本文目录
名词性从句规则
名词性从句
一. 什么叫“名词性从句”?名词性从句在功能上相当于名词
His job is important. I don’t like his job.
主语 宾语
What he does is important. I don’t like what he does every day.
This is his job. We students should study hard.
表语 同位语
This is what he does every day. I don’t know about the fact that he is a teacher.
相关概念:
1.名词:表示人或事物的名称的词
2.名词的句法作用:名词在句中主要作主语,宾语,表语和同位语。另外还可以作定语,状语。
3.名词性从句:在英语的句子结构中,本来该由名词充当的主 语、宾语、表语和同位语,由一个句子来充当,这个句子就叫:名词性从句。
二、 名词性从句的种类
1.When we will start is not clear.主语从句
2.Mrs Black won’t believe that her son has become a thief.宾语从句
3. My idea is that we should do it right now.表语从句
4.I had no idea that you were her friend.同位语从句
三、常见引导词:
连接词 : that、 if、 whether
连接代词 :who、 whose、 what、which
连接副词: when、 where、why、how、 how long
各种连接词的用法:
连接词 that、whether、if 不在它们引导的主语从句 中充当句子成分。
1. whether引导主语从句时,既可以直接位于句首,也可以位于句末;if 引导主语从句时只能用于it作形式主语的从句中。whether可以与or not连用,if则不行.
2. 连接代词who、whose、what、 which等都在句子中 担当一个句子成 分。比如:主语、宾语、定语等等。
3. 关系副词when、where、how、how long等分别在句子中作时间状语、地点状语、方式状语等等。
四、名词性从句七大常考考点:
考点1:连接词: that 与 what 的区别
That (a new teacher will come to our school ) is true .
What we can’t get seems better than what we have .
that 只起连接作用,无意义,在从句中不充当任何成分 what 既有连接作用, 又要在从句中作成分( 主语,宾语, 表语)(… 的东西;物;话;时间;地点;人物;数目等不同概念)
what (什么) / which ( 表选择, 哪一个)
1. ---Do you know____what____Mr Black’s address is ?
---He may live at No. 18 or No. 19 of Bridge Street. I’m not sure of ______which___.
2. I read about it in some book or other, does it matter ___which____ it was?
考点 2 :it作形式主语,形式宾语的用法
☺ it 作形式主语
1. It is a pity that he made such a mistake.
2.他来不来不重要。
Whether he will come or not doesn’t matter.=It doesn't matter whether he will or not.
It is well known/reported/ thought/said that…
It is clear/necessary/certain/true that…
It is a pity/a shame/an honor that…
It doesn’t matter whether…
It seems that…
It happens that…
☺. it 作形式宾语
(1) make /find/ feel / consider / think it + adj / n + that… / to do…
(2) it 指代后面从句所叙述的内容, 常用于这些动词后, like/dislike/love/hate /appreciate/make+it 后常跟if 或when从句
I hate it when people laugh at the old
(3) depend on it that….
1. I like __C_ in the autumn when the weather is clear and bright.
A. this B. that C. it D. one
2.You may depend on __C__ that you parents will help you whenever you need it.
A.them B. yourself C. it D. me
考点3 语序问题
★在名词性从句中,除了关联词要提到句首之外,一律要用陈述句语序
4.What time do you think _B_?
A.will Besty come here B.Besty will come here
C.is Besty coming here D.can Besty get here
疑问词+do you think\suggest\believe\suppose …+陈述语序
考点4 同位语从句和定语从句的区别
同位语从句一般跟在名词fact, news, promise, truth, belief, thought, idea, answer, information, knowledge, doubt, hope, law, opinion, plan, suggestion后面, 用以说明或解释前面的名词的内容.
定语从句:对先行词起修饰限制作用
The news that she passed the exam excited her parents . 同位语从句
解释说明;that在从句中不充当成分,但是不能省。
The news that we know from her excited all of us .
修饰限定;that在从句中有成分、作宾语时可以省。
判断方法:同位语从句可以变成表语从句。
1.The suggestion that he should not go there is of great value.
2. The suggestion that he made is of great value.
3.The fact that he won the first place can’t be denied.
4.The fact that he told me excited me.
注: 1. 同位语从句多用that 引导
2. 在have no idea 之后常用wh-引导同位语从句.
I have no idea where he has gone.
I have no idea when he did it.
I have no idea what he did.
考点5.选择填空
Whoever,whatever等引导的名词性从句不含有疑问意义,相当于名词后加一个定语从句,而what,who等引导的名词性从句都含有疑问意义。
高考题选萃
注:wh-ever 既可引导名词性从句
又可引导让步状语从句,no matter wh- 只引导让步状丛
3. It is generally considered unwise to give a child ___B_ he or she wants.
A. however B. whatever C. whichever D. whenever
考点6.whether 与 if 均为 “是否” 的意思。但在下列情况下,whether 不能被 if 所取代:
1.不是it做形式主语的主语从句
Whether he will come is unknown.
2. 表语从句,如:The question is whether you should accept it.
3. 同位语从句,如:The question whether he’ll attend the meeting is not decided.
4.在介词后:如:I’m not interested in whether they’ll go or not.
It depends on whether we have got enough money.
5. 直接跟不定式连用,如:She hasn’t decided whether to go or not.
用if 或whether 填空
1.___A__ we’ll go camping tomorrow depends on the weather.
A. If B.Whether
C. That D.Where
考点7虚拟语气问题
1.在order,suggest(建议),demand,request,advise,insist(坚持应该)等所接的宾语从句中用should 型虚拟语气。should 常省略。
2.在order,suggestion等名词后同位语从句,表语从句中用should 型虚拟语气,可省略should
3.在as if,as though引导的表语从句中,在必要的情况下应用过去式虚拟语气。
4.在主语从句中用来表示惊奇、不相信、惋惜、理应如此等,谓语动词用虚拟语气“(should) +do”,常用的句型有:(1)It is necessary (important, natural, strange, etc.) that...
(2) It is a pity(a shame, no wonder, etc.) that...
(3) It is suggested (requested, proposed, desired, etc.) that...如: It is strange that she (should) think so.
wish后,从句中的时态在原本的时态上退一步
I wish that I __B__that film star yesterday.
A saw B. had seen C would see D has seen
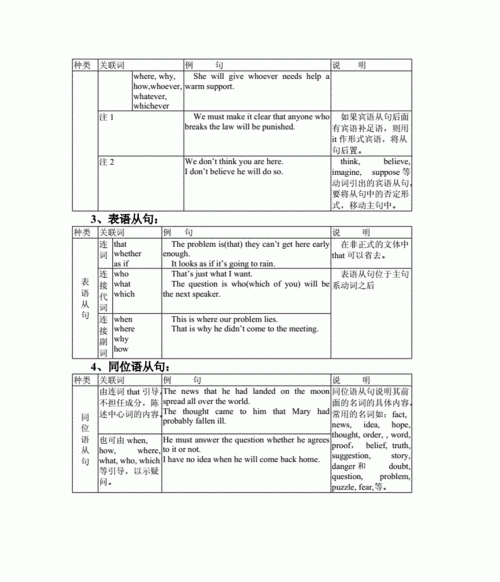
名词性从句规则
语法基础知识 名词性从句结构从句根据性质不同可分为:名词性从句、形容词性从句和副词性从句。根据句法功能的不同,名词性从句可分为:主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。名词性从句多由连词that, wh-word疑问词,连接代词who, which,连接副词when where等引导。这一单元我们重点讲解表语从句(即名词性从句用作表语)和宾语从句(即名词性从句用作宾语)的情况。1.名词性从句用作表语(表语从句)名词性从句放在系动词之后,用作表语,构成系表结构,用来表示某一事实,也能表示某人的意见、信念、要求和希望等。表语从句由连词that, whether, if连接,也可以用连接代词what, who或连接副词why, where, when, how等连接。例如:①The first question I put to him was whether he would do it.我向他提的第一个问题就是他是否要做那工作。②The problem was if they would attend the conference.问题是他们是否去参加会议。③This is what I had wanted to say.这就是我本来要说的话。④The question was how we could get to the railway station.问题是我们怎样到达火车站。⑤That was why I was so frightened at that time.那就是为什么我当时如此害怕的原因。⑥Our plan is that we'll finish the experiment in a quarter.我们的计划是在一刻钟内完成这项实验。⑦His wish is that he should go to work in the United States.他的愿望是到美国去工作。⑧Our greatest happiness is that we can serve the people with all our hearts.我们最大的幸福是全心全意为人民服务。2.名词性从句用作宾语(宾语从句)由连词、连接代词或连接副词引导的名词性从句,放在谓语动词、非谓语动词或介词之后,用作宾语,表示动作的对象。例如:①They said that they had been there for a year.他们说他们在那儿呆了一年了。②I don't understand what they are talking about.我不明白他们在谈些什么。③I wish that I knew where they live at present.但愿我知道他们目前在哪儿住就好了。④I wonder if you would mind helping me.不知道你是否能帮我的忙。⑤I shall not forget when the meeting will open.我不会忘记开会的时间。⑥We always gave whoever came to us valuable guidance.无论谁到我们这里来,我们总是给予有用的指导。⑦You have to think of what you should do next.你必须考虑下一步怎么办。⑧“We can write about whatever topic we prefer.”said the teacher.老师说我们可以写我们喜欢的任何题目。⑨We found it very strange that no one would take the money.我们很感到奇怪,谁也不要这笔钱。3.名词从句用作同位语同位语从句是名词性从句,一般跟在某些抽象名词(如belief, fact, hope, idea, news, problem, possibility等)的后面,用以说明或解释前面的名词。同位语从句用连词that, whether引导,也可用连接代词what或连接副词why等引导。例如:①We ought to discuss carefully the important question whether we can do it or not.我们应该细心讨论一下这个重要问题,就是我们是否能做这项工作。②I have no idea that such a little girl knows much about the experiment.我没有想到这个小女孩对这项实验知道的那么多。③The news that his daughter had won the first prize was a great pleasure to him.他女儿获得一等奖的消息对他来说是很值得开心的事情。④The fact that this book is completely sold out speaks in its favour.这本书全卖出去的事实说明了它是受欢迎的。⑤The idea that computers will recognize human voices surprises many people.电脑将能辨出人的声音,这个想法让很多人吃惊。⑥The possibility that the majority of the labour force will work at home is often discussed. 多数劳动者都可以在家上班,这种可能性常常被提出来探讨。⑦I have no idea when Jack will be back.我不知到杰克什么时候回来。⑧He can't answer the question how he got the money.这笔钱他是怎样得到的,对这个问题他不能回答。4.同位语从句与定语从句的区别比较下列两个例句:①We expressed the hope(that)they had expressed.我们表达了他们曾经表达的那种希望。(定语从句)②We expressed the hope that they would come to visit China again.我们表示希望他们再来中国访问。(同位语从句)1)从语法的角度上看,引导同位语从句的that是连词,只起连接的作用,在从句中并不作任何句子成分;而引导定语从句的that是关系代词,除了起连接作用外,还在从句中作句子成分(如句①中的that在从句中作宾语)。又如:③We were overjoyed at the news(that)he told us.我们听到他说的消息,高兴极了。④We were overjoyed at the news that the school would organize a trip to the Great Wall.听到学校将组织大家去长城游览的消息,我们高兴极了。2)从语意的角度上看,同位语从句与它前面的名词(如hope)是同位关系,表示这个“希望”的内容是“他们再来中国访问”;而定语从句与它前面的名词是所属关系,表示“……的”(如句①中的“他们曾经表示过的”),起修饰作用。又如:⑤Have you heard the news that a war has broken out in the Middle East? 你听到在中东爆发战争的消息了吗?⑥Have you heard the news(that)I just told you?你听说过我刚告诉你的消息了吗?3)同位语从句的连词that一般不能省略;而定语从句中的关系代词that,当其在句中作宾语时,常常可以省略(如①中的that可以省略)。又如:⑦The suggestion that we clean the classroom by turns is good.我们轮流打扫教室这个建议很好。
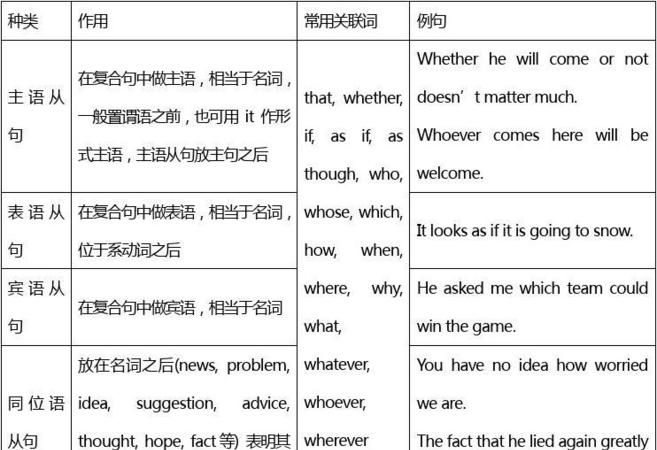
名词性从句有哪些
楼主,您好在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词从句。名词从句的功能相当于名词词组, 它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。 引导名词性从句的连接词 引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连接词: that, whether ,if (不充当从句的任何成分)
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, which
连接副词:when, where, how, why
不可省略的连词:
1. 介词后的连词
2. 引导主语从句和同位语从句的连词不可省略。例如:
That she was chosen made us very happy. 她被选上了,我们很高兴。
We heard the news that our team had won. 我们听到消息说我们队赢了。
比较:whether与if 均为"是否"的意思。 但在下列情况下,whether 不能被if 取代:
1. whether引导主语从句并在句首
2. 引导表语从句
3. whether从句作介词宾语
4. 从句后有"or not"
大部分连接词引导的主语从句都可以置于句末,用 it充当形式主语。例如:
It is not important who will go. 谁去,这不重要。
It is still unknown which team will win the match. 到底谁赢呢,形势尚不明朗。 名词性that-从句 1)由从属连词that引导的从句叫做名词性that-从句。That只起连接主句和从句的作用,在从句中不担任任何成分,本身也没有词义。名词性that-从句在句中能充当主语、宾语、表语、同位语和形容词宾语。例如:
主语:That he is still alive is sheer luck. 他还活着全靠运气。
宾语:John said that he was leaving for London on Wednesday. 约翰说他星期三要到伦敦去。 表语:The fact is that he has not been seen recently. 事实是近来谁也没有见过他。
同位语:The fact that he has not been seen recently disturbs everyone in his office.
近来谁也没有见过他,这一情况令办公室所有的人不安。
形容词宾语:I am glad that you are satisfied with your job. 你对工作满意我感到很高兴。
2)That-从句作主语通常用it作先行词,而将that-从句置于句末。例如:
It is quite clear that the whole project is doomed to failure. 很清楚,整个计划注定要失败。
It's a pity that you should have to leave. 你非走不可真是件憾事。
用it作形式主语的that-从句有以下四种不同的搭配关系:
a. It + be +形容词+ that-从句
It is necessary that… 有必要……
It is important that… 重要的是……
It is obvious that… 很明显……
b. It + be + -ed 分词+ that-从句
It is believed that… 人们相信……
It is known to all that… 从所周知……
It has been decided that… 已决定……
c. It + be +名词+ that-从句
It is common knowledge that… ……是常识
It is a surprise that… 令人惊奇的是……
It is a fact that… 事实是……
d. It +不及物动词+ that-分句
It appears that… 似乎……
It happens that… 碰巧……
It occurred to me that… 我突然想起…… 名词性wh-从句 1)由wh-词引导的名词从句叫做名词性wh-从句。Wh-词包括who, whom,. whose, whoever, what, whatever, which, whichever等连接代词和where, when, how, why等连接副词。Wh-从句的语法功能除了和that-从句一样外,还可充当介词宾语、宾语补语和间接宾语等。例如:
主语: How the book will sell depends on its author. 书销售如何取决于作者本人。
直接宾语:In one's own home one can do what one likes. 在自己家里可以随心所欲。
间接宾语:The club will give whoever wins a prize. 获胜者俱乐部将颁奖。
表语: My question is who will take over president of the Foundation. 我的问题是谁将接任该基金会主席职位。
宾语补足语:She will name him whatever she wants to. 她高兴给他起什么名字就取什么名字。
同位语:I have no idea when he will return. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
形容词宾语:I'm not sure why she refused their invitation. 我尚不能肯定她为什么拒绝他们的邀请。
介词宾语: That depends on where we shall go. 那取决于我们去哪儿。
2)Wh-从句作主语也常用先行词it做形式主语,而将wh-从句置于句末。例如:
It is not yet decided who will do that job. 还没决定谁做这项工作。
It remains unknown when they are going to get married. 他们何时结婚依然不明。 if, whether引导的名词从句 1)yes-no型疑问从句
从属连词if, whether引导的名词从句是由一般疑问句或选择疑问转化而来的,因此也分别被称为yes-no型疑问句从句和选择型疑问从句,其功能和wh-从句的功能相同。例如:
主语:Whether the plan is feasible remains to be proved. 这一计划是否可行还有等证实。
宾语:Let us know whether / if you can finish the article before Friday. 请让我们知道你是否能在星期五以前把文章写完。
表语:The point is whether we should lend him the money. 问题在于我们是否应该借钱给他。
同位语:They are investigating the question whether the man is trustworthy. 他们调查他是否值得信赖。
形容词宾语: She's doubtful whether we shall be able to come. 她怀疑我们是否能够前来。
介词宾语: I worry about whether he can pass through the crisis of his illness. 我担心他是否能度过疾病的危险期。
2)选择性疑问从句
选择性疑问从句由关联词if/whether…or或whethe…or not构成。例如:
Please tell me whether / if they are Swedish or Danish. 请告诉我他们是瑞典人还是丹麦人。
I don't care whether you like the plan or not. 我不在乎你是否喜欢该计划。 否定转移1)将think, believe, suppose, expect, fancy, imagine等动词后面宾语从句的否定词转移到主句中,即主句的谓语动词用否定式,而从句的谓语动词用肯定式。例如:
I don't think I know you. 我想我并不认识你。
I don' t believe he will come. 我相信他不回来。
注意:若谓语动词为hope,宾语从句中的否定词不能转移。例如:
I hope you weren't ill. 我想你没有生病吧。
2)将seem, appear 等后的从句的否定转移到前面。例如:
It doesn't seem that they know where to go. 看来他们不知道往哪去。
It doesn't appear that we'll have a sunny day tomorrow. 看来我们明天不会碰上好天气。
3)有时将动名词,介词短语或整个从句的否定转变为对谓语动词的否定。例如:
I don't remember having ever seen such a man. 我记得从未见过这样一个人。(not否定动名词短语 having…)
It's not a place where anyone would expect to see strange characters on the street.
在这里,人们不会想到在街上会碰上陌生的人。(anyone 作主语,从句中的谓语动词不能用否定形式。)
4)有时状语或状语从句中否定可以转移到谓语动词前。例如:
The ant is not gathering this for itself alone. (否定状语) 蚂蚁不只是为自己采食。
He was not ready to believe something just because Aristotle said so. (否定because状语)
他并不因亚里斯多德说过如何如何,就轻信此事。
She had not been married many weeks when that man's younger brother saw her and was struck by her beauty.(否定状语many weeks) 她结婚还不到几个月,这个人的弟弟就看见她了,并对她的美貌着了迷。 谢谢采纳!

which引导名词性从句的用法
名词性从句就是句子担任名词性的成分,如主语,宾语,表语,同位语。它包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
1. 主语从句
(1)What he said is true.
(2)When they will arrive is not known yet.
(3)That he succeeded in doing the experiment was encouraging.
(4)Whether he will accept the invitation remains a secret.
(5)It is important that we should learn English well.
2. 宾语从句
(1)I don't know if he has done the work.
(2)Did he say that he liked football ?
(3)They expected that they would be given another chance.
(4)The girl told me that she had longed to visit China.
3. 表语从句
(1)The question is whether we have enough time to do the experiment again.
(2)His greatest wish was that someday he would become a general.
(3)His suggestion was that we should discuss the plan carefully.
(4)My question is when they can finish the work.
4. 同位语从句
(1)You have no idea how eager they are to know the result.
(2)He made a suggestion that the work should be given to him.
(3)Have you heard the news that Premire Wen visited our school last Friday ?
(4)The fact that he got full mark in the composition made his parents very happy.
名词性从句主要从以下几点把握:
1. 语序。从句一定要是陈述语序。如:
(1)These pictures will show you what the village looks like now.
(2)How many guests will be invited isn’t decided yet.
2. 时态。宾语从句的时态需要和主句进行协调。如主句是过去时,从句要用相应的过去时。
(1)He told me that he had seen the film.
(2)They said they would spend their holiday in Hainan.
(3)Father said he was carrying out an important project.
(4)Did you know where the accident took place ?
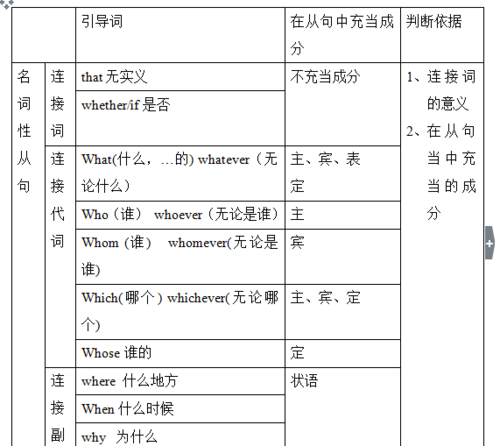
3. 连词。引导名词性从句的连词分为三种:连词 that, whether, if (在主语、表语、同位语从句中用 whether 不用if );连接代词 who, whom, whose, which, what 等; 连接副词 when, where, how, why 等。
(1)Whether the team has won the game is not announced yet. (主语从句)
(2)How many people will take part in the competition will be known soon. (主语从句)
(3)My idea is that we should spend our holidays by the seaside. (表语从句)
(4)My question is how they finished the work in such a short time. (表语从句)
(5)Many people are shocked at the news that there are so many SARS cases in Beijing. (同位语从句)
(6)His suggestion that we should discuss the plan again has been received. (同位语从句)
(7)I didn’t know if they had seen the film. (宾语从句)
(8)We haven’t decided when we’ll start the project. (宾语从句)
4. 形式主语和形式宾语的应用:
当主语从句比较长,主句比较短时,通常用形式主语it,而把从句放在后面,如:
(1)It is said that they have succeeded in working out the problem.
(2)It was important that we should make the plan carefully.
(3)It remains a secret how the animals came to live in the sea.
当宾语从句后面有补语的时候,我们也需要用形式宾语it, 而将宾语从句放在补语之后,如:
(1)I found it very difficult that one learns several languages at the same time.
(2)He thinks it necessary that we should be given more time practising oral English.
(3)He made it clear that he would leave the office soon.
5. 虚拟语气在名词性从句中的运用: 在demand, insist, suggest, command, require, request, order, propose 等表示命令, 要求,请求,建议等意义的动词后,宾语从句要用虚拟语气,动词形式为: should do , should 可省,直接用动词原形,如:
(1)He suggested that we (should) go outing this weekend.
(2)The Emperor ordered that the clothes (should) be made for him at once.
(3)He insisted that we (should) stay for lunch.
这种虚拟语气也可以运用在其他的名词性从句中,从句内容不变, 如:
(1)It was suggested that we should go outing this weekend. (主语从句)
(2)He made a suggestion that we should go outing this weekend. (同位语从句)
(3)His suggestion was that we should go outing this weekend. (表语从句)
6. 定语从句与同位语从句的区别:
定语从句修饰前面的名词,而同位语从句说明前面名词的内容,引导定语从句的that在从句中担任名词性成分,而同位语从句中的 that 不担任任何句子成分.如:
(1)Have you heard the news that was broadcast this morning ? (定语从句)
(2)Have you heard the news that we defeated the Japanese football team ?(同位语从句)
(3)What do you think of the suggestion that was put forward by Lily ?(定语从句)
(4)What do you think of the suggestion that we should speak only English in class ?(同位语从句)
7. 几个容易混淆的连词:
A. whether 和 if:whether可以用在所有的名词性从句中;而if 只能用于宾语从句,另外,如果有介词的话,仍然用whether。
(1)Whether the advice will be accepted is not known. (主语从句,不可以用if)
(2)I have no idea whether he will come. (同位语从句,不可以用if.)
(3)The problem is whether we have enough time to do it again. (表语从句,不可以用if .)
(4)He didn’t tell me whether (if ) he would accept my invitation. (宾语从句,两者都可以)
(5)Everything depends on whether we have enough manpower. (介词之后不用if )
B. what 和 that:that 在名词性从句中不担任句子成分;what 在名词性从句中做主语,宾语,表语等,通常译为”所...的”,如:
(1)What we have done is very important. (what 做宾语)
(2)That they have done the work is good news. (that 无句子成分)
(3)I believe what he said. (what 做宾语)
(4)I believe that he told truth. (that 无句子成分)
以上就是关于名词性从句共用的规则 ,名词性从句规则的全部内容,以及名词性从句共用的规则 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

