本文目录
英语中的名词性从句的分类及详细介绍大全
引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连接词:that,whether,if
不充当从句的任何成分)
连接代词:what,
whatever,
who,
whoever,
whom(ever),
whose(ever),
which(ever).
连接副词:when,
where,
how,
why
,how
many,how
much,等,代词在从句中可以作主语,宾语,表语,定语,而副词在从句中作状语
eg.What
you
said
sounds
reasonable.
Whatever
you
said
is
right.(这两句中都是主语从句)
eg:He
wants
to
know
whether/if
we
can
help
him.(动词后宾语从句用这两个是否都可以)
They
are
talking
about
whether
we
will
go
for
a
picnic.(介词后宾语从句,只用这一个是否)
eg:What
I
can't
understand
is
why
he
left
without
saying
a
word.(why引导的是表语从句)
eg:
I
have
no
idea
why
he
left
without
saying
a
word
.(why引导的同位语从句,即对前一个名词的解释或说明)
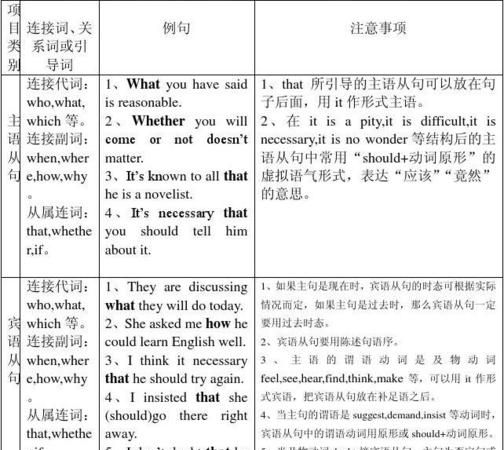
名词性从句分类
名词性从句包括;主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句及同位语从句。
分别在句中作主语、宾语、表语及同位语。
名词性从句讲解
在主从复合句中,从句可以充当主句的主语、表语、宾语或同位语。由于在多数情况下,主语、表语、宾语或同位语这四种句子成分由名词性词类充当,所以,我们把这些作用相当于名词的从句统称为名词性从句,把充当主语、表语、宾语或同位语的从句分别称为主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句或同位语从句。也就是说充当什么成分就叫什么从句。名词性从句由连接词(或关联词)引导。常用的连接词有:
连接词
作用
whether 是否
that (本身无词义)
只起连接词作用,引导从句,在从句中不作任何成分
who, whom, whose
which 哪一个
what 什么,所…的
在从句中分别作主语、宾语和定语
在从句中分别作主语、宾语和定语
在从句中分别作主语、宾语和定语
when什么时候,where什么地方
how怎样、怎么,why为什么
除了起连接词作用外,还在从句中作状语
疑问词(who, whom, whose, what, which, where, why, when, how)可以引导主语、宾语和表语从句。它们的特点是:1、疑问词有本身的词义;2、疑问词在从句中担当句子成分,如主语、宾语或状语;3、这种疑问词引导的从句一律用陈述语序,不能用疑问语序。
For example:
Do you know whom they are looking for? 你知道他们在找谁吗?(宾语从句,陈述语序。不能是whom are they looking for?)
I don’t know who did it.我不知道这是谁干的。(宾语从句。在从句中如果疑问词作主语,其陈述语序和疑问语序一致。)
She asked me where I had been.她问我到哪儿去了。(宾语从句。陈述语序,不能是where had I been. 直接引语,间接引语。注意这句话的时态。)
Can you tell me when the train will arrive? 你能告诉我火车什么时候到吗?(宾语从句。陈述语序,不能是when will the train arrive. 直接引语,间接引语。)
I don’t know why he hasn’t come yet. 我不知道他为什么还没来。(宾语从句,陈述语序。不能是why hasn’t he come yet.)
He didn’t tell me what you were doing. 他没和我说你在干什么。(宾语从句,陈述语序。不能是what were you doing.)
What you have done might do harm t other people. 你所做过的事情有可能伤害别人。(主语从句。what 作从句的宾语。陈述语序,不能是what have you done. 如果用疑问语序,意思发生了变化,成了“你做了什么?”。)
I don’t know where he is now. 我不知道他现在在哪里。(宾语从句,陈述语序。不能是where is he now.)
Where he went for his weekend is not known. 不知道他去哪里过的周末。(主语从句,where 作从句的地点状语。陈述语序,不能是where did he go for his weekend.)
Whose fault this is is not important. 这是谁的过错并不重要。(主语从句,whose 作从句的定语。陈述语序,不能是whose fault is this.)
What I want to know is where he has gone for his weekend. 我想知道的是他到哪里度周末去了。(这句话包含两个名词性从句:what I want to know是主语从句,what 在从句中作宾语,从句用陈述语序,不能是What do I want to know. Where he has gone for his weekend 是表语从句,where 在从句中作状语,从句用陈述语序,不能是where has he gone for his weekend.)
下面我们再分别讲述主语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句和表语从句。
一、 主语从句
1.that 引导主语从句时,that 没有意义,但不能省略。(that 引导宾语从句时可以省略。)
For example:
It worried her a bit that her hair was turning gray.她的头发正在变白,这使她很不安。that引导主语从句,it 作形式主语,that 不能省略。
That she is a rich woman is known to us all. 众所周知,她是个富有的女人。这是that 引导主语从句,that 不能省略。这句话可以改为用it 作形式主语的句型。请同学们改写:It is known to us all that she is a rich woman.)
We didn’t know (that) you had sold your house. 我们不知道你已经把你的房子卖了。这是that引导宾语从句,that 可以省略。注意这句话的时态。
2.从句作主语时,多数情况下由 it 作形式主语,而把主语从句放在后面,尤其是谓语部分(包括宾语)较短的情况下。
For example:
It wasn’t very clear what she meant. 不清楚她是什么意思。
It is important that he should come on time. 他按时来是很重要的。
It is true that that man on the left is a well-known writer here. 左边那个人是本地的一位著名作家,这是真的。这里,第一个that 引导主语从句,是单纯的连词,无词义,不作句子成分。第二个that 是指示代词,作句子成分,是man 的定语。
3.whether 既可以引导主语从句也可以引导宾语从句,但if不能引导主语从句。whether 后面可以加or not, 而if 不能与or not 连用。作介词宾语时不用if.如:
Whether I knew John doesn’t matter. = It doesn’t matter whether I knew John. 我是否认识约翰没有关系。
Whether or not she’ll come isn’t clear. = Whether she’ll come or not isn’t clear. = It isn’t clear whether …. 她是否来还不清楚。
It all depends on whether we can get their cooperation. 这是主语从句还是宾语从句?it 是形式主语吗?it 是代词,whether 引导的是宾语从句,作介词on 的宾语,不能用if引导。请翻译这句话。这完全取决于我们是否能得到他们的合作。
I worry about whether I hurt her feelings. 宾语从句,介词宾语,不能用if 引导。请翻译这句话。
She asked me whether/if you were married. 宾语从句,既可以用whether, 又可以用if 引导。注意时态的对应。请翻译这句话。
We haven’t decided whether/if we shall give them aid.
I’m not sure whether/if the report is believable.
Now let’s do some translation:
现在还很难预测谁会赢得下一届总统选举。
It is still hard to predict who will win the next presidential election.
对于多数公民来说,谁当选总统无关紧要。
Who will become the president doesn’t matter much to most citizens.
这位前总统是否会被判处死刑还有待观察。
It remains to be seen whether the ex-president will be sentenced to death.
真可惜,王教授不能出席我们的英语晚会。
It is a pity that Prof. Wang can’t attend our English Evening.
我们需要的是更多的时间。
What we need is more time.
二、 宾语从句
在谓语动词、介词、动词不定式、分词、动名词之后都可以带有宾语从句。某些形容词如sure, happy, glad, certain, pleased 等之后也可以带有宾语从句。
1. that 引导的宾语从句: that 没有意义,在口语或非正式文体中常省略
例如:
I really feel she’s making a mistake. 我的确感到她正犯错误。
James said (that) he was feeling better. 詹姆斯说他感到好些了。
Hearing that his son was badly wounded, he hurried to the hospital to see him.听说儿子受了重伤,他急忙赶到医院去看望他。
I suggested that we should go home. 我建议我们回家去。虚拟语气,that 一般不能省略。
2.whether/if (是否)引导的宾语从句:如果要突出“究竟是…还是不…”,常在whether 后面加or not; if 一般不与or not连用。如:
He asked me if/whether I knew John. 他问我是否认识约翰。
Let me know whether you can come or not. 你能来还是不能来,告诉我一声。
3.在think, believe, suppose, expect 等动词的宾语从句中,否定不用在从句中,而是将think 等词变为否定形式。For example:
I don’t think the film is interesting.我觉得这部电影没什么意思。
I don’t suppose we are going outing tomorrow. 我认为我们明天不会出去郊游。
4.如果从句作宾语而后面还有补语,为了保持句子的平衡,用it 作形式宾语,而将宾语从句放在句尾。常跟这样的复合宾语的动词有:make, find, see, hear, feel, think, consider, regard, take….for granted等。如:
George made it clear that he opposed this project. 乔治已明确表示他反对这个项目。it 代表that 引导的句子,作宾语,clear 是宾语补足语。
They kept it quiet that he was dead. 对他已经死亡的消息,他们秘而不宣。
I took it for granted that you’d stay with us. 我想当然认为你会和我们呆在一起。
三、 同位语从句
同位语从句是对名词的内容给予具体、详细的说明。常在后面接同位语从句的名词有fact, news, idea, truth, hope, suggestion, question, problem, doubt, fear, belief等。同位语从句常用的引导词为that,有是也用when, where 等疑问词。
如:
The news that the United States was hit by terrorist attacks took the whole world by surprise. 美国受到恐怖主义分子袭击的消息令全世界吃惊。
The idea that you can do this work well without thinking is quite wrong.你认为不动脑筋就能做好这件工作的想法是完全错误的。
People used to hold the belief that the earth was the center of the universe. 人们曾认为地球是宇宙的中心。
The difficulty lies in the fact that we are short of money.困难在于我们缺乏资金这个事实。
They have no idea at all where he has gone.他们一点儿也不知道他去哪儿了。
注意:同位语从句的that 只是引导词,没有其他语法作用,在句子中不作句子成分,不能省略;而定语从句中的that 除了引导定语从句外,还是定语从句的一个成分,在定语从句中作主语或宾语,作主语时不能省略,作宾语时可以省略。
如:
The idea that some peoples are superior to others is sheer nonsense.有些民族优越于其他民族这种想法简直荒谬。(请辨别是同位语从句还是定语从句。)(同位语从句)
The idea that he proposed at the meeting is sheer nonsense. 他在会议上提出的这个想法简直荒谬。(请辨别是同位语从句还是定语从句。)(定语从句)
No one is happy with the fact that he found out. 没有人对他发现的事实感到高兴。(请辨别是同位语从句还是定语从句。)(定语从句)
No one is happy with the fact that he will become their boss.没有人对他将成为他们的老板这一事实感到高兴。(请辨别是同位语从句还是定语从句。)(同位语从句)
四、表语从句
表语从句位于主句的连系动词之后,在非正式文体中引导词that可以省略。如:
That’s not what I want. 那不是我要的。
That’s why I have come.那就是我为什么来了。
My opinion is that things will improve.我的意见是事情会好起来的。
One advantage of solar energy is that it will never run out. 太阳能的一个优点是永远也不会枯竭。
The truth is that he didn’t really try. 实际情况是他没有真正努力。
The problem is who is to pay and when we can start.问题是谁来付帐、我们又何时开始。
The fact is that he didn’t notice the car until too late. 事实是他注意到车时已经太晚了。
What surprised me was that he spoke English so well.使我感到吃惊的是他英语讲得那么好。
All I can say is that I have nothing to do with it. 我能说的就是我与此事没有关系。
What I want to know is where we shall go and whether she will join us. 我想知道的是我们要去什么地方以及她是否加入我们。
此外,表语从句还可由as if (好像)引导。如:
It looked as if it was/were going to rain. (虚拟语气)
Now let’s do some translation:
这就是她昨天请一天假的原因。
That is why she had a day off yesterday.
我的想法是,个人的权利应该得到充分尊重。
My idea is that individual rights should be fully respected.
问题在于上帝是否真的存在。
The question is whether the God really exists.
我想知道的是,他是如何在这么短的时间内完成这个项目的。
What I want to know is how he managed to complete the project in such a short time.
五、形容词后的that 从句
that 引导的名词性从句还可以用在一些形容词后面。这种句型一般都用人作主语,所用的形容词都是表示思想状况或感情色彩的形容词,如certain, sure, positive, afraid, convinced, anxious, disappointed, worried, glad, happy, sorry, amazed, surprised, aware, doubtful, confident等等。
如:
I am sure/certain that he’s at home now.我肯定他现在在家。
He became angry that you made the same mistake. 你犯了同样的错误,他生气了。
He remains confident that he will win. 他仍然自信他会赢
She is aware that I can’t help her. 她知道我帮不了她的忙。
I am glad that you’ve come. 你来了我很高兴。
He appeared/seemed surprised that I said “no”. 我说不,他似乎很吃惊。
I am afraid that I can’t promise you anything. 恐怕我不能向你保证什么。
We were rather disappointed that you were not able to come yesterday. 昨天你没能来我们有点失望。
I am a bit worried that she will not be able to make it. 我有点担心她做不成这件事情。
六、what 从句的小结
1. 意思是“所….的事/物”, 相当于the thing(s) that…, that which…, 或those which… 可以用于以下情况:
(1) 引导主语从句。如:
What she saw frightened her. 她看到的事情吓了她一跳。
What was once regarded as impossible has now become a reality. 曾经被认为不可能的事情,现在已经变成了事实。
What I’m afraid of is their taking him to that place. 我怕的是他们带他到那地方去。
What we are worrying about is just her innocence. 我们担心的是她的幼稚。
But what hurt our feelings most was the personal comment of the judge. 最伤我们感情的是法官的私下评论。
What will be, will be. 要发生的事总是要发生的。(谚语)
What is gone is gone. 过去的事就过去了。
(2) 引导表语从句。如:
That’s what I hope. 那就是我希望的。
I should like to be a teacher. That’s what I want to be. 我想当老师,那是我想干的事。
Times are not what they used to be. 时代不同了。
He’s not what he was a few years ago. 他不是几年前的他了。
Your health is not what it ought to be. 你的身体应该更好。
(3) 引导宾语从句,包括介词宾语。如:
He could not express what he felt. 他不能表达他的感受。
Well, I’ll do what I can. 好吧,我尽力。
I can’t do what you’ve just asked of me. 我不能做你刚才要求我的事。
And having got what he wanted, he took his hat and went away. 得到了他要的东西,他拿上帽子就走了。
As a friend of yours, I want to tell you what I hear. 作为你的朋友,我想告诉你我所听到的。
The father began to criticize what the boy had done. 父亲开始批评男孩所做的事。(注意时态)
She was not happy at what he had said. 她对他说的话不高兴。
Don’t poke your nose into what doesn’t concern you. 不要多管闲事。
The city is different from what it was ten years ago. 这座城市和十年前不同了。
It was a small place then compared to what it is now. 和现在比起来,它那时候是个小地方。
I don’t care about money or what people call position. 我不在乎金钱或者别人所谓的地位。
Philip was depressed by what he had gone through. Philip经历过的事情使他很消沉。
They paid fifty percent of what they were able to earn to the state.
他们能挣来的东西,百分之五十交给了国家。
2. 用作插入语,指代后面的成分。这和非限定性定语从句正好相反,非限定性定语从句指代的是前面的成分。如:
Then I discovered, what was news to me, that his wife was Mary’s niece. 后来我发现,他妻子原来是Mary的侄女,这对我是个新闻。
He never joined in the usual sports of the boys, and, what is remarkable, never went out in a boat on the river. 他从来不参加男孩子通常做的体育活动,更奇怪的是,他从来不坐船出去到河上面去。
He’s an interesting speaker, and, what is more important, he knows his subject thoroughly. 他讲话生动有趣,更重要的是,他对课题了如指掌。
He went to the meeting and, what was worse, insisted on speaking. 他去参加了会议,而且更糟糕的是,他坚持要发言。
It is a useful book, and, what is more, not an expensive one. 这是本很有用的书,再说也不贵。
You’ll have nobody but yourself to blame, and, what’s more, you’ll get no sympathy from anybody. 你怪不着别人,只能怪你自己;还有,你得不到任何人的同情。
We invited a new speaker and, what’s more, he was happy to come. 我们请到了一位新的发言人,而且他很乐意来。
3. 引导让步状语从句,等于“不管什么…”。注意状语从句的语序。如:
Do what she would, she could not invent a reason for not going. 不管她会做什么,她都编不出不去的理由。状语从句把实义动词放在句首,句子倒装。=No matter what she would do, …
Come what may, you’ll always keep it secret. 无论怎样,你都要保守秘密。=No matter what may come, ….
Jack has made up his mind that, come what might, he would stay there. Jack已经拿定主意,无论如何他也要呆在那里。=…no matter what might come, …
Say what he will, in his heart he knows that he is wrong. 不管他怎么说,内心里他知道自己错了。= No matter what he will say, …
文章来自:***/
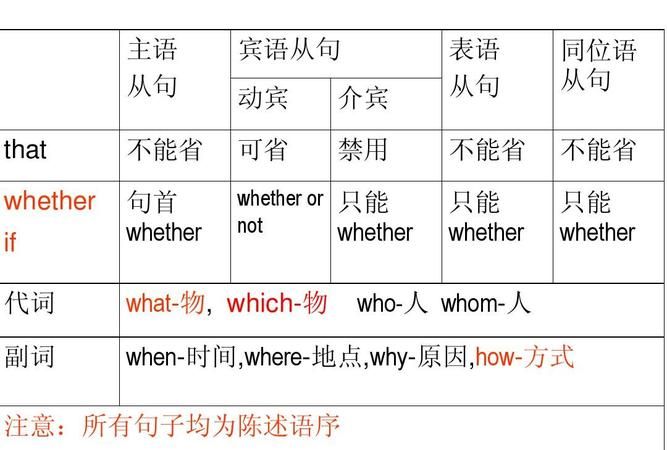
名词性从句有哪几种
名词性从句共有四种,分别是主语从句(整个从句在主句中做主语),表语从句(整个从句在主句中做表语),同位语从句(整个从句在主句中做同位语),宾语从句四类(整个从句在主句中做宾语)。
你的问题过于宽泛,因为不知道你要具体问什么,所以要是有更进一步问题,可以继续问我,我一直在线。
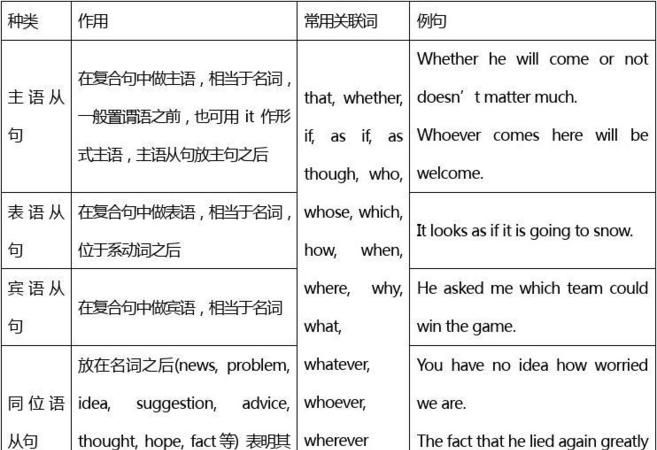
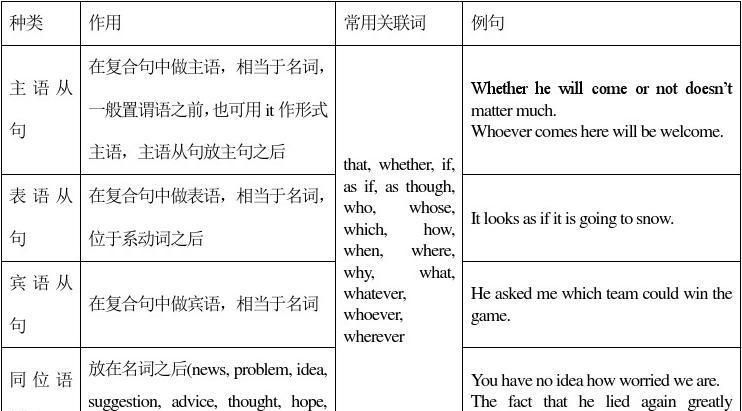
名词性从句的用法和分类 用法的区别
名词性从句用法详解
来源:英语语法网
一、概说
名词性从句,即指性质相当于名词的从句,它包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句.从高考的考查的实际情况来看,名词性从句考得最多的是宾语从句,其次是主语从句,再次是表语从句,而同位语从句则很少考查.
二、名词性从句的一般引导词
1. 连接词 that 只起连接作用,没有任何意思,也不充当句子成分,在宾语从句中可省略,但引导其他名词性从句时通常不省略.如:
I hope (that) you enjoy your holiday. 希望你假期过得好.
That he likes you is very obvious. 很显然他喜欢你.
2. 连接词 whether 也不充当句子成分,但有自己的意思,表示“是否”;引导宾语从句时,可换成 if,但引导其他名词性从句时不能换成 if.
He asked whether [if] I would show him the way. 他问我是否可以给他带路.
Whether it will do us harm remains to be seen. 是否对我们有害还要看一看.(引导主语从句,不能用 if 代替 whether)
3. 连接代词 who(m), whose, which, what 等,均有各自的意义,在从句中作主语、宾语、定语等.如:
That’s why she wanted to leave. 这就是她想离开的原因.
When we arrive doesn't matter. 什么时候到没有关系.
Tell me which one you like best. 告诉我你最喜欢哪一个.
4. 连接副词 when, where, why, how 等,也各自有自己的意义,在从句中作状语.如:
The question is how we should carry out the plan. 问题是怎样执行这个计划.
When she’ll be back depends much on the weather. 她什么时候回来在很大程度上要看天气.
Why he did it will remain a puzzle forever. 他为什么这样做将永远是一个谜.
三、名词性从句的重要引导词
1. what 用于引导名词性从句是一个十分重要的引导词,它可引导主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句,但不用于引导同位语从句.它引导的名词性从句有两个意思是:一是表示“什么”,带有疑问意味;二是表示“…所…的”,相当于一个先行词后接一个关系代词.如:
I don’t know what you want. 我不知道你想要什么.
I don’t know what you want is this. 我不知道你所想要的是这个.
2. what 引导名词性从句时可用作限定词,其后修饰名词.如:
I gave him what books I had. 我把我所有的书都给他了.
He gave me what money he had about him. 他把身边带有的钱全给了我.
注:what 后的名词可以是复数名词或不可数名词,但通常不能是单数可数名词,并且后接不可数名词时,有时可有little修饰,两者的区别是:what+不可数名词=所有的都,what little+不可数名词=虽少但全部.如:
What friends she has are out of the country. 她有的那些朋友全在国外.
We gave him what (little) help we could. 我们给了他我们力所能及的帮助.
3. whoever, whatever, whichever 等也可引导名词性从句,其意分别为“所…的一切事或东西”、“任何…的人”、““…的任可人或物”等.如:
Whoever wants the book may have it. 任何人要这书都可拿去.
I’ll do whatever I can to help him. 我们将尽我们所能来挽救他.
Buy whichever is cheapest. 买最便宜的.
注意以下受汉语意思影响而弄错的句子:
任何人来都欢迎.
误:Who comes will be welcome. / Anyone comes will be welcome.
正:Whoever comes will be welcome. / Anyone who comes will be welcome.
另外,它们也可引导让步状语从句,其意为“无论…”、“不管…”,其意相当于 no matter who [what, which].如:
Whatever happens, you must be calm. 不管发生什么情况,你都必须镇静.(whatever = no matter what)
He won't eat you, whoever he is. 不管他是谁,他也不能把你吃掉.(whoever = no matter who)
注:whoever 既用作主格也用作宾语;作宾语时不宜用 whomever,因为在现代英语中 whomever 这个已几乎废弃不用.
4. why 与 because 的用法区别.两者均可引导表语从句,但前者强调结果,后者强调的原因.如:
I had a cold. That’s why I didn't come. 我感冒了,因此我没来.
I didn’t come. That’s because I had a cold. 我没有来,那是因为我感冒了.
五、名词性从句的语序
名词性从句的词序与陈述句语序相同,尤其注意那些由连接代词who(m), whose, which, what 和连接副词 when, where, why 等引导的名词性从句,不要受它们在特殊疑问句中用法的影响而误用疑问句词序.如:
Why was she crying? 她为什么在哭?
I don’t know why he was crying. 我不知道她为什么哭.
六、名词性从句的时态问题
1. 当主句的谓语动词是过去式时,宾语从句若不是一个客观事实或真理,其谓语动词也必须用某种过去时态.如:
She said that she didn't want to know. 她说她不想知道.
I asked her whether she would agree. 我问她是否会同意.
2. when, if 这两个词既可引导名词性从句,也可引导状语从句.当它们引导名词性从句且表示将来意义时,要直接使用将来时态;但当它们引导状语从句且表示将来意义时,则必须用一般现在时表示将来意义.如:
I don’t know when he will come, but when he comes, I’ll call you. 我不知道他什么时候,但当他来的时候,我会打电话给你.
句中第一个when 引导的是宾语从句,故用将来时态表示将来意义;第二个when 引导的是时间状语从句,故用一般现在时表示将来意义.
以上就是关于名词性从句类型 ,英语中的名词性从句的分类及详细介绍大全的全部内容,以及名词性从句类型 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

