本文目录
高中英语主语从句课件

大学英语从句语法总结
各种从句的语法总结
导语:高级的英语语法知识比初级英语的要难得多,下面我分享高级英语的重要语法,欢迎学习!

虚拟语气在各种从句的应用
主语从句的虚拟
1. It is + adj. + that sb. (should) do
常见的形容词有:necessary, important, strange, natural
It's important that he take my advice.
2. It is + n. + that sb. (should) do
常见的名词有:a pity, a shame, no wonder, one's wish
It's a pity that he be so silly.
3. It is + done + that sb. (should) do
常见的过去分词有:suggested, advised, demanded, requested, required, asked, ordered,
proposed, decided, desired, insisted等。
It's requested that she go home as soon as possible.
宾语从句的虚拟
1. 表命令,表建议,表要求的动词,后接宾语从句虚拟。虚拟的构成为(should) do。
I advise that he stay at home.
2. wish后接从句,虚拟的构成是往过去推一个时态。
I wish I had watched the football match last night.
注意以下几组词或短语用于虚拟语气中。
1. as if, as though
He speaks English as if he were a native speaker.
2. otherwise, but, even though
He was ill. Otherwise he would have been there.
3. with, without, but for
Without your help, I would have died two years ago.
But for your help, I would have died two years ago.
4. would rather I'd rather you told me yourself.
5. It's time that
It's time that you went to bed.
It's time that you should go to bed.
表语从句中的虚拟
在表语从句中,表示间接的命令,要求、请求、建议、决定等,主句中的主语通常是suggestion, proposal, request, orders, idea等。从句谓语形式是"(should)+动词原形"。如:
His suggestion is that we (should) leave at once.
名词从句部分:
1. that不可省略的情况
2. that引导同位语从句和that引导定语从句的区别:同位语从句中的that是连词,不做成分,只连接主从句,不能省略;定语从句中的'that要代替先行词在从句中做主语、宾语或者表语,并且做宾语时可以省略。从语义上看,同位语从句是对前面名词的解释、说明或内容;而定语从句时对前面名词的限定。
We should consider the students’request that the school library provide more books on
popular science. (that引导同位语从句)
The only hope that he expressed was that they would do what they could to help the people
in disaster areas. (that引导定语从句)
3. 要根据句子结构尤其是谓语动词判断从句的类型:
What is known to us all is that the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.
本句含有一个主语从句和一个表语从句,主句的动词为is。
It is known to us all that the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.
本句含有一个主语从句,主句的动词为is known to。
As is known to us all, the 2008 Olympic Games took place in Beijing.
本句含有一个定语从句,主句的动词为took place,as引导非限制性定语从句。
4. 名词性从句的语序和语态。
名词性从句均应用陈述语序,不能用疑问语序,其时态应该和主句时态保持一致。
5. 名词性从句中连词的省略 。
介词后的连词以及引导主语从句和同位语从句的连词不可省略。that引导名词从句(除了引导第一个宾语从句可省略外)都不可省略,但是引导定语从句并在从句中做宾语时可以省略。 that不能省略的情况:1)介词后面的that不能省略:
Peter is a good student except that he is sometimes careless.
2)当that引导的宾语从句位于句首时:
That he ever did such a thing I don’t believe.
3)主句谓语动词和that从句之间有插入语,that不省略:
She said that, if she failed, she would try again.
4)当宾语从句有其他从属连词时,that不省略:
He told me that if it was necessary they would work extra time.
6.名词性从句中it的使用:
为了保持句子平衡,多数情况下,it作形式主语或形式宾语,将真正的主语或宾语从句后置。 定语从句关系代词有who, whom, whose, which, that, as,和关系副词when, where, why。
(1)that指物时一般可与which互换,但在下列情况下,要用that而不用which。
a. 先行词有all, everything等不定代词时,如,
Everything (that) he did is wrong.
b. 先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much等修饰时,如,
I'll read all the books (that) you lend me.
c. 先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时,
This is the first letter (that) the boy has written.
d. 先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时,如
He is the very man (that) I'm looking for.
e. 只用which的情况
在介词后或在非限定性定语从句中
This is the book about which we have talked a lot.
The book, which he gave me yesterday, is very interesting.
f. where和when作关系副词
This is the room where I worked.
This is the room which I stayed in.
I remembered the day when we lived there.
I remembered the day that I spent there.
g. as和which
as 可以放于句首,而which 不可以
As you know, he is good at English.
three of them 和three of which
I have a lot of books, three of which are in Russian.
I have a lot of books and three of them are in Russian.
(2. )“介词+关系代词”的情况:
在固定短语中介词不能提前;判断介词的口诀:瞻前顾后看意义
瞻前——看先行词;顾后——找从句动词;看意义——看全句表达含义
(3. )先行词在从句中充当地点状语时,关系词用where 或者介词加which;先行词在从句中充当时间状语时,关系词用when或者介词加which;先行词在从句中充当原因状语时,关系词用why或者for which。
(4. )注意as和which在非限制性定语从句中代表主句所表达的内容的区别:
位置不同:as从句放在主句前或后均可;而which从句只能放在主句后
作用不同:as从句动词常常是see know等,因而相当于插入语;which从句则在陈述一件事实。
状语从句部分
1.while 是高考中的高频词,它既可引导时间状语从句,又可引导并列句,还可引导让步状语从句,表示“尽管”。
2. no matter wh- 与wh-ever 的联系及区别:no matter wh- 只引导让步状语从句,此时与wh-ever通用。wh-ever又可引导名词性从句,No matter wh-不能。
No matter when / Whenever he comes back, he should be invited to the party.
3. 在条件,时间和让步从句中,用一般现在时表示一般将来时,用现在完成时表将来完成时,
用一般过去时表过去将来时。在since 引导的时间状语从句中,动词一般都用一般过去时,而主句常用现在完成时。
4. 状语从句的倒装一般有下面几种情况:①否定词开头;②so 加adj. 开头;③as /
though引导的让步状语从句。
5. 连词before小结:
We had sailed four days before we saw land. (……才)
We hadn’t run a mile before he felt tired. (不到……就)
Please write it down before you forget it. (趁……)
Before I could get in a word, he had measured me. (还没来得及)
It will be/was…before…要过多久才……
6. because, since, as 引导原因从句的区别:because表达直接原因,语气最强,回答why;
since通常放句首,译为“既然”;as引导不谈自明的原因,语气最弱;
7. as可以引导多种从句,要注意其中的区别。
8. till, until和not…until的区别;if和unless的区别
非谓语动词部分动词不定式几点注意。
1.下列动词或动词短语后接不定式:agree, seem, appear, offer, happen, wish, hope, pay,
expect, long, plan, intend, promise, pretend, decide, afford, manage, choose, be said to,would like to等。
2. 不定式常用的句型:too…to do (太……而不能), …enough to do…(够……就能……), so as to do/in order to do(为了……),so…as to do/such…as to do(如此……结果……)。
3. 不定式的三个结构:即否定结构、复合结构和疑问结构。
否定结构为“not (never) to do”;疑问结构是特殊疑问词“how (what, which, who, whether…) to do”;复合结构是“for/ of +名词(或代词宾格)+ to do ”。
4. let/ make/ have/ see/ hear/ notice/ observe/ listen to/ look at/ watch/feel
这些动词带不定式作宾补时,省掉to, 若这些动词以被动形式出现时,应加上to。
5. 当前面是the first, the second, the last, need, plan, time, chance, right,determination,ability, opportunity(机会),way时,一般用不定式作定语。
6. but/ except + to do/ do 结构,要根据谓语动词来确定其后面的形式。当谓语动词是do,does, did时,but后用动词原形;谓语动词是其他动词时,but后用“to + 动词原形”的形式。
7. 形容词后一般用不定式(除busy, worth 两个外)。
You are sure to succeed. 你一定能成功。
He is busy preparing his lessons at present. 他现在正忙于预习功课。
8. 不定式作定语和表语时,有时需要在后面放上一个适当的介词。
This is a bench to sit on.(这是用来坐的凳子。)
This room is comfortable to live in. (这个房间住起来很舒适。)
9. 在“主语+系动词+adj.+不定式”这个句型中,当主语是不定式的逻辑宾语时,不定式不用被动,不能在动词后再放宾语。
The question is easy to answer. (question是answer的宾语,不能说:The question is easy to be answered. 也不能说:The question is easy to answer it .)
;名词性从句怎么讲解
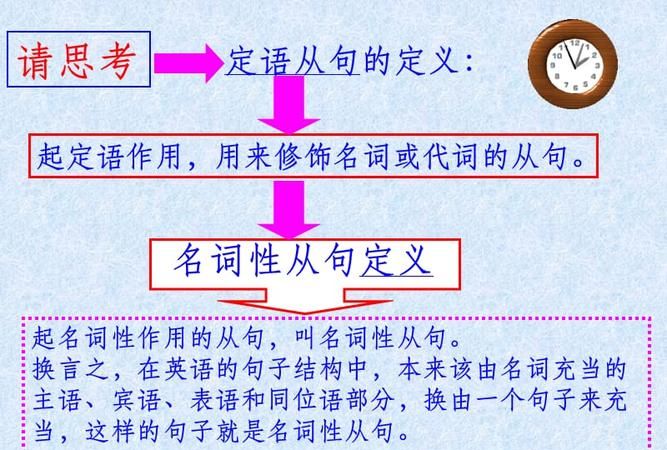
在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词从句 (Noun Clauses)。 名词从句的功能相当于名词词组, 它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
[编辑本段]一、引导名词性从句的连接词
引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连词:that(无任何词意)
whether,if(均表示“是否”表明从句内容的不确定性)
as if ,as though(均表示“好像”,“似乎”)
以上在从句中均不充当任何成分
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom,
whose, which.whichever,whomever
连接副词:when, where, how, why
不可省略的连词:
1. 介词后的连词
2. 引导主语从句和同位语从句的连词不可省略。
That she was chosen made us very happy.
We heard the news that our team had won.
比较:
whether与if 均为"是否"的意思。 但在下列情况下,whether 不能被if 取代:
1. whether引导主语从句并在句首
2. 引导表语从句
3. whether从句作介词宾语
4. 从句后有"or not"
Whether he will come is not clear.
大部分连接词引导的主语从句都可以置于句末,用 it充当形式主语。
It is not important who will go.
It is still unknown which team will win the match.
[编辑本段]二. 主语从句
作句子主语的从句叫主语从句。主语从句通常由从属连词that,whether,if和连接代词what,who,which,whatever,whoever以及连接副词how,when,where,why等词引导。that在句中无词义,只起连接作用;连接代词和连接副词在句中既保留自己的疑问含义、又起连接作用,在从句中充当从句的成分。例如:
What he wants to tell us is not clear. 他要跟我们说什么,还不清楚。
Who will win the match is still unknown. 谁能赢得这场比赛还不得而知。
It is known to us how he became a writer. 我们都知道他是如何成为一名作家的。
Where the English evening will be held has not yet been announced. 英语晚会将在哪里举行,还没有宣布。
有时为避免句子头重脚轻,常用形式主语it代替主语从句作形式主语放于句首,而把主语从句置于句末。主语从句后的谓语动词一般用单数形式。常用句型如下:
(1) It + be + 名词 + that从句
(2)It + be + 形容词 + that从句
(3)It + be + 动词的过去分词 + that从句
(4)It + 不及物动词 + that 从句
另注意在主语从句中用来表示惊奇、不相信、惋惜、理应如此等语气时,谓语动词要用虚拟语气“(should) +do”,常用的句型有:
It is necessary (important, natural, strange, etc.) that …
It is a pity (a shame, no wonder, etc.) that…
It is suggested (requested, proposed, desired, etc.) that…
[编辑本段]三、宾语从句
名词句用作宾语的从句叫宾语从句。引导宾语从句的关联词与引导主语从句表语从句的关联词大致一样,在句中可以作谓语动词或介词及非谓语动词的宾语。
1. 由连接词that引导的宾语从句
由连接词that引导宾语从句时,that在句中不担任任何成分,在口语或非正式的文体中常被省去,但如从句是并列句时,第二个分句前的that不可省。例如:
He has told me that he will go to Shanghai tomorrow. 他已经告诉我他明天要去上海。
We must never think (that) we are good in everything while others are good in nothing. 我们决不能认为自己什么都好,别人什么都不好。
注意:在demand、order、suggest、decide、insist, desire, request, command等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,宾语从句常用“(should)+ 动词原形”。例如:
I insist that she (should) do her work alone. 我坚持要她自己工作。
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once. 司令员命令部队马上出发。
2. 用who,whom, which, whose, what, when, where, why, how, whoever, whatever, whichever等关联词引导的宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,应注意句子语序要用陈述语序。例如:
I want to know what he has told you. 我想知道他告诉了你什么。
She always thinks of how she can work well. 她总是在想怎样能把工作做好。
She will give whoever needs help a warm support. 凡需要帮助的人,她都会给予热情的支持。
3. 用whether或if引导的宾语从句,其主语和谓语的顺序也不能颠倒,仍保持陈述句语序。此外,whether与if 在作“是否”的意思讲时在下列情况下一般只能用whether,不用if:
a. 引导主语从句并在句首时;b. 引导表语从句时;c . 引导从句作介词宾语时;d. 从句后有“or not”时;e. 后接动词不定式时。例如:
Whether there is life on the moon is an interesting question. 月球上有没有生命是个有趣的问题。
The question is whether she should have a low opinion of the test?现在的问题是她是否应该有一个低意见的测试?
Everything depends on whether we have enough money. 一切要看我们是否有足够的钱。
I wonder whether he will come or not. 我想知道他来还是不来。
Can you tell me whether to go or to stay? 你能否告诉我是去还是留?
4. 注意宾语从句中的时态呼应,当主句动词是现在时,从句根据自身的句子情况,而使用
不同时态。例如:
he studies English every day. (从句用一般现在时)
he studied English last term. (从句用一般过去时)
I know (that) he will study English next year. (从句用一般将来时)
he has studied English since 1998. (从句用现在完成时)
当主句动词是过去时态(could, would除外),从句则要用相应的过去时态,如一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时等;当从句表示的是客观真理,科学原理,自然现象,则从句仍用现在时态。例如:
The teacher told us that Tom had left us for America.
5. think, believe, imagine, suppose等等动词引起的否定性宾语从句中,要把上述主句中的动词变为否定式。即将从句中的否定形式移到主句中。例如:
We don’t think you are here. 我们认为你不在这。
I don’t believe he will do so. 我相信他不会这样做。
[编辑本段]四、表语从句
在句中作表语的从句叫表语从句。引导表语从句的关联词与引导主语从句的关联词大致一样,表语从句位于连系动词后,有时用as if引导。其基本结构为:主语 + 系动词 + that从句。例如:
The fact is that we have lost the game. 事实是我们已经输了这场比赛。
That’s just what I want. 这正是我想要的。
This is where our problem lies. 这就是我们的问题所在。
That is why he didn’t come to the meeting. 那就是他为什么不到会的原因。
It looks as if it is going to rain. 看上去天要下雨了。
需要注意的,当主语是reason时,表语从句要用that引导而不是because。例如:
The reason why he was late was that he missed the train by one minute this morning .
【注意】whether 可引导表语从句,但与之同义的if却通常不用于引导表语从句。
[编辑本段]五、同位语从句
同位语从句说明其前面的名词的具体内容。同位语从句通常由that引导,可用于同位语从句的名词有advice、demand、doubt、fact、hope、idea、information、message、news、order、problem、promise、question、request、suggestion、truth、wish、word等。例如:
The news that we won the game is exciting. 我们赢得这场比赛的消息令人激动。
I have no idea when he will come back home. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
The thought came to him that Mary had probably fallen ill. 他想到可能玛丽生病了。
同位语从句和定语从句的区别:
that作为关系代词,可以引导定语从句,充当句子成分,在从句中作宾语时可以省略; that引导同位语从句时,起连词的作用,没有实际意义,不充当句子成分,一般不能省略。
试比较下面两个例句:
I had no idea that you were here.(that引导同位语从句,不能省略)
Have you got the idea(that)this book gives you of life in ancient Greece?(that引导定语从句,作宾语,可以省略)
[编辑本段]六、名词性that-从句
1)由从属连词that引导的从句叫做名词性that-从句。 That只起连接主句和从句的作用,在从句中不担任任何成分,本身也没有词义。名词性that-从句在句中能充当主 语、宾语、表语、同位语和形容词宾语,例如:
主语:That he is still alive is sheer luck. 他还活着全靠运气。
宾语:John said that he was leaving for London on Wednesday. 约翰说他星期三要到伦敦去。
表语:The fact is that he has not been seen recently. 事实是近来谁也没有见过他。
同位语:The fact that he has not been seen recently disturbs everyone in his office.
近来谁也没有见过他,这一事实令办公室所有的人不安。
形容词宾语:I am glad that you are satisfied with your job.
你对工作满意我感到很高兴。
2)That-从句作主语通常用it作先行词,而将that-从句置于句末,例如:
It is quite clear that the whole project is doomed to failure. 很清楚,整个计划注定要失败。
It's a pity that you should have to leave. 你非走不可真是件憾事。
用it作形式主语的that-从句有以下四种不同的搭配关系:
a. It + be +形容词+ that-从句
It is necessary that… 有必要……
It is important that… 重要的是……
It is obvious that… 很明显……
b. It + be + -ed 分词+ that-从句
It is believed that… 人们相信……
It is known to all that… 从所周知……
It has been decided that… 已决定……
c. It + be +名词+ that-从句
It is common knowledge that… ……是常识
It is a surprise that… 令人惊奇的是……
It is a fact that… 事实是……
d. It +不及物动词+ that-分句
It appears that… 似乎……
It happens that… 碰巧……
It occurred to me that… 我突然想起……
[编辑本段]七、名词性wh-从句
1)由wh-词引导的名词从句叫做名词性wh-从句。Wh-词包括who, whom,. whose, whoever, what, whatever, which, whichever等连接代词和where, when, how, why等连接副词。Wh-从句的语法功能除了和that-从句一样外,还可充当介词宾语、宾语补语和间接宾语等,例如:
主语: How the book will sell depends on its author. 书销售如何取决于作者本人。
直接宾语:In one's own home one can do what one likes. 在自己家里可以随心所欲。
间接宾语:The club will give whoever wins a prize.
俱乐部将给得胜者设奖。
表语: My question is who will take over president of the Foundation. 我的问题是谁将接任该基金会主席职位。
宾语补足语:She will name him whatever she wants to. 她高兴给他起什么名字就取什么名字。
同位语: I have no idea when he will return.
我不知道他什么时候回来。
形容词宾语:I'm not sure why she refused their invitation. 我尚不能肯定她为什么拒绝他们的邀请。
介词宾语: That depends on where we shall go.
那取决于我们去哪儿。
2)Wh-从句作主语也常用先行词it做形式主语,而将wh-从句置于句末,例如:
It is not yet decided who will do that job.
还没决定谁做这项工作。
It remains unknown when they are going to get married. 他们何时结婚依然不明。
[编辑本段]八、if, whether引导的名词从句
1)yes-no型疑问从句
从属连词if, whether引导的名词从句是由一般疑问句或选择疑问转化而来的,因此也分别被称为yes-no型疑问句从句和选择型疑问从句,其功能和wh-从句的功能相同, 例如:
主语:Whether the plan is feasible remains to be proved. 这一计划是否可行还有等证实。
宾语:Let us know whether / if you can finish the article before Friday. 请让我们知道你是否能在星期五以前把文章写完。
表语:The point is whether we should lend him the money. 问题在于我们是否应该借钱给他。
同位语:They are investigating the question whether the man is trustworthy. 他们调查他是否值得信赖。
形容词宾语: She's doubtful whether we shall be able to come. 她怀疑我们是否能够前来。
介词宾语: I worry about whether he can pass through the crisis of his illness. 我担心他是否能度过疾病的危险期。
2)选择性疑问从句
选择性疑问从句由关联词if/whether…or或whether…or not构成,例如:
Please tell me whether / if they are Swedish or Danish. 请告诉我他们是瑞典人还是丹麦人。
I don't care whether you like the plan or not.我不在乎你是否喜欢该计划。
if和whether的区别:
1、 在动词不定式之前只能用whether 。如:
例8 I can’t decide whether to stay. 我不能决定是否留下。
2、 在whether …… or not 的固定搭配中。如:
例9 I want to know whether it’s good news or not . 我想知道是否是好消息。
3 、在介词后,只能用whether。如:
例10 His father is worried about whether he lose his work . 他的父亲担心是否会失去工作。
4、宾语从句放在句首表示强调时,只能用whether 。如:
Whether this is true or not, I really don’t know. 这是否真的,我真的不知道。
(例11 Whether they can finish the work on time is still a problem . 他们是否能准时完成这项工作还是个问题。--此例为主语从句,有误,感谢指出)
5、用if会引起歧义时,只用whether。如:
例12 Could you tell me if you know the answer ?
这句话有两种意思:“你能告诉我是否知道答案吗?”或“如果你知道答案,请告诉我,好吗?”。如用whether可避免歧义.
[编辑本段]九、否定转移
1) 将think, believe, suppose, expect, fancy, imagine等动词后面宾语从句的否定词转移到主句中,即主句的谓语动词用否定式,而从句的谓语动词用肯定式。
I don't think I know you. 我想我并不认识你。
I don' t believe he will come. 我相信他不回来。
注意:若谓语动词为hope,宾语从句中的否定词不能转移。
I hope you weren't ill. 我想你没有生病吧。
2) 将seem, appear 等后的从句的否定转移到前面。
It doesn't seem that they know where to go.
看来他们不知道往哪去。
It doesn't appear that we'll have a sunny day tomorrow.
看来我们明天不会碰上好天气。
3) 有时将动名词,介词短语或整个从句的否定转变为对谓语动词的否定。
I don't remember having ever seen such a man.
我记得从未见过这样一个人。 (not否定动名词短语 having…)
It's not a place where anyone would expect to see strange characters on the street.
在这里,人们不会想到在街上会碰上陌生的人。
(anyone 作主语,从句中的谓语动词不能用否定形式。)
4) 有时状语或状语从句中否定可以转移到谓语动词前。
The ant is not gathering this for itself alone. (否定状语) 蚂蚁不只是为自己采食。
He was not ready to believe something just because Aristotle said so. (否定because状语) 他并不因亚里斯多德说过如何如何,就轻信此事。
She had not been married many weeks when that man's younger brother saw her and was struck by her beauty. (否定状语many weeks) 她结婚还不到几个月,这个人的弟弟就看见她了,并对她的美貌着了迷。
[编辑本段]十、高考热点透视
1. ___ is a fact that English is being accepted as an international language. (NMET 1995)
A. There B. This C. That D. It
答案D。当名词从句在句中作主语时,为避免句子头重脚轻,常用it作形式主语置于句首,而将真正的主语从句放在句尾。此时it只起先行引导作用,本身无实义。此句也可以改写为:That English is being accepted as an international language is a fact.
2.A computer can only do ____ you have instructed it to do.(NMET2001)
A.how B.after C.what D.when
答案C。从句子结构可知,句子的空白处应该填引导宾语从句的连词,做主句谓语动词do的宾语,同时该连接词还是从句中的do的宾语,因此,此处的连接词应该用what。
3. He asked ____ for a violin.(MET1992)
A. did I pay how much B. I paid how much
C. how much did I pay D. how much I paid
答案:D。宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,句子语序要用陈述语序。
4. What the doctors really doubt is ____ my mother will recover from the serious disease soon.(上海2001年春季招生)
A. when B. how C. whether D. why
答案C。这是一个表语从句。根据 doubt一词可知,所怀疑的应是是否能治好病,所以要填whether。这句话的意思是“医生真的怀疑我妈妈是否能很快从重病中恢复过来。”
5.It is generally considered unwise to give a child _____he or she wants. (NMET1997)
A. however B. whatever C. whichever D. whenever
答案B。根据句意“一般认为孩子要什么就给什么是不好的。”可以看出后面的从句应是一个宾语从句,而从句中wants缺少宾语,A. however 和D. whenever是不能作宾语的;排除A和D,whichever表示“无论哪一个,无论哪些”,应表示一定范围内的人或物,此处没有涉及事物的范围,所以应选 B.whatever,表示“无论什么”。
6. ______leaves the room last ought to turn off the lights. (MET1988)
A. Anyone B. The person C. Whoever D. Who
答案C。本题句子的意思是:无论谁最后离开房间一定要把灯关掉。本题考查连接代词whoever引导的名词性从句,连接代词whoever可以引导名词性从句,并在从句中作主语,相当于any person who或The person who, 意为“一切……的人”。而anyone和the person均非连词,不能引导从句,况who leaves the room last意为“某个最后离开房间的人”,与题意不符,如果要选A. Anyone或B. The person,都必须在它们后面再加上引导定语从句的关系代词who。如果要选D. Who就体现不出“无论谁”的含义了。
7. Sarah hopes to become a friend of ______shares her interests. (Shanghai1995)
A. anyone B. whomever C. whoever D. no matter who
答案为C。本题句子的意思是:Sarah希望跟自己有共同爱好的人交朋友。疑问词+ever引导的名词性从句与no matter+疑问词引导的从句的区别是:前者既可以引导名词性从句也可以引导让步状语从句;后者只能引导让步状语从句。首先排除A和D,从句中需要的是主语,所以whomever也不行。
8. ---- I drove to Zhuhai for the air show last week.
---- Is that ______ you had a few days off ? ( NMET1999)
A. why B. what C. when D. where
答案A。根据语境,甲说上周驱车去珠海观看航模展览。乙据此来询问甲这是否是请几天假的原因,故答案是A。答案B,C, D均与该题语境不符。根据上句提供的语境,下句应该问“那就是你为什么离开几天的原因吗?”
9. I still remember ______ this used to be a quiet village. ( NMET1993)
A. when B. how C. where D. what
答案A。根据从句中缺少的句子成分是状语,排除D.what,而答案C, D均与题意不符,所以应选A.when。used to be表示一种过去存在的状态,本句的意思是“我仍然记得这里在什么时候是个宁静的地方。”
10.I read about it in some book or other,does it matter ____ it was?(2001春季招生)
A.where B.what C.how D.which
答案D。这是一个主语从句。主语从句中缺少表语。从上句的意思分析,应是哪本书,所以要填which,这句话的意思是“我在某本书中读到过有关这方面的内容,是哪一本书重要吗?”。
11. Information has been put forward ____ more middle school graduates will be admitted into universities.
A. while B. that C when D. as (2001年上海)
答案B。该题考查that引导的同位语从句。同位语从句通常由that引导,接在fact, news, promise, possibility, information, doubt, message名词后,用来解释或说明名词的内容。
12. —I think it is going to be a big problem.
—Yes, it could be.
—I wonder ______ we can do about it. (北京 2002春季)
A、if B、how C、what D、that
答案C。本题考察名词性从句的连接词的用法。wonder后面应跟宾语从句,而从句中的谓语动词do是及物动词,可见从句缺少一个代替宾语的成分,我们可以用排除法排除不作成分的if和that,再排除引导方式状语的how,答案是C,句子的意思是“我们能就此做些什么”。

名词性从句有哪些
1.that引导的同位语从句,they would come to visit China是对the hope的内容的解释说明。that再此句中部充当任何成分,即不做主语,谓语,不做表语,或者是宾语。总之,这个时候的that是摆设用的,好听些称之为“引导用的”。
2 这个是表语从句,is 是系动词后面一般跟表语,what she used to be 是个句子,位于系动词后面,因此称之为表语从句。句子一般有主+谓+宾构成,在这个句子what she used to be 中what是宾语,she是主语,used to be 是谓语,谁叫what 是引导词,所以只能至于从句前面引导这个标语从句。what在此处充当的成分是宾语,意思为“什么”,其他选项如“ which”夜课充当宾语,但意思是“哪一个”不符合题意,how是用来做状语的,意思为“怎么样”,也不符合题意。
3,第三题,楼上解答的很详细了。再补充一点就是_____class Tom will study in为整个句子的主语,因为它是个句子,因此把它称为主语从句,remains是整句话的谓语。
以上就是关于名词性从句优质课获奖课件 ,高中英语主语从句课件的全部内容,以及名词性从句优质课获奖课件 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

