本文目录
判断时态的三种方法有哪些
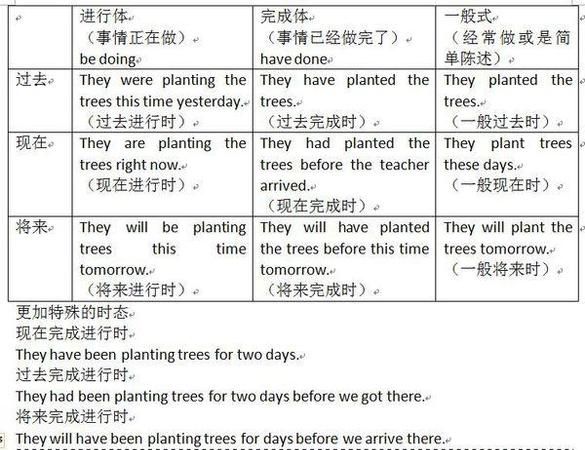
一、根据时间状语与时态的对应关系 动词特定的时态常常与特定的时间状语联系在一起,如由this time yesterday可知用过去进行时;由so far, in the past three years, till now可知要用完成时,等等。
1、句中含有yesterday; last year(last + 具体时间); two days ago(一段时间 + ago); just now; this morning; in 2008(in + 过去的年代); the other day; over the weekend等时间状语时,谓语动词用一般过去时;
2、句中含有tomorrow; next week(next +具体时间); in two hours(in +一段时间); (how) soon; from now on; 10 years from now(一段时间+from now); in the future; in 2012(in +将来的年代); by (the end of) next month(by+将来时间); for the weekend; this afternoon; this evening; tonight; this weekend等时间状语时,谓语动词用一般将来时;
3、句中既有yesterday等过去时间状语,又有一个具体时间点(at 5:00; this time; at that time)时,谓语动词用过去进行时;
4、句中含有recently; in the last/past two years(in the last/past+一段时间); over the years(over the+一段时间); since 2005(since+具体时间或从句); for two years(for+一段时间,句中无其它时间状语); before(单独用于句尾)等时间状语时,谓语动词用现在完成时;
5、by (the end of) last year(by+过去时间); two days before(一段时间+before); for和since说明的时间同时用于句中;by the time + 从句(过去时态)等时间状语时,谓语动词用过去完成时;
6、简单句中如不含上述时间状语或有含说话时间在内的表示现在时间关系的词语时(如now; today; these days等词)解析:由时间状语at this time tomorrow可知用将来进行时,故选B。
二、固定句型与动词时态间的对应关系 在英语中,不少句型与一些动词在时态的运用方面都存在着特定的对应关系,
1.在“祈使句+and/or+陈述句”句型中,陈述句中用will表示的一般将来时;
2.在This/如That/It is t he second time that…句型中用现在完成时,若is改为was,就用过去完成时;
3.在no soon er…than…和hardly…when…句型中,前面常用过去完成时,when/than后的句子用一般过去时;
4.was/were about to do…when…或was/were doing…when…或was/were on the point of doing…when…句型中,when分句的谓语动词用一般过时;
5.在一个含有时间状语从句的主从复合句中,如果主从句的谓语动词都是过去发生的动作,一般来说,表示短暂性动作的动词用一般过去时,表示持续性动作的动词用过去进行时;等等。
Let’s keep to the point or we _______ any decisions.
A. will never reach B. have never reached C. never reach D. never reached
解析:这是“祈使句+or +陈述句”句型,陈述句的谓语要用“will+动词原形”,故选A。
三、根据某些动词与时态的对应关系 在英语里有些动词与时态有着特定的对应关系,如see(看见),hear(听见),find(找到) 等都不可用于进行时态;work表示机器不能正常运行、运转时,常用一般现在时的否定式;open, close, lock等词表示门、窗等不能正常关、开、锁的意思时,常用won’t open /close /lock等,这时它们是以主动形式表示被动意义。
—Can I help you, sir? —Yes. I bought this radio here yesterday, but it _____.
A.didn’t work B. won’t work C. can’t work D. doesn’t work 解析:此处的work是指radio不能正常运行,应用一般现在时的否定式,故选D。
四、根据上下语境来确定时态 在绝大多数情况下,动词的时态是由上下文来决定的,这就要求我们一方面要熟记各种时态的适用范围,另一方面要求我们注意上下文的提示。
— Is this raincoat yours? — No, mine ______ there behind the door.
A.is hanging B. has hung C. hangs D. hung
解析:根据上下文的提示,hang表示的是目前的状态,故选A。
五、主从句时态的一致性原则:主从复合句可根据其时态一致性原则,通过主从句中任意一个句子的时态确定另外一个句子的时态;含有时间状语从句的主从句还可通过其引导词所表示的不同时间关系,确定主句和从句的时态。
时态与英语句型有什么关系吗
1. 一般情况下,同一种英语句型可以用很多种不同的时态。具体用哪种时态需要看时间状语。
比如:There is an apple on the table. 桌子上现在有一个苹果。
There was a pear on the table yesterday. 昨天桌子上有一个梨。
2. 但是某些句型的时态是规定好了的。
如:It is the first time that...,that从句后需要用现在完成时。
It's the first time that I have read this book. 这是我第一次读这本书。
如果把这个句型的is换成was,that从句就要用过去完成时。
又如:no sooner... than...的句型,前面需要用过去完成时,后面用一般过去时。而且前面还得用倒装。
No sooner had I gone outside the classroom than the bell rang. 我刚出教室铃就响了。

英语动词时态思维导图简单
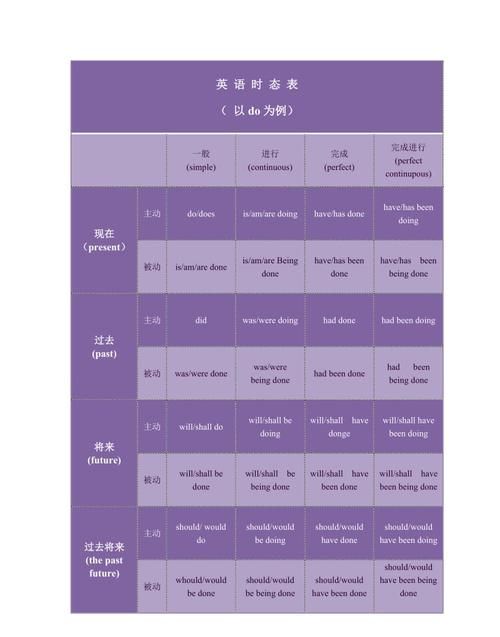
由动作所发生的时间决定,若动作发生在过去,用过去时;若发生在现在,用现在时;若将来才发生,用将来时。
英语中从句时态取决于主句时态吗
这个问题有点大,时态最重要的原则是: 取决于说话的意图,因为除了一般规则限定的原则外,还有“具体问题具体分析的情况
比如,非真实条件状语从句虚拟语气的“对过去的虚拟”,“对现在的虚拟”和“对未来的虚拟”有固定的模式外,还有“错综条件句”,这个就没有什么“规则概念”,如果说“取决于”,那么要取决于“说话人的意图”。

以上就是关于时态是由什么决定的 ,判断时态的三种方法有哪些的全部内容,以及时态是由什么决定的 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

