本文目录
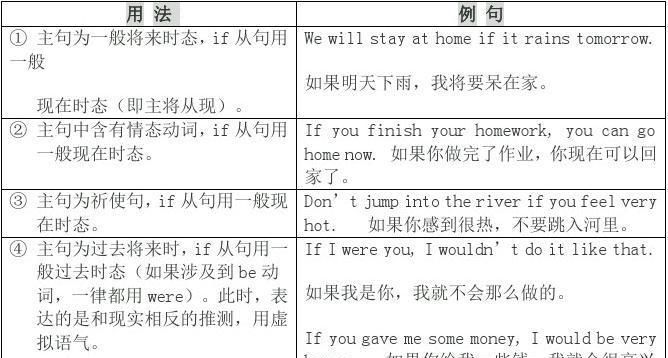
if引导从句的三种时态结构
1、对现在情况的虚拟
条件从句中谓语动词用一般过去式,主句用“would/should/might/could+动词原形”形式,表示对现在不可能实现情况的假想。
If I were you,I would choose to work in a small town.
如果我是你,我会选择在小城镇工作。(事实上我不是你)
注意:在条件从句中,如果谓语动词是be的形式,不管主语是单数还是复数,书面语中用were,而口语中如果是单数,也可以用was,不过在if I were...中一般用were.
2、对过去情况的虚拟
条件从句中谓语动词用过去完成式,主语用“would/could/should/might+have+动词的过去分词”形式。
If it had not been for your help yesterday,I could not have caught the bus.
如果昨天没有你的帮助,我不会赶上公交车。(事实是你昨天已经帮助了我,所以我赶上了车)
3、对将来情况的虚拟
在表示与将来事实相反的条件从句中,谓语动词可用should do,were to do或动词的过去式三种形式表示,但意义略有不同。should表示的可能性最大,动词过去式的可能性次之,were to do 的可能性最小。
If things were to be twice,all would be wise.
假如凡事都可以重新做一次,人人皆可成为聪明人。(事实是并不是所有的事都可以重新做一次)
注意:在书面语中,如果虚拟条件从句中有were,had 或 should,可以把if省略,把这几个词放到主语之前,构成主谓倒装。

其他条件句:
1、错综时间条件句
有些条件句的主句谓语和从句谓语表示的动作在时间上并不一致,这类句子称为错综时间条件句。
If you had taken my advice then,you would not be in trouble now.
如果当时听我的劝,你现在就不会有麻烦了。(if 条件句是对过去的虚拟,故用过去完成时,而主句是对现在的虚拟,故用“would+动词原形”形式)
2、含蓄条件句
有些句子虽不含条件从句,但意思和条件句相差不多,这种句子称为“含蓄条件句”,这种句子有时候会用虚拟语气。
如: Without air (If there were notair), there would be no living things.
But for your help (If it ha dn'tbeen for your help) I couldn't have don e it.
if引导的从句用什么时态
1.if
引导真实条件句时
从句用一般现在时表示将来,主句用一般将来时。
e.g.
If
it
doesn't
rain
tomorrow,
I'll
come
to
see
you.
2.
if
引导的虚拟条件句
1)当与现在事实相反时
if条件从句的谓语用过去式(be通常用were),主句谓语用“should
(would,
could,
might)+动词原形”
e.g.
If
I
knew
her
number
,I
would call her.
2)
与过去事实相反时,
if条件句的谓语用过去完成时(had+过去分词),主句谓语用“should
(would,
could,
might)+have+过去分
词”
e.g.
If
I
had
left
sooner,I
would have
been
on
time.
要是我早点动身,我就准时到了
3)当与将来事实相反时
if条件从句的谓语用过去式(be通常用were)/
were
to
+动词原形/should+动词原形,主句谓语用“should
(would,
could,
might)+动词原形”
e.g.
If
I
asked/were
to
ask/should
ask him,he
would
help
us.

if引导的条件状语从句什么时候用虚拟语气
if引导的条件状语从句的分类及虚拟条件句的判断
1、可以把条件句分为两类:
1).真实条件句(Sentences of Real Condition):凡是假设的情况发生性可能很大,就是真实条件句.例如:
⑴、If I have time ,I will help you with this work.如果我有时间会帮助你做此工作的.
⑵、As long as I say anything wrong,you must point it out.只要我说了什么错话,你一定要指出来.
⑶、If time permits,we'll go fishing together.(如果有时间的话,我们就一起去钓鱼.)
2).虚拟条件句(Sentences of Unreal Condition):当假设是不大可能实现时,就是虚拟条件句.例如:
⑴、If I were you ,I would have attended the meeting.如果我是你的话,就去参加会议了.
⑵、If he had come here yesterday,he would have seen his old friend.假如他昨天来这儿的话,就会看见他的老朋友.
⑴、If it had rained yesterday,we would have stayed at home.(如果昨天下雨的话,我们就会留在家里.)
2、.if条件状语从句中虚拟语气的判断
判断是真实条件句还是非真实条件句.只有在非真实条件句中才使用虚拟语气.通过句子意思,看假设的条件是否能够实现,能够实现是真实条件句,不能使用虚拟语气;假设的条件不能实现则是非真实条件句,要用虚拟语气.
判断这个假设是与哪个事实相反.通常有三种情况:
①与过去事实相反.
②与现在事实相反.
③与将来事实可能相反.
3、“后退一步法”
后退一步法是指在准确地判断了该句与哪一事实相反后,按虚拟语气的后退一步法处理从句谓语动词的时态.即:在非真实条件状语从句中,谓语动词按正常情况“后退一步”.也就是:
①与过去事实相反,在从句中用过去完成时形式表示.
②与现在事实相反,在从句中用过去一般时形式表示.
③与将来事实可能相反,在从句中用过去将来时形式表示.
主句中则用情态动词would,should,could 等加一个与从句一致的动词形式.例:
⑴、If I had come her yesterday,I would have seen him.
⑵、If I were a teacher,I would be strict with my students.
⑶、If it should snow tomorrow,they couldn't go out.
4、注意事项
①if条件句中如有were,should,had,可以省去if,并使用倒装语序.
②在现代英语中if条件状与从句中的谓语动词如果是be其过去形式一般用were.

扩展资料:
1、在for fear that,in case,lest引导的从句中,若用虚拟语气时,从句谓语为:(should) + do。并且should能省略(for fear that,lest),in case不能省略
She examined the door again for fear that a thief (should) come in.
她又把门检查了一遍,以防盗贼的进入。
He started out earlier lest he (should) be late.
他早早地就出发了以防迟到。
2、在so that,in order that所引导的目的状语从句中,从句中的谓语为:can / could / may / might / will / would /should + do
He goes closer to the speaker so that he can hear him clearer.
他走近说话的人以便能听得更清楚。
He read the letter carefully in order that he should not miss a word.
他把信读得很仔细以便不漏掉一个字。
一想要(desire) 一宁愿(prefer) 一坚持(insist)二命令(order , command) 三建议(advise , suggest , propose/recommend) 四要求(demand , require , request , ask)中,无论主句谓语动词为何种时态,从句的谓语动词都用:"should + do"。should可以省略。
eg:He suggested that we (should) take the teacher's advice.
He insisted that we (should) take the teacher's advice.
He demand that we (should) take the teacher's advice.
He ordered that we (should) take the teacher's advice.
insist意为“坚持某种动作”才用虚拟语气;意为“坚持某种观点,某个事实”则不用虚拟语气。
语法引导条件状语从句最常用的连词是if,由if引导的条件状语从句表示在某种条件下某事很可能发生。如:
1) If you ask him,he will help you.如果你请他帮忙,他会帮你的。
2) If you fail in the exam,you will let him down.如果你考试不及格,你会让他失望的
if引导的条件状语从句既可以将从句放前面也可以将从句放后面
(如果天下雨,我们就不玩了)If it rains,we will stop playing.‘
转为We will stop playing if it rains.
另外,if从句还表示不可实现的条件或根本不可能存在的条件,也就是一种虚拟的条件或假设,从句多用一般过去时或过去完成时。
如:
If I were you,I would invite him to the party.如果我是你,我会邀请他参加聚会。
I would have arrived much earlier if I had not been caught in the traffic.如果没有堵车,我会到的早一点儿。
unless = if...not.
e.g. Let's go out for a walk unless you are too tired.
If you are not too tired,let's go out for a walk.
if 引导的条件句有真实条件句和非真实条件句两种:
真实条件句
如:If it rains tomorrow,we won’t go on a park
非真实条件句是虚拟语气的一种,表示与事实相反,如:
If I were you,I would go with him.
so/as long as只要
由as (so) long as,in case引导。
So long as you’re happy,it doesn’t matter what you do.
只要你高兴,你做什么都没有关系。
You may borrow my book as long as you keep it clean.
只要你保持书的清洁,你就可以把我的书借去。
Take your umbrella in case it rains.
带着你的伞吧,以防下雨。
参考资料:百度百科——虚拟语气 百度百科——条件状语从句
if的三种时态
1.if引导的条件状语从句中用一般现在时态。引导条件状语从句,用一般现在时代替将来时。
2.if后可以接虚拟语气。
(1)第一种是与现在事实相反,if从句谓语用过去式或者were。
(2)第二种是与过去事情相反,if从句谓语用过去完成时:had+过去分词。
(3)第三种是与将来事实相反,if从句谓语用动词过去式,should +动词原形,或were to + 动词原形。
以上就是关于if从句的谓语形式 ,if引导从句的三种时态结构的全部内容,以及if从句的谓语形式 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
