本文目录
初中英语定语从句讲解课件

大学定语从句讲解课件
大学定语从句讲解
定语从句(Attributive Clauses)在句中做定语,修饰一个名词或代词,有时也可以修饰部分或整个句子。
被修饰的名词,词组或代词即先行词。定语从句通常出现在先行词之后,由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引出。
关系代词有:who, whom, whose, that, which, as。
关系副词有:when, where, why, how。
关系代词和关系副词放在先行词和定语从句之间,起连接作用,同时又可做定语从句的一个成分。当关系代词做宾语时可以省略。
定语从句中的谓语动词必须在人称上和数量上和先行词保持一致。
定语从句分为限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。
1 、关系代词引导的定语从句
1) who, whom, that 这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中所起作用如下:
Is he the man who/that wants to see you?(who/that在从句中作主语)
He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday.(whom/that在从句中作宾语)
2) whose 用来指人或物,(只用作定语,若指物,它还可以同of which互换),例如:
Please pass me the book whose (of which) cover is green.
3) which, that 它们所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可作主语、宾语等,例如:
A prosperity which / that had never been seen before appears in the countryside.(which / that在句中作宾语)
The package (which / that) you are carrying is about to come unwrapped. (which / that在句中作宾语)
关系代词that和which 都可以指物,that 和Who 都可以指人,其用法区别:
不用that的情况:
a) 在引导非限定性定语从句时
(错)The tree, that is four hundred years old, is very famous here.
b) 介词后不能用
We depend on the land from which we get our food.
c) 多用who 的情况
①关系代词在从句中做主语
A friend who helps you in time of need is a real friend.
②先行词为those, people 时
Those who were either fools or unfit for their offices could not see the cloth.
③先行词为all, anyone, ones, one 指人时
One who doesn't work hard will never succeed in his work.
④在There be句型中
There is a stranger who wants to see you.
⑤在被分隔的`定语从句中
A new teacher will come tomorrow who will teach you German.
⑥在有两个定语从句的句子中,其一用who,其二用that,但若先行词后接两个以上的并列定语从句时,后一个必须重复前一个关系代词。
The student who was praised at the meeting is the monitor that is very modest and studies very hard.
There is a teacher who is always ready to help others and who enjoys what he does.
2) 只能用that作为定语从句的关系代词的情况
a)在不定代词,如:anything, nothing, everything, all, much, few, any, little等作先行词时,只用that,不用which。
All that is needed is a supply of oil.
Finally, the thief handed everything that he had stolen to the police.
b)先行词有the only, the very, the just修饰时,只用that。
He is the very man that helped the girl out of the water.
c)先行词为序数词(the last)、数词、形容词最高级时,只用that。
The first English book that I read was "The Prince and the Pauper" by Mark Twin.
d)先行词既有人,又有物时。
He talked about the teachers and schools that he visited.
e)当主句是以who 或which 开始的特殊疑问句时,用that 以避免重复。
Who is the person that is standing at the gate.
f)关系代词在从句中做表语
He is not the man that he used to be.
2 、关系副词引导的定语从句
关系副词可代替的先行词是时间、地点、方式或理由的名词,在从句中作状语。
关系副词when, where, why, how的含义相当于"介词+ which"结构,因此常常和"介词+ which"结构交替使用,例如:
There are occasions when (on which) one must yield.
Beijing is the place where (in which) I was born.
Is this the reason why (for which) he refused our offer?
I'm surprised the way how (by which) he works out the problem.
注意:
①在非限制性定语从句中,"介词+ which"结构不能代替关系副词。
如:They set up a state for their own , where they would be free to keep Negroes as slaves.
②含有介词短语的动词一般不能拆开,介词仍放在动词后面。
Is this the book which (that) she was looking for?
3、名词/数词/代词 /形容词最高级 + 介词 + 关系代词引导定语从句
She has written a book , the name of which I have forgotten.
There are fifty-five students in our class , all of whom are working hard.
There are five continents in the world , the largest of which is Asia.
4、as, which 引导非限定性定语从句的差别
由as, which 引导的非限定性定语从句,as和which可代整个主句,相当于and this或and that。As一般放在句首,which在句中。
As we know, smoking is harmful to one's health.
The sun heats the earth, which is very important to us.
as可引导非限制性从句,常带有“正如”的意思。
As is know, smoking is harmful to one's health.
用法区别:
(1) as 引导的定语从句可置于句首,而which不可。
As we all know, he never smokes.
(2) as 代表前面的整个主句并在从句中作主语时,从句中的谓语必须是系动词;若为行为动词,则从句中的关系代词只能用which。
(3)非限定性定语从句中出现expect, think, suppose 等表示猜测、想象、预料等时。
She succeeded in her doing the research work , as we expected.
(4)As 的用法 the same… as; such…as 中的as 是一种固定结构, 和……一样……。
I should like to use the same tool as is used here.
We should have such a dictionary as he is using.
定语从句语法专项练习习题精选
用适当的关系词填空:
1. I still remember the night _______I first came to the house.
2. I'll never forget the day________ we met each other last week.
3. Mr Black is going to Beijing in October, _______is the best season there.
4. I will never forget the days _______I spent with your family.
5. I'll never forget the last day______ we spent together.
6. This is the school ______I used to study.
7. Do you still remember the place______ we visited last week?
8. Do you still remember the place_______ we visited the painting exhibition?
9. Have you ever been to Hangzhou,_____is famous for the West Lake?
10. Have you ever bee to Hangzhou, ______lies the West Lake?
11. Tom will go to Shanghai,______live his two brothers.
12. I live in Beijing,____is the capital of China.
13. There was a time ______there were slaves in the USA.
14. It is the third time ______you have made the same mistake.
15. It was in the street _____I met John yesterday.
16. It was about 600 years ago____the first clock with a face and an hour hand was made.
17. The moment _____I saw you, I recognized(认出)you.
18. This is the very novel about____we've talked so much.
19. This is the way____he did it.
20. Who is the student _____was late for school today?
21. Who _____knows him wants to make friends with him?
22. What else was there in my brother____you didn't like?
23. He lives in the room____window faces to the south.
24. He lives in the room, the window_____faces to the south.
25. This is Mr. John for____son I brought a book yesterday.
26. This is Mr. John for_____I bought a book yesterday.
27. This is the hour_____the place is always full of women and children.
28. And there is one point ______I'd like your advice.
29. Winter is the time of year______the days are short and nights are long.
30. I hope you will find this valley a beautiful place____you may spend your weekend.
KEYS:
1. when 2. when 3. which 4. that/which 5. that
6. where 7. that/which 8. where 9. which 10. where
11. where 12. which 13. when 14. that 15. that
16. that 17. (that) 18. which 19. (that/in which) 20.that
21.that 22 that 23.whose 24. of which 25. whose
26. whom 27. when 28. that 29. that 30. where

定语从句讲解视频
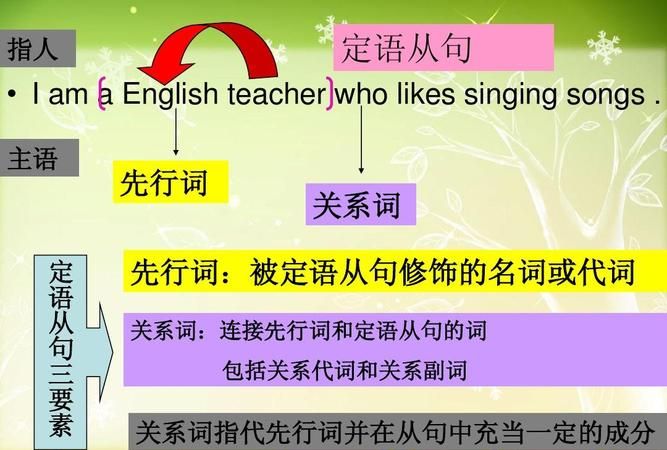
一、了解定语从句及相关术语
1. 定语从句:修饰一个名词或代词的从句称为定语从句,一般紧跟在它所修饰的先行词后面,相当于形容词在句中作定语。
2. 先行词:被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词。
3. 关系词:引导定语从句的关联词称为关系词。关系词有关系代词和关系副词。关系代词有that,which,who,whom,whose,as等;关系副词有where,when,why等。
He is the man who I want to see. 他就是我想见的人。
先行词 关系词 定语从句
二、掌握关系代词及其作用
最常用的关系代词是who, whom, whose, that,which和as。关系代词同时起了两个作用。它们可以像别的代词一样,可以代表一个名词,在定语从句中用作主语或宾语,同时,它们又起到了连词的作用,把主句和从句连接起来。
1. who指人,在定语从句中一般做主语。如:
Do you know the man who is speaking to your father? 你认识和你爸爸讲话的那个人吗?(定语从句修饰先行词the man,who在定语从句中作is speaking的主语)
This is the stranger who helped us yesterday. 这是昨天帮助我们的那个陌生人。
She is the girl who works hard at maths. 她就是那个努力学习数学的女孩。
2. whom指人,在定语从句中作宾语。在口语或非正式文体中,whom可以省略。如:
He is the man (whom) we just talked about. 他就是我们刚才谈论的那个人。
The boy (whom) we met in the street yesterday is my classmate. 我们昨天在大街上遇到的那个男孩是我的同学。
3. whose既可以指人,也可以指物,在定语从句中作定语修饰它后面的名词。如:
This is the girl whose father is a policeman. 这就是那个爸爸是警察的女孩。
They live in a house whose windows face south. 他们住在一座窗子朝南的房子里。
4. which指物,在定语从句中做主语或宾语。作宾语时可以省略。如:
Physics is a subject which is very difficult to learn. 物理是一门很难学的科目。(在定语从句中做主语,不能省略)
Apples are the fruit (which) she likes best. 苹果是她最喜欢的水果。
5. that既可以指人,也可以指物,在定语从句中做主语或宾语。指人时,相当于who或whom;指物时,相当于which。that在从句中作宾语时可省略。如:
He is the man that lives next door. 他就是住在隔壁的那个人。
We like programs that are very interesting. 我们喜欢有趣的节目。
She is the woman (that) we saw in the bookshop. 她是我们在书店见到的那名妇女。
6. that指人时,相当于who或者whom;指物时,相当于which。在定语从句中作主语或者宾语。如:
The number of the people that/who come to visit the city each year rises one million. 来这个城市参观的.人数每年增长一百万。
Where is the man that/whom I saw this morning? 今天早晨我看见的那个人在哪里?
三、掌握关系副词及其作用
关系副词有when、where、why,他们在引导定语从句时,既在定语从句中充当状语,又起连接作用。
1. When指时间,在定语从句中充当时间状语。如:
I still remember the day when I first came to Dalian. 我仍然记得第一次来大连那天的情景。
He told me the date when he joined the party. 他告诉了我他入党的时间。
They stayed with me for three weeks when they drank all the wine I had.他们和我一起住了三个星期,在那三周里,把我所有的葡萄酒都喝光了。
2. where指地点、在定语从句中充当地点状语。如:
This is the house where we lived when we were young. 这就是我们小时候住的房子。
This is the village where I grew up. 这就是我长大的那个村庄。
Hangzhou is a city where there is a beautiful lake. 杭州是个有一个美丽的湖泊的城市。
3. why指原因,在定语从句中充当原因状语。如:
I know the reason why he was late for the meeting. 我知道他开会迟到的原因。
Do you know the reason why he refused the invitation? 你知道他拒绝应邀的原因吗?
That is the reason why I’ve changed so much. 那就是我变化这么快的原因。
四、学习定语从句应该注意的问题
1. 关系代词和关系副词的选用
如果先行词是表示时间或地点的名词,不能就一律断定要用关系副词when或where,务必要看引导词在从句中作什么成分,如果作状语,用关系副词,如做主语或宾语要用关系代词。当reason做先行词时,也需注意其引导词在从句中作什么成分,不能断定一概用why来引导。如:
I’ll never forget the time when we worked together. 我将永远不会忘记我们一起工作的时光。 (work是不及物动词,when在定语从句中作状语,故用关系副词。)
I’ll never forget the time (which/that) we spent together. 我将永远不会忘记我们一起渡过的时光。
spend是及物动词,which/that在定语从句中作宾语,故用关系代词,也可以省略。)
This is the factory where he worked before. 这是他以前工作过的工厂。(work是不及物动词,where在定语从句中作状语。)
This is the factory which/that he visited before. 这是他以前参观过的工厂。(visit是及物动词,which/that在从句中作宾语,亦可省略。)
The reason why I was absent yesterday was that I was ill. 我昨天缺席的原因是我生病了。定语从句中缺状语,表示原因,故用关系副词why)
The reason that he explained for his being late was that he had missed the early bus.他所解释的迟到的原因是他误了头班汽车。(explain是及物动词,that在从句中作其宾语)
再看一个例题:
(1)This is the factory ________ I visited last year.
(2)This is the factory _______ I worked last year.
(3)This is the factory _______ produces all kinds of TV sets.
A. where B. which C. whom D. whose
以上三个句子只有细微的差别,但答案却不同:(1)和(3)选B. which。(2)选A. where。做这种题时,要看先行词与定语从句中谓语动词之间的关系;(1)中是动宾关系,即I visited the factory,因此选which。(2)中factory应在定语从句中作地点状语,即:I worked in the factory,因此选where。(3)中是作定语从句中的主语,不作地点状语,因此选which。
2. 限制性定语从句只能用that的几种情况
1)当先行词是anything, everything, nothing (something 除外), few, all, none, little, some等代词时,或者是由every, any, all, some, no, little, few, much等修饰时。如:
Have you taken down everything that Mr. Li has said? 你把李先生说的话都记下来了吗?
There seems to be nothing that seems impossible for him in the world. 在他看来世界上似乎没有不可能的是。
All that can be done has been done.所有能做的事情都做了。
2)当先行词被序数词修饰。如:
The first place that they visited in London was the Big Ben. 他们在伦敦参观的第一个地方就是“大本钟”。
3)当先行词被形容词最高级修饰时。如:
I think the film Assembly is the best film that I have seen. 我认为电影《集结号》是我看过的最好的电影。
4)当形容词被the very, the only 修饰时。如:
This is the very dictionary that I want to buy. 这就是我想买的那本辞典。
After the fire in his house, the old car is the only thing that he owned. 房子失火以后,那辆旧汽车就是他唯一的财产。
5)当先行词前面有who, which等疑问代词时。如:
Who is the man that is standing there? 站在那儿那个人是谁?
Which is the T-shirt that fits me most?哪件T恤适合我穿?
6)当先行词既有人,也有动物或者物体时。如:
Can you remember the scientist and his theory that we have learned?你还记得我们学到的那个科学家及他的理论吗?
3. 区分定语从句和同位语从句
1)定语从句修饰先行词,它和先行词是修饰关系;同位语从句说明先行词的具体内容,是补充说明的关系。如:
The plane that has just taken off is for London. 刚起飞的飞机是去伦敦的。(定语从句)
The fact that he has been dead is clear. 他已经死亡的事实是清楚的。(同位语从句)
2)定语从句由关系代词或者关系副词引导,关系词在句中充当成分,有时可以省略;同位语从句主要由that引导,在句中一般不做成分;句子也可以由when, where, how, why, whether, what等词引导,充当成分。如:
The problem that we are facing now is how we can collect so much money.我们现在面临的问题是怎样筹集那么多钱。 (定语从句)
The problem how we can collect so much money is difficult to solve. 怎样筹集钱的问题很难解决。(同位语从句)
3)同位语从句和先行词一般可以用be动词发展成一个完整的句子,而定语从句不可以。如:
The fact that the earth moves around the earth is known to all.地球绕着太阳转这一事实是众所周知的。(同位语从句)
The fact is that the earth moves around the earth. 这个事实就是地球绕着太阳转。
3. 关系副词when, where, why的含义相当于"介词+ which"结构,因此常常和"介词+ which"结构交替使用,例如:
There are occasions when (on which) one must yield. 任何人都有不得不屈服的时候。
Beijing is the place where (in which) I was born. 北京是我的出生地。
Is this the reason why (for which) he refused our offer? 这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗?
4. that代替关系副词
that可以用于表示时间、地点、方式、理由的名词后取代when, where, why和"介词+ which"引导的定语从句,在口语中that常被省略,例如:
His father died the year (that / when / in which) he was born. 他父亲在他出生那年逝世了。
He is unlikely to find the place (that / where / in which) he lived forty years ago. 他不大可能找到他四十年前居住过的地方。
五、考点链接
1. 考查that
Do you still remember the chicken farm _______ we visited three months ago?
A. where B. when C. that D. what (2005北京春)
【解析】C、从句中visited 是及物动词,而且没有宾语,要用关系代词引导定语从句。
2. 考查who,whom和whose
1)Women _______ drink more than two cups of coffee a day have a greater chance of having heart disease than those ________ don’t.
A. who; 不填 B. 不填; who C. who; who D. 不填表; 不填(2006北京卷)
【解析】C、第一空定语从句缺少主语,必须用who,不能省略;第二空也是关系代词作主语,不能省略。
2)Look out! Don’t get too close to the house______ roof is under repair.
A. whose B. which C. of which D. what (2006福建卷)
【解析】A、从句中缺少的是roof的定语,在定语从句中关系代词作定语用whose,whose可以修饰人,也可以修饰物。
3. 考查when,where和when
1)—Where did you get to know her?
—It was on the farm _________ we worked. (2007 山东卷)
A. that B. there C. which D. where
【解析】D、work是不及物动词,不需要宾语,所以用where引导定语从句。

初中英语定语从句讲解
内容提要
定语从句是由关系代词和关系副词引导的从句,其作用是作定语修饰主句的某个成分,定语从句分为限定性和非限定性从句两种。状语从句分为时间状语从句,结果状语从句,让步状语从句,原因状语从句,条件状语从句以及行为方式状语从句。名词从句包括主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句和同位语从句及there be句型。
一、 限定性定语从句
1. that即可代表事物也可代表人,which代表事物;它们在从句中作主语或宾语,that在从句中作宾语时常可省略关系词,which在从句中作宾语则不能省略。而且,如果which在从句中作“不及物动词+介词”的介词的宾语,注意介词不要丢掉,而且介词总是放在关系代词which的前边,但有的则放在它原来的位置
2. which作宾语时,根据先行词与定语从句之间的语义关系,先行词与which之间的介词不能丢
3. 代表物时多用which,但在带有下列词的句子中用that而不用which,这些词包括all, anything, much等,这时的that常被省略
4. who和whom引导的从句用来修饰人,分别作从句中的主语和宾语,whom作宾语时,要注意它可以作动词的宾语也可以作介词的宾语
5. where是关系副词,用来表示地点的定语从句
6. when引导定语从句表示时间
〔注〕值得一提的是,表示时间“time"一词的定语从句只用when引导,有时不用任何关系代词,当然也不用that引导
By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed there for two weeks.
I still remember the first time I met her.
Each time he goes to besiness trip, he brings a lot of living necessities, such as towers, soap, toothbrush etc.
7. whose是关系代词,修饰名词作定语,相当于所修饰成分的前置所有格
8. 当从句的逻辑主语是some, any, no, somebody, anybody, nobody, something, anything, everything或nothing时,常用there is来引导
二、非限定性定语从句:非限定性定语从句的作用是对所修饰的成分作进一步说明,通常和主句间用逗号隔开,将从句拿掉后其他部分仍可成立
1. which引导的非限定性定语从句来说明前面整个句子的情况或主句的某一部分
2. 在引导限定性定语从句时,that有时相当于in which, at which, for which或at which
Attitudes towards daydreaming are changing in much the same way that(in which) attitudes towards night dreaming have changed. 人们对白日做梦的态度正在改变,这与人们对夜间做梦的看法的变化有非常相似之处。
I like the music for the very reason that(for which) he dislike it. 我出于某种原因喜欢这种音乐,而他恰恰与我相反。
We arrived the day that(on which) they left. 刚好我们到的那天他们走了。
3. 有时as也可用作关系代词
4. 在非限定性定语从句中,不能用that,而用who, whom代表人,用which代表事物
三、定语从句结构错误
1. 缺关系词
2. 从句中缺成分
摘自《简明英语语法》
在英文中,有两种定语从句:限定性定语从句与非限定性定语从句。这两种定语从句在其功能和形式方面都有明显的区别:
限定性定语从句限定性定语从句与主句的关系很紧奏,对其先行词起限定、修饰的作用。如果将其去掉,会影响句子意思的完整性;有时甚至于引起费解、误解。例如:
Rainforests are being cleared for valuable timber and other resources to speed up the economic growth of the nationsin which they are located .
为了加速他们各自所在国家的经济发展,热带雨林作为有价值的原木和其他资源正为人们所砍伐。
Ocean currents affect the climates of the lands near which they flow.
洋流影响其流经的附近地区的气候。
They explained the reason to us why they had hated us before.
他们向我们解释为什么他们不喜欢我们的原因。
非限定性定语从句非限定性定语从句在形式上就与主句很松散,它与主句之间有一个逗点","隔开;它对其先行词没有限定、修饰的作用,只起补充、说明的作用。有时也用它来对全句进行补充、说明。即使将其去掉,也不会影响句子意思。由于上述原因,非限定性定语从句在表达意思方面也有别于限定性定语从句。另外,非限定性定语从句在中文译文里,我们往往将其作为一个分句处理,而不把它作定语翻译。 例如:Earlier , the Babylonians had attempted to map the world , but they presented it in the form of a flattened disc rather than a sphere , which was the form adopted by Ptolemy .
(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对先行词a sphere进行补充、说明。)
更早之前,巴比伦人曾试图绘制世界地图,但是他们把它绘制成平盘状而不是托勒密所采用的球体状。
The combination of satellites, which transmit information , computers , which store information , and television , which displays information , will change every home into an education and entertainment center .
(此句中,三个非限定性定语从句分别对三个先行词:satellites ,computers和television进行补充、说明。如果去掉这三个非限定性定语从句,那么句子可简化为:
The combination of satellites , computers and television will change every home into an education and entertainment center .)卫星能传输信息,计算机能储存信息,电视能显示信息,把这些手段结合起来可以使每个家庭都成为教育娱乐的中心。
The sun heats the earth , which makes it possible for plants to grow .(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对全句进行补充、说明,将全句表达的意思看成"一件事情)。太阳给予大地热,这就使植物的生长成为可能。
The old man has a son , who is in the army .(此句中,非限定性定语从句是对先行词son进行补充、说明。但本句所传达的信息是:"这位老人只有一个儿子" 。如果将此句改写成限定性定语从句:
The old man has a son who is in the army . 那位老人有一个在部队工作的儿子。那么,限定性定语从句就要对先行词son进行限定、修饰。这样一来,句子所传达的信息就变成了:"这位老人有一个儿子在部队工作,还有其他的儿子在干别的工作"。)那位老人有一个儿子,他在部队工作。
以上就是关于定语从句趣味讲解课件 ,初中英语定语从句讲解课件的全部内容,以及定语从句趣味讲解课件 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
