是用谓语动词的特殊形式来表示与现在、过去事实相反的情况或对将来发生的情况表示怀疑,和直陈语气条件句的谓语动词形式以及所表达的含义完全不同。虚拟语气条件句中所用的谓语动词过去式、过去完成式、过去将来式等只表示不同的虚拟语气,与直陈语气句子的过去时、过去完成时等毫无关系,在学习时应注意加以区别,不要混淆。
现将虚拟语气在条件句中的各种具体形式和用法分述如下:
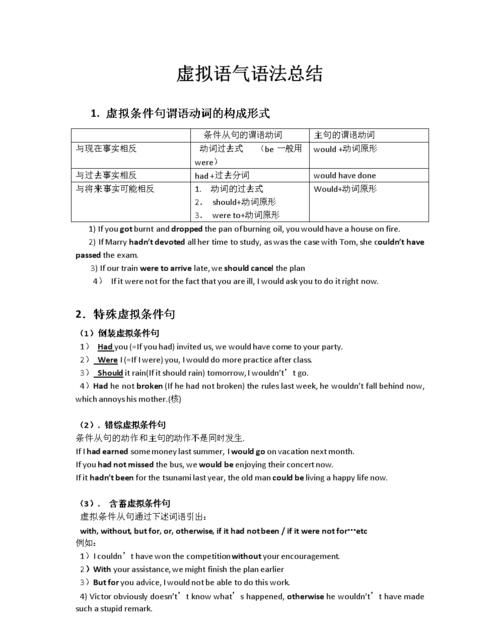
1、 对现在的虚拟,表示与现在事实相反的假设时,条件状语从句的谓语动词用过去式(be的过去式用were.而主句中的谓语动词用would (should, could, might) + 动词原形。见下表:
条件状语从句的动词形式
主句的动词形式
If+主语+动词过去式(be的过去式were.在口语等非正式场合中,I,he,she,it等后面也可用was.但在If I were you中,一定要用were,不能用was.
I (we)should+动词原形
主语+would (might,could)十动词原形
例句:
If I were you, I should study English.
(fact: I am not you, so I shall not study English.)
If he had time, he would attend the meeting.
(fact: He does not have time, so he will not attend the meeting.)
If they didn’t take physical exercises every day, they wouldn’t be so healthy.
(fact: They take physical exercises every day, so they are very healthy.)
If you went to bed earlier, you would not be so sleepy in the morning.
(fact: You often go to bed late, so you are always sleepy in the morning.)
If this were the case, it would be very awkward.
(fact: This is not the case, so it is not awkward.)
Now let’s do some translation:
要是没有虚拟语气英语就会容易多了。
英语虚拟语气语法总结表格
虚拟语气是什么
在英语中,虚拟语气表示说话人的主观愿望、猜疑、建议或与事实不符的假设等,而不表示客观存在的事实。如:
If I were a bird,I would be able to fly in the air.
如果我是一只小鸟,我就能在空中飞行。
虚拟语气英语语法
虚拟语气是由句中的谓语动词的特殊形式表示出来的。
1、主语从句中的虚拟语气主要取决于某些形容词和过去分词,用来表示建议、命令、要求、惊异和失望等。其形式为:(should)+动词原形。
2、表语从句和同位语从句中的虚拟语气在表示建议、命令、主张、目的和愿望等名词后面的表语从句和同位语从句中谓语动词要求使用虚拟语气。其形式为:(should)+动词原形。
3、宾语从句的动词后所接宾语从句中的谓语动词要求用虚拟语气,用来表示建议、命令和要求等。其形式为:(should)+动词原形。
以上就是英语虚拟语气的语法知识点。在表示假想的虚假的、与事实相反的或难以实现的情况时用虚拟语气,表示主观愿望或某种强烈情感时,也可以用虚拟语气。
以上就是关于虚拟语气语法总结笔记 ,我的虚拟语气的全部内容,以及虚拟语气语法总结笔记 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
