本文目录
初中英语感官动词的用法
学好了动词,就相当于学好了英语。的确是这样,英语动词在初中阶段可谓举足轻重。那么接下来给大家分享一些关于初中英语常用的动词用法,希望对大家有所帮助。
初中英语常用动词用法:
1. allow sb. to do sth. 允许某人去做某事
My father allowed me to go out for a walk after finishing my homework.
2. asked sb. (not) to do sth. 叫某人做事某事(叫某人不要去做某事)
My father asked me to study hard.He asked me not to swim alone.
be asked to do sth. 被叫去做某事/被邀请去做某事
I was asked to have a dinner with them yesterday.
3. be afraid to do sth. 害怕做某事She is afraid to ask me questions.
4. be afraid of doing sth. 害怕做某事I am afraid of going out at night.
5. be afraid of sth. 害怕某物He is afraid of snakes.
6. be amazed to do sth. 对做某事感到惊讶He was amazed to meet the girl there.
be amazed at sth. 对某事感到惊讶they were amazed at the news
7. be busy doing/with sth. 忙于做某事 (常考)
e.g: I was busy washing my car at that time. 那时候我正忙于清洗我的车子。
I am busy with my work.
8. be coming/going/leaving/flying/moving/dying(某些位移动词用进行时态时表将来)
the bus is coming/the dog is dying.
9. be excited to do sth. 对做……感到兴奋
Jacky was excited to travel there by plane.
be excited at sth.
Lily was excited at his words.
be excited about doing sth.
he was excited about passing the exam without going overing books.
10. be frightened to do sth. 害怕去做某事
Sam is frightened to ride a horse.
11. be glad/happy to do sth. 高兴去做某事
she is happy to clean the blackboard with me.
be pleased to do sth. 高兴做某事
she was pleased to help the old man yesterday
be pleased with sth. 对某事感到高兴/满意
the teacher was pleased with my answer.
12. be interested in sth./doing sth. 对某事感兴趣/对做某事感兴趣
she is interested in swimming in the river.
My brother is interested in Chinese.
13. be/get ready for/to do sth.Be ready for sth. 为某事做好了准备
We are ready for the exam.Be ready to do sth. 为做某事做好了准备
We are ready to have a birthday party for her.
get ready for sth.为某事在做准备
We are getting ready for the exam.
13. be sorry to do sth. 对做某事感到抱歉
14. be surprised to do sth. 对做某事感到惊奇
be surprised at sth. 对某事感到惊奇
15. be worth doing sth. 值得做某事 (worth 后接动词-ing形式,常考)
16. begin to do sth.begin/start to do/doing sth.
17. can/be able to afford (to buy) sth. 有能力购买(供)……
18. can/may/must do sth. could/would/should/might do sth.
19. can't wait to do sth. 迫不急待地去做某事
20. decide to do sth. 决定去做某事
make up one's mind to do sth. 下决心去做某事 (常考)
make a decision to do sth. 对做某事作出决定
21. deserve to do sth. 值得/应该做……
22. encourage sb. to do sth.鼓励某人去做某事
23. enjoy doing sth. 乐意去做某事
24. expect (sb.) to do sth. 期望去做某事
25. fail to do sth. 做某事失败succeed doing sth. 成功做了某事
26. finish doing sth. 做完某事(后接动词-ing形式) (常考)
27. follow sb to do sth. 跟随某人去做某事
28. get sb. to do sth.make sb. do sth.let sb. do sth.
29. get/have a chance to do sth.得到一个做某事的机会
30. give/pass/show/lend/sell sb. sth./ sth. to sb.buy/get/bring sb. sth. / sth. for sb.
31. go on to do sth. 继续做事(常考)
go on doing sth. 继续做事(常考)
32. hate to do/doing sth. 讨厌/不喜欢做某事
33. have fun doing sth.
34. have problems doing sth.做某事遇到困难
35. have sb. do sth.have sth. donehave sth. to do 有事要做
36. hear sb. do sth. 听到某人做某事(后接动词原形,常考)hear sb. doing sth. 听到某人正在做某事(常见)
37. help to do sth. 帮忙做某事help sb. (to) do sth. 帮助某人做某事
38. hope/wish to do sth. 希望做某事wish sb. to do sth. 希望某人做某事
39. I t seems that 这像是……(后接从句)seem to do sth.seem +adj.
40. It's + adj.+(for sb.) to do sth.
It's + adj. +(of sb.) to do sthe.g: It's glad for him to hear the news.
41. It takes sb. some time/money to do sth. 花费某人多长时间做某事(常考)
42. pay …for…costspend…on…..it take …to do sth.
43. It's best for sb to do sth.. 对某人来说做某事是最好的
had better do sth. 最好做某事 (注意had没有时态和人称的变化,better后接动词原形)
44. It's time for sb. to do sth. 是某人做某事的时候了
45. keep (on)doing sth. 坚持做某事(常考)keep sb. doing sth. 让某人做某事(常考)
keep sb. from doing sth. 阻止某人做某事(常考)keep sb./ sth. +adj.
keep the book for 2 days 借这本书两天(不要用borrow或lend)
46. learn to do sth. 学做某事learn sth. from sb. 向某人学习
47. like to do/doing sth. 喜欢做某事like sb. to do sth. 喜欢某人做某事
48. need to do sth.need doing sth./to be doneneed sth .needn't do sth.
49. prefer to do sth. rather than do sth. 宁愿……而不愿……(常考)
prefer doing sth. to doing sth. 喜欢做……胜过做……
e.g: I prefer reading books to going shopping. 比起购物来,我更爱读书。
prefer to do sth. 喜欢(爱)做某事
50. refuse to do sth. 拒绝做……
初中英语动词固定搭配:
1. want to do sth. 想要做某事
I want to buy a new computer this afternoon.
我想今天下午买台新电脑。
2. would like to do sth.想要做某事
I would like to invite you to come to my birthday party this Saturday.
我想邀请你这周六来我的聚会。
3. wish to do sth. 希望做某事
I wish to live on the moon one day.
我希望有一天在月球上生活。
4. help to do sth. 帮助做某事
I often help to do some chores at home.
我在家经常帮着做家务。
5. hope to do sth. 希望做某事
I hope to have a good rest this weekend.
我希望这周末好好休息一下。
6. learn to do sth. 学会做某事
He finally learned to play the piano with the help of the teacher.
在老师的帮助下,他最终学会了弹钢琴。
7. manage to do sth. 设法做成某事
They managed to escape the fire yesterday.
昨天他们设法逃脱了火灾。
8. offer to do sth. 主动提出做某事
Never offer to teach fish to swim.
别在强人面前逞能。
9. plan to do sth. 计划做某事
He plans to travel around the world.
他计划要周游世界。
10. afford to do sth. 负担得起做某事(时间或金钱方面)
We can’t afford to go abroad this summer.
今年夏天我们没有足够的钱 出国 。
11. agree to do sth. 做某事
He agreed to do it at once.
他同意立刻行动。
12. arrange to do sth.安排做某事
I arrange to wash clothes tomorrow morning.
我安排好明天上午洗衣服。
13. ask to do sth. 要求做某事
The boy asks to go to school by bike.
这个男孩要求骑自行车去上学。
14. beg to do sth. 恳求做某事
He begged not to be put into prison.
他祈求不要被关进监狱。
15. care to do sth. 愿意/喜欢做某事
16. choose to do sth. 选择做某事
He chose to believe what she had said.
他选择相信她说的话。
17. decide to do sth. 决定做某事
She has decided to travel all over the world.
她已经决定周游世界了。
18. demand to do sth. 要求做某事
19. determine to do sth. 决心做某事
He determined to learn French.
他下定决心学习法语。
20. expect to do sth. 等待做某事
I am expecting to hear from you soon.
我期待着早点收到你的来信。
21. fear to do sth. 惧怕做某事
She fears to live on the mountain.
她害怕住在山上。
22. prepare to do sth. 预备做某事
They prepared to go hiking this Sunday.
他们准备周日去远足。
23. pretend to do sth. 伪装做某事
She pretended not to see me.
她假装没有看到我。
24. promise to do sth. 答应做某事
I have promised to give the children some books.
我已经答应给孩子们一些书了。
25. refuse to do sth. 拒绝做某事
She refused to buy a new cellphone for her boy.
她拒绝给她儿子买新手机。
初中英语常用动词注意事项:
一、主动表被动的情况
1. 感观系动词,look, seem, sound, feel, smell, taste等
eg. The fish tastes nice.
2. measure, weigh等表示度量的动词。
eg. The elephant weights nearly a ton.
3. wash, clean, open, sell, read, last, write, steer等不及物动词可以表示被动意义。eg. The ship steer easily.
二、被动句表示主动含义。
She was dressed in a red skirt.
此类动词常见于dress, seat, devote, adapt, accustom 等后面可以接反身代词的动词。
二、时态,语态
1. 用进行时表示一种情绪。
She is always helping others.(表赞扬)
The man is always smoking in the office, which offends others very much.
2. 一般过去时表示某一动作已完成,过去进行时表示动作可能未完成。
He wrote a letter yesterday morning.(信已写完)
He was writing a letter yesterday evening. (信可能还未写完)
3.现在完成时可表示动作持续至今,一般过去时则表示动作已结束,并不强调对现在造成的影响或结果。
I have lived in this street.(我一直住这条街上)
I lived in this street.(我曾住在这条街上)
4.表示几个连续动作时,尽管有先后,仍要用相同时态。
He came into the classroom, put down the book and wrote a few words on the blackboard.
5. 在条件和时间状语从句中常用一般时表示将来。
6.叙述过去发生的某件事情常用一般过去时,表示过去某个时间或动作之后发生的事情才用过去将来时,过去某个时刻/段内正发生的事情,才用过去进行时,过去某个时间或动作之前发生的事情才用过去完成时。因此找准时间的参照点,是正确运用时态的关键。
7.罗列并熟记各种时态的被动形式。
三.动词的类别与特征中的注意点
1.兼作Vt., Vi.的动词
(1)对兼作Vt., Vi.的动词,要注意根据不同的情况选择使用。
The children are flying their kites in the square.( Vt.)
We saw a plane flying high up in the sky.( Vi.)
(2)有些动词后跟从句时为Vt., 其它 情况为Vi.,但意义基本不变。典型的有wonder, think, insist, agree,等。
The headmaster insisted that the students should wear school uniforms .
The headmaster insisted on the students wearing school uniforms.
(3)有些动词在Vt. Vi.之间,意义有所不同。如run, stand, lie等
She stood alone under the tree.
I can’t stand such cold weather.
2.常用的双宾动词有give, teach, lend, bring, explain, send, offer, pay, sell, buy, tell, show, write, ask, wish, read等,这些动词都带有一定的趋向性。因此转换成带介词的情况时,常可用for , to 来转换。
注意:explain sth. to sb.=explain to sb. sth., describe sth. to sb.=describe to sb. sth.
3.带宾补的动词,注意宾补的逻辑主语是动词宾语
宾补常是名词、形容词、介词 短语 ,副词和非谓语动词等。常见的此类动词有make, have, let, get, keep, find, see, feel, notice等,但要注意不同的动词有不同的接法。
He kept the children (keep不能用不定式作宾补)
Make…do, have…do/doing/done,get…to do/done, find…doing/done, leave…to do/doing/介词短语/a./ad., see…doing/do/done
4.后面常接-ing的动词及短语:suggest, finish, avoid, can’t help, mind, need, enjoy, require, postpone, delay, practice, fancy, excuse, pardon, advise, consider, deny, admit, endure, escape, miss, appreciate, dislike, have a good time doing, put off, call off, give up
5.有些动词后面接to do 和-ing时意义基本相同,而有的则完全不同,要注意
Love, like, hate, forget, remember, stop, begin, start, continue, prefer, regret, intend, mean, want, need, require, neglect, try, deserve, can’t bear等
6.注意状态动词和动态动词的选用
Mother asked the son to notice his manners at the party. (notice就改为mind)
再如:listen/hear, look/see, look for/find, advise/persuade, marry/be married, join/be in等。
7.注意have表“有”时,及系动词一般不能用进行时态。
8.注意表示“有”时,have与there be 的选用
9.注意动词词组分类(见<零距离>),尤其要注意各类动词词组的使用特点及有的动词词组的主被动转换使用。
Make use of sth→sth is made use of(介词不要掉了)/use is made of sth.
10.Hope, intend, expect, plan, want, think, mean 等动词用过去完成时表示没有实现的愿望,计划,打算等
初中英语常用的动词用法相关 文章 :
★ 初中英语动词的知识点总结
★ 初中英语动词知识点:Be动词定义及用法
★ 初中英语常用词组有哪些?以及它们的用法是?
★ 初中英语中的常见语法
★ 初中英语语法专题代词与常用动词
★ 初中英语必须掌握的19个重点语法知识点
★ 初中英语情态动词的用法归纳
★ 初中英语动词短语大全
★ 初中英语语法专题动词语常用短语
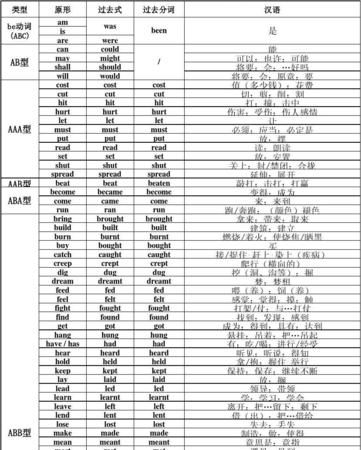
初二英语各单元知识点归纳
初二英语情态动词知识点归纳
1.1 初中英语情态动词的语法特色CopyRight .com
1)初中英语 情态动词不能表示正在发生或已经发生的事情,只表示等候或估计某事的发生。
2) 情态动词 除ought 和have 外,后面只能接不带to 的不定式。
3) 情态动词没有人称,数的变更,即情态动词第三人称单数不加-s。
4) 情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有不定式,分词,等形式。
21.2 比较can 和be able to的初中英语情态动词
1)can could 表示才干;可能 (过去时用could),
只用于现在式和从前式(could)。be able to能够用于各种时态。
They will be able to tell you the news soon. 他很快就能告诉你消息了。
2)只用be able to
a. 位于助动词后。
b. 情态动词后。
c. 表示从前某时刻动作时。
d. 用于句首表示前提。
e. 表示成功地做了某事时,只能用was/were able to, 不能用could。
He was able to flee Europe before the war broke out.
= He managed to flee Europe before the war broke out.
初中英语情态动词注意:could不表示时态内容来自
1)提出委婉的恳求,(留神在答复中不可用could)。
--- Could I have the television on?
--- Yes, you can. / No, you can't.CopyRight .com
2)在否定,疑问句中表示推测或猜疑。
He couldn't be a bad man.
他不大可能是坏人。
21.3 比较may和might内容来自
1) 表示允许或要求;表示不控制的推测;may 放在句首,表示庆祝。
May God bless you!
He might be at home.
初中英语情态动词注意: might 表示推测时,不表示时态。只是可能性比may 小。
2) 成语: may/might as well,后面接不带to 的不定式,意为"不妨"。
If that is the case, we may as well try.
初中英语情态动词典型例题
Peter ___come with us tonight, but he isn't very sure yet.
A. must B. may C. can D. will
答案B. 表可能性只能用may. 此句意可从后半句推出。
初二英语情态动词学习巩固
21.4 比较have to和must
1) 两词都是'必须'的意思,have to 表示客观的须要, must 表示谈话人主观上的看法,既主观上的必要。
My brother was very ill, so I had to call the doctor in the middle of the night. 我弟弟病得很厉害,我只得深夜里把医生请来。(客观上需要做这件事)
He said that they must work hard. 他说他们必须努力工作。(主观上要做这件事)
2) have to有人称、数、时态的变革,而must只有一种形式。但must 可用于间接引语中表示过去的必要或义务。
He had to look after his sister yesterday.
3) 在否定构造中: don't have to 表示"不必"CopyRight .com
mustn't 表示"禁止",
You don't have to tell him about it. 你不一定要把此事告诉他。
You mustn't tell him about it. 你一定不要把这件事告知他。
21.5 must表示推测
1) must用在肯定句中表示较有把握的推测,意为"一定"。
2) must表对现在的状态或现在正产生的事件的推测时, must 后面通常接系动词be 的本相或举动动词的进行式。
You have worked hard all day.You must be tired. 你辛苦干一终日,必定累了。(对现在情形的揣测判断)内容来自
He must be working in his office. 他一定在办公室工作呢。
初中英语情态动词比较:
He must be staying there.
他现在肯定呆在那里。
He must stay there.
他必须呆在那。
3) must 表示对已发生的事情的推测时,must 要接完成式。
I didn't hear the phone. I must have been asleep. 我刚才没有听到电话,我想必是睡着了。内容来自
4) must表示对过去某时正发生的事情的推测,must 后面要接不定式的完成进行式。
---Why didn't you answer my phone call?
---Well, I must have been sleeping, so I didn't hear it.
5) 否定推测用can't。
If Tom didn't leave here until five o'clock, he can't be home yet. 如果汤姆五点才离开这儿,他此时一定还未到家。
21.6 表示推测的用法
can, could, may, might, must 皆可表示推测,其用法如下:CopyRight .com
1)初中英语情态动词+动词原形。
表示对当初或将来的情况的揣摩,此时动词通常为系动词。
I don't know where she is, she may be in Wuhan.
2)情态动词+动词现在进行时。
表示对现在或未来正在进行的情况进行推测。
At this moment, our teacher must be correcting our exam papers.
这时,咱们老师想必在批改试卷。
3)初中英语情态动词+动词实现时。
表示对过去情况的推测。
We would have finished this work by the end of next December.
明年十二月底前咱们很可能已完成这项工作了。
The road is wet. It must have rained last night.
地是湿的,昨天晚上一定下雨了。
4)情态动词+动词的当初实现进行时。内容来自
表示对过去正在发生事件的推测。CopyRight .com
Your mother must have been looking for you.
你妈妈一定始终在找你。CopyRight .com
5)推测的否定形式,疑问形式用can't, couldn't表示。
Mike can't have found his car, for he came to work by bus this morning.
迈克一定还没有找回他的车,因为早上他是坐公共汽车来上班的。
初中英语情态动词注意:could, might表示推测时不表示时态,其推测的程度不如can, may。CopyRight .com
21.7 情态动词+ have +过去分词
1) may(might) have + done sth, can (could) have + done sth 表示过去,推测过去时光里可能发生的事情。
Philip may (might) have been hurt seriously in the car accident.
Philip can (could) have been hurt seriously in the car accident.
2) must have +done sth,对过去时间里可能发生的事情的推测,语气较强,存在"肯定","谅必"的`意思。CopyRight .com
---Linda has gone to work, but her bicycle is still here.
---She must have gone by bus.
3) ought to have done sth, should have done sth
本应该做某事,而事实上并不做。否定句表示"不该做某事而做了"。
You ought to (should) have been more careful in this experiment.
He ought not to have thrown the old clothes away.(事实上已扔了。)
ought to 在语气上比should 要强。
4) needn't have done sth 本没必要做某事
I dressed very warmly for the trip, but I needn't have done so. The weather was hot.CopyRight .com
5) would like to have done sth 本打算做某事
I would like to have read the article, but I was very busy then.CopyRight .com
21.8 should 跟ought to
should 和ought to 都为"应当"的意思,可用于各种人称。
---Ought he to go?
---Yes. I think he ought to.
表示请求,命令时,语气由 should(应该)、had better最好)、must(必须)渐强
21.9 had better表示"最好"
had better 相当于一个助动词,它只有一种形式,它后面要跟动词原形。CopyRight .com
had better do sth
had better not do sth
It is pretty cold. You'd better put on my coat.内容来自
She'd better not play with the dog.
had better have done sth表示与事实相反的结果,意为"本来最好"。
You had better have come earlier.
21.10 would rather表示"甘心"
would rather do
would rather not do
would rather… than… 宁愿……而不愿。
还有would sooner, had rather, had sooner都表示"宁愿"、"宁肯"的意思。CopyRight .com
If I have a choice, I had sooner not continue my studies at this school.
I would rather stay here than go home. = I would stay here rather than go home.
初中英语情态动词典型例题
----Shall we go skating or stay at home?
----Which ___ do?
A. do you rather B. would you rather C. will you rather D. should you rather
谜底B。本题考察情态动词rather的用法,would rather +do sth 意为"情愿",本题为疑问句,would 提前,所以选B。
21.11 will和would
初中英语情态动词注意:
1)would like; Would like to do = want to 想要,为固定搭配。
Would you like to go with me?
2)Will you…? Would you like…? 表现断定含意的请求奉劝时,疑难句中个别用some, 而不是any。
Would you like some cake?
3)否定结构中用will,一般不用would, won't you是一种委婉语气。
Won't you sit down?
21.12 情态动词的回答方式CopyRight .com
问句 肯定回答 否定回答
Need you…? Yes, I must. No,I needn't
Must you…? /don't have to.
典范例题
1)---Could I borrow your dictionary?
---Yes, of course, you____.
A. might B. will C. can D. should
答案C.could表示委婉的语气,并不为时态。答语中of course,表示确定的语气,允许某人做某事时,用can和 may来表白,不能用could或might。复习: will 与you连用,用来提出要求或下命令。should与you 连用,用来提出劝告。
2)---Shall I tell John about it?
---No, you ___. I've told him already.
A. needn't B. wouldn't C. mustn't D. shouldn't
答案A。needn't 不必,不用。 wouldn't 将不, 不会的。 mustn't 制止、不能。 shouldn't 不应该。本题为不需要,不必的意思,应用needn't。
3)---Don't forget to come to my birthday party tomorrow.
---______.
A. I don't B. I won't C. I can't D. I haven't内容来自
答案B. will既可当作情态动词,表要求、倡导、也可作为实义动词表"意愿、意志、信心",本题表示信念,选B。
21.13 带to 的情态动词
带to 的情态动词有四个:ought to, have to, used to, be to, 如加上have got to ,(=must), be able to,为六个。它们的疑问,否认情势应予以留心:
Do they have to pay their bill before the end of the month?
She didn't use to play tennis before she was fourteen.
You ought not to have told her all about it.
Ought he to see a heart specialist at once.?
ought to 本身作为情态动词应用。其余的词作为实义动词利用,变疑问,否定时,须有do 等助动词辅助。
初中英语情态动词典型例题
Tom ought not to ___ me your secret, but he meant no harm.
A.have told B.tell C.be telling D. having told
答案A。由于后句为过去时,告诉秘密的动作又发生在其前因,此地应用过去完成时,但它在情态动词 ought to 后,所以用have。
21.14 比拟need和dareCopyRight .com
这两词既可做实义动词用,又可做情态动词用。作为情态动词,两者都只能用于疑难句,否定句跟条件句。 need 作实义动词时后面的不定式必需带to,而dare作实义动词用时, 后面的to 时常可能被省略。
1) 实义动词: need (需要, 请求)
need + n. / to do sth
2)初中英语 情态动词: need,只用原形need后加do,否定形式为need not。
Need you go yet?内容来自
Yes, I must. / No, I needn't.
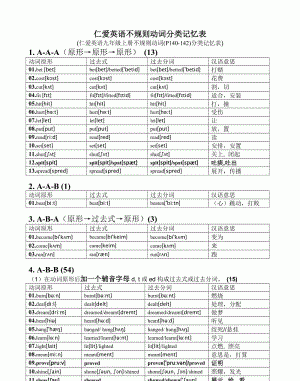
初中英语动词的种类重要知识点总结图片
动词是表示动作或状态的词,按其词义和在句子中的'作用可分为行为动词,连系动词,助动词和情态动词。
1.行为动词
行为动词可分为及物动词(vt)和不及物动词(vi),及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,后跟宾语;不及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,但后面不能直接跟宾语,如要带宾语则与介词或副词构成短语。
如:
More and more people study English.(vt)
The students are listening to the teacher carefully.(vi)
2.连系动词
连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。常用的连系动词有be,get,turn,become,look,feel,grow,seem,sound,taste,smell等。
如:
Our country is becoming stronger and stronger.
It feels damp.
3.助动词
助动词本身无词义,不能单独作谓语,只能和主要动词一起构成谓语动词,表示否定,疑问及动词的时态、语态、人称和数等语法特征,助动词有be,do,have,shall,will等。
如:
How do you usually come to school?
The children are playing yo-yo now.
4.情态动词
情态动词本身有一定的意义,但不能独立作谓语,只能和主要动词原形一起构成谓语,表示说话人的语气和情态。情态动词没有人称和数的变化。情态动词有can(could),may(might),must,need,ought to,dare等。
如:
Can I help you?
-Must we go now?-No,you needn't.
a.can与be able to的用法有所区别。can只用于一般现在时和过去时,指本身有能力的"能";be able to用于各种时态均可,指须经过努力而"能"。
b.must与have/has to的用法。must表示说话人主观认为"必须",只用于一般现在时和一般将来时;have/has to表示客观需要,意为"不得不",它可用于各种时态。
c.need和dare既可作情态动词也可作行为动词。
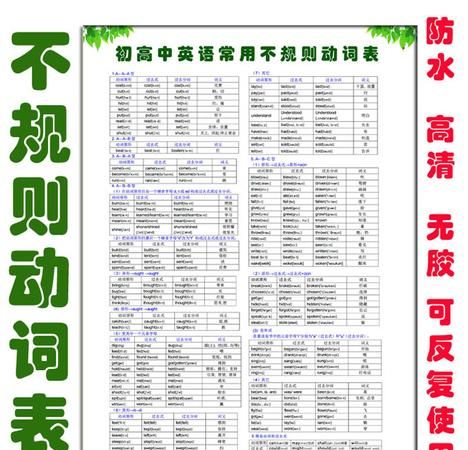
初中英语八大时态归纳表格
动词的时态有很多。初中阶段主要掌握八种:一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、过去进行时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在完成时、过去完成时。下面是我整理的内容,希望多大家有所帮助。
1.一般现在时
1)一般现在时态的构成:主语是I,we,you,they和名词复数时作谓语的行为动词用原形。
2)常用于一般现在时态的时间状语:often、usually、sometimes、always、every、day、never、in、the、morning等。
2.现在进行时
1)现在进行时的构成:Am/is/are+v-ing是现在进行时的构成形式。
2)现在进行时的用法:1.说话时正在进行或发生的动作(动作是在说话时正在进行);2.现阶段正在进行或发生的动作(但是动作并不是必须在说话时正在进行)。
3.一般将来时
1)一般将来时的构成:
1.助动词will(shall)+动词原形
2.am/is/are+going to+动词原形
2)一般将来时的用法:
1.将要发生的动作。
2.将要存在的状态。
3.打算要做的事。
3)常用于一般将来时的时间状语:tomorrow、next、week、in2008等。
4.一般过去时
1)一般过去时的构成:用动词的过去式。
3)一般过去时的用法:
1.过去发生的动作。
2.过去存在的状态。
3)常用于一般过去时的时间状语:yesterday,three months ago,last year,in1979,often,always等。
5.现在完成时
1)现在完成时的构成:have/has+v-ed
2)现在完成时的用法:
1、表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果.常与already,just,ever,never,before等词连用.
2、表示“过去的动作”一直延续到现在并有可能继续延续下去.常与for(后跟段时间)或since(后跟点时间)等连用.
6、过去进行时
1)过去进行时的构成:was/were+v-ing
2)过去进行时的用法:过去某一阶段或某一时刻正在进行的动作。
例如:This time last year I was living in Brazil.
3)常用于过去进行时的时间状语:at four yesterday afternoon,then,at that time/moment 等。
7、过去完成时态
1)过去完成时态的构成:
肯定式:had+动词的过去分词
否定式:hadn’t+动词的过去分词
疑问式:Had…+动词的过去分词
简略回答:Yes,主+have/has had.
No,主+had现在完成时的用法
过去完成时的用法:
1、表示在过去某一时间或动作之前已经发生或完成的动作。他表示的时间是“过去的过去”常与by last year, by the time of yesterday,等连用。
2、表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到过去另一时间的动作或状态。常与for(后跟段时间)或since(后跟点时间)等连用.
8.过去将来时
1)用法:从过去看将要发生的动作。
2)结构:would+动原was/were/going to
以上就是关于初中英语动词考点 ,初中英语感官动词的用法的全部内容,以及初中英语动词考点 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
