本文目录
定语从句的例句
定语从句的例句1
在复合句中 , 修饰名词或代词的从句叫定语从句, 被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词 , 引导定语从句的有关系代词 who, whom, whose, which, that等和关系副词where, when, why等 , 关系代词和关系副词在定语从句中担任句子成份。
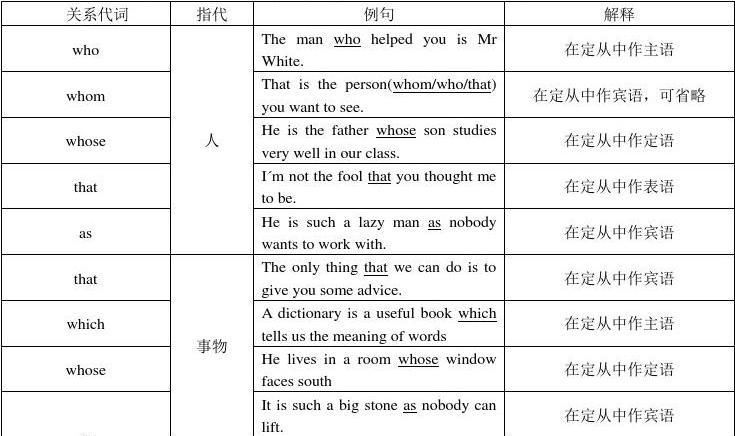
1.由who引导的定语从句中 , who用作主语 , 如 : This is the boy who often helps me.
2.由whom引导的定语从句中,whom用作宾语,如:The man whom you are waiting for has gone home.
3.由whose引导的定语从句中 , whose用作定语 , 如 : Do you know the girl whose skirt is white?
4.由which引导的定语从句中,which用作主语或谓语动词的宾语或介词的宾语,如:
The room in which there is a machine is a work shop.
The river which is in front of my house is very clean.
This is the pen which you want.
注意 :
(1)whom, which用作介词宾语时 , 介词可放在 whom、which之前 , 也可放在从句原来的位置上;但在含有介词的动词固定词组中,介词只能放在原来的位置上。如: He is the very person whom we must take good care of.
(2)引导非限制性定语从句时,必须用关系代词which,不用that,如:I have lost
my bag, which I like very much.
(3)关系代词在句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词的人称和数必须和先行词保持一致。
5.由that引导的定语从句中,that可以指人或物,在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语,但不能放在介词后面作介词宾语,如:
The book that I bought yesterday was written by Lu Xun.
注意在下面几种情况下必须用 that引导定语从句。
(1)先行词是不定代词all, few, little, much, something, nothing, anything等 , 如 :
All that we have to do is to practise English.
(2)先行词被序数词或形容词最高级所修饰,如
The first letter that I got from him will be kept.
(3)先行词被all, any, every, each, few, little, no, some等修饰 , 如
I've eaten up all the food that you gave me.
(4)先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时如
He is the only person that I want to talk with.
(5)先行词既有人又有物时,如:
They talked about persons and things that they met.
(6)当句中已有who时 , 为避免重复 , 如 : Who is the man that is giving us the
class?
6.由when, where, why引导的定语从句,如:
I don't know the reason why he was late.
This is the place where we have lived for 5 years.
I'll never forget the day when I met Mr Li for the first time.
注意:先行词是表示地点时,如果从句的谓语动词是及物的,就用 that(which),如果从句的谓语动词是不及物的,就用where引导。This is the house Which /that he has lived in for 15 years.(Where he has lived for 15 year.)
7. 限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
(1)限制性定语从句是句中不可缺少的组成部分,主句和从句之间不用逗号分开。引导非限制性定语从句的关系代词有who, whom, whose, which, of which等,这些关系代词都不能省略。
(2)非限制性定语从句是对主句先行词的补充说明 , 没有这种从句 , 不影响主句意思的完整 , 一般用逗号把主句和从句分开 , 关系代词用 which,不用that;指人时可用who,如 : I have two brothers, who are both students.
8.如何简化定语从句
(1).定语从句简化为形容词或形容词短语作后置定语。如:
My grandfather lives in a village that is far away from here.
→My grandfather lives in a village far away from here.我祖父住在离这儿很远的一个村子。
This is a book that is worth reading.
→This is a book worth reading. 这是一本值得看的书。
(2) 定语从句简化为现在分词或现在分词短语作前置或后置定语。
The man who is standing under the tree is our English teacher.
→The man standing under the tree is our English teacher.
站在树下面的那个人是我们的英语老师。
I saw the house that was burning at that time.→I saw the burning house at that time.
当时我看到那房子在燃烧。
(3)定语从句简化为过去分词短语作后置定语。
I like to see the films which are directed by Zhang Yimou.→I like to see the films directed by Zhang Yimou. 我喜欢看张艺谋导演的电影。
She is the girl who was praised at the school meeting.→She is the girl praised at the school meeting. 她就是在校会上受表彰的那个女孩。
(4)定语从句简化为不定式作后置定语。
He is always the first person that comes to school.→He is always the first person to come to school.他总是第一个到校。
The report which will be given tomorrow is important to us.→The report to be given tomorrow is important to us. 明天要作的'报告对我们很重要。
(5)定语从句简化为what 从句。
I couldn't remember the words that he said.→I couldn't remember what he said.
我记不得他说的话。
【典型例句解析】
例 1 The second book ______I want to read is Business @ the Speed of Thought.
A. which B. what C. that D. as
解析 先行词 book被序数词修饰时要用that引导定语从句,故选C。
例 2 I'll never forget the days _____I stayed with you.
A. when B. in which C. that D. for which
解析 本题指时间,故选 A。
例 3 The book______ is sold out at the moment.
A. you need B. what you need
C. which you need it D. that you need it
解析 B、C、D中的what和it与先行The book相抵触 , 故选 A。
例 4 Is this the place ______Lincoln once lived.
A. that B. which C. where D. when
解析 本题指地点,故选 C。
例 5 I'm one of the boys _________ never late for school.
A. that is B. who are C. who am D. who is
解析 本题中 who用作主语,谓语动词与先行词the boys保持一致,故选B。
【选讲例句】
例 6 Her sister,______ you met at my home, was a teacher of English.
A. whom B. that C. which D. who is
解析 非限制性定语从句中 , 关系代词用 which,不用that,但指人时用who或whom.故选A。
例 7 These book are for students _____ mother language is not English.
A. of whom B. that C. which D. whose
解析 whose引导的定语从句中,whose用作定语,故选D。
定语从句的例句2
定语从句that的例句
1. He is a good boy. 形容词作定语
2. Two boys need two pens. 数词作定语
3. His son needs Tom's pen. 形容词性物主代词或名词所有格作定语
4. The boy in blue is Tom. 介词短语作定语
5.There is a woman doctor. 名词作定语
6. The boy there needs a bike. 副词作定语
7.There is nothing to do today. 不定式作定语
8. The smiling boy needs a friend. 现在分词作定语
9. A boy called Tom saved the girl. 过去分词(短语)作定语
10. He is the man that I met yesterday. 定语从句
一、定语从句的概念:在复合句中,用作定语的从句叫做定语从句。
二、定语从句的位置:通常位于它所修饰的名词或代词之后。
三、被修饰的名词或代词叫做先行词。
四、引导定语从句的关联词为关系代词和关系副词。关系代词(who, whom, whose, that, which等)在定语从句中可用作主语、定语、宾语等;关系副词(when, where, why等)在定语从句中只用作状语。关系代词和关系副词放在先行词及定语从句之间起连接作用,同时又作定语从句的重要成分。
五、定从基本形式:先行词(名词/代词) + 关系代词/关系副词+ 定从
六、that引导的定语从句
She is the girl that talked to you yesterday. (that作主语)
The coat (that) I put on the desk is blue. (that作宾语)
结论:that引导的定语从句既可以修饰人,也可以修饰物;
that在从句中作主语或宾语;
作主语时不可省略,作宾语可省略。
例如:
1. I like music. I can dance to music.
I like music that I can dance to. (that在从句中用作宾语。)
2. I prefer a sandwich. A sandwich is really delicious.
I prefer a sandwich that is really delicious.(that在从句中用作主语。)
注意:that在定语从句中作主语时,定语从句中谓语动词的单复数应与先行词保持一致.
例如:I prefer movies that are scary.
I like a sandwich that is really delicious.
I love the singer that is beautiful.
I have a friend that plays sports.
定语从句的例句3
1. A miracle is something that seems impossible but happens anyway.
奇迹就是看似不可能,却发生了。
2. If you wait, all that happens is that you get older.
如果你等待,发生的只有变老。
3. When life gets hard and you want to give up, remember that life is full of ups and downs, and without the downs, the ups would mean nothing.
当生活很艰难,你想要放弃的时候,请记住,生活充满了起起落落,如果没有低谷,那站在高处也失去了意义。
4. Eventually, you'll learn to cry that on the inside.
终有一天,你会学会让泪往心里流。
5. Success is not final, failure is not fatal: it is the courage to continue thatcounts.--Winston Churchill
成功不是终点,失败也并非末日,最重要的是继续前进的勇气。

定语从句有几种关系词形式
(一) 由 who,whom,whose引导的定语从句
e.g.The student who answered the question was Jack
(二) 由which引导的定语从句
1) which在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语。
e.g.:I found a door which was unlocked.
Where is the book I bought yesterday?
2) which(whom)在从句中作介词的宾语时,介词一般可放在which(whom)之前,也可放在从句原来的位置上,在含有介词的动词固定词组中介词只能放在原来的位置上,而不能放在which(whom)之前。
e.g.:Please tell me from whom you borrowed the English novel. (=Please tell me whom you borrowed the English novel from.)This is the magazine which you are looking for. (look for是固定词组)
(三) 由that引导的定语从句在这种定语从句中that可以指人或物,代替who,whom,which,在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语(不能放在介词后面作介词宾语)。
e.g.:Would you like to have lunch at a new restaurant I heard about? (that可省略)但下列两种情况只能用that
1) 序数词或最高级形容词修饰先行词时,要用that. e.g.:The first English novel that I read was A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens.
2) all, everything, nothing, something, anything等不定代词作先行词时,要用that。e.g.:Everything that we saw at the Industrial Exhibition greatly interested us.
(四) 由when, where, why引导的定语从句
I will never forget the day when I arrived in London.
. (五) 限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句限制性定语从句是句中不可缺少的组成部分,如果没有从句,先行词的意思就不明确,主句也不完整,从句和主句之间一般不用逗号分开。
非限制性定语从句是主句先行词的补充说明,没有从句并不影响主句意思的明确或完整,这种定语从句一般用逗号与主句分开。在非限制性定语从句中通常不用关系代词that。
e.g:He once bought a railway ticket for a woman, which was reported in the newspapers.(which代表主句所述事实)
英语八大从句类型与用法总结视频
从句,即从属子句,是复句中具有分属地位的分句,它是一种绝大部分语言都有的语法结构。在现代汉语的语法中,“从句”不作为专业术语被使用。在现代英语的语法中,从句指复合句中不能独立成句,但具有主语部分和谓语部分,由that、who、whom、when、why、where、how、whether、which等引导词(Connective)引导的非主句部分。
从句用法总结
1.主语从句
1)主语从句可直接位于主语的位置,如果从句较长,谓语又较短,可用it作形式主语,而将从句放在句末。常见的句型有:
*It is a facta pitya questiongood news that...
*It seemsappearshappenedhas turned out that...
*It is clearimportantlikelypossible that...
*It is saidreportedestimatedhas been proved that...
It is said that comic books create a connection between people of the same generation.
It seems that the performance is very useful.
2)what引导的主语从句表示“...的东西时”,一般不用it作形式主语。
What we lack is experience.
3)what,who,when,why,whether等词含有各自的疑问意义,但它们引导的主语从句,都用陈述语序。
How the plan is to be carried out should be discussed again.
I did know why I felt like crying.
2.宾语从句
1)宾语从句可位于及物动词、介词和某些形容词后。连词that常可省略。介词后一般接疑问词引导的宾语从句。in that(因为),except that(除了),but that(只是)已构成固定搭配,其他介词后一般不接that引导的宾语从句。
*I promised that I would change the situation.
*All this is different from what American young people would say about friendship.
*He is certain that watching so much television is not good for children.
*This article is well-written except that it is a bit too long.
2)宾语从句后如有宾补,要用形式宾语it来代替,而把宾语从句移至宾补之后。
He has made it clear that he would not change his mind.
3)在think,believe,suppose,expect等动词后的宾语从句中,如果谓语是否定的,一般将否定词移至主句谓语上,宾语从句则变成肯定形式。
He didn't think that the money was well spent.
3.表语从句
表语从句出现在结构为“主语+系动词+表语从句”的句子中。表语从句除可用that,what,when,why,whether,how等引导外,还可由because,as if(though)等引导。that常可省略。如主句主语为reason,只能用that引导表语从句,不可用because.
Perhaps the most important thing to remember is that there is no one common type of life in America.
The reason why so many people died there is that there were not enough food supplies.
It looks as if successful international cultural communication will make the world smaller.
4.同位语从句
同位语从句用于对前面出现的名词作进一步说明,一般用连词that引导,由于先行名词的意义不同,也可用whether,who,when,where,what,why,how等引导。常见的先行名词有fact,idea,belief,news,hope,conclusion,evidence,suggestion,order,problem,report,decision.有时由于谓语较短,将同位语从句位于谓语之后。
She finally made the decision that she would join the fashion show.
I had no idea how many books I could borrow at a time.
The news came that their team had won the championship.
5.定语从句
定语从句所修饰的先行词可以是名词或代词,也可以是一个句子。定语从句通常位于先行词之后,由关系代词或关系副词引导。
*限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句修饰先行词,对先行词起修饰作用,紧接先行词之后,无逗号,若省去,原句意思不完整。引导定语从句的关系代词有who,whom,whose,which,that等。who,whom,whose用于指人,whose有时也可指物,相当于of which;which用于指物;that既可指人也可指物,但只用于限制性定语从句中。关系代词除了引导定语从句,替代先行词外,还在从句中担任主语、宾语、定语等。
The computers and cables which make up the Internet are owned by people and organizations.
Those who live alone or who are sick may have trouble in getting close to other people.
The girl whose parents died in an accident is living with her grandmother.
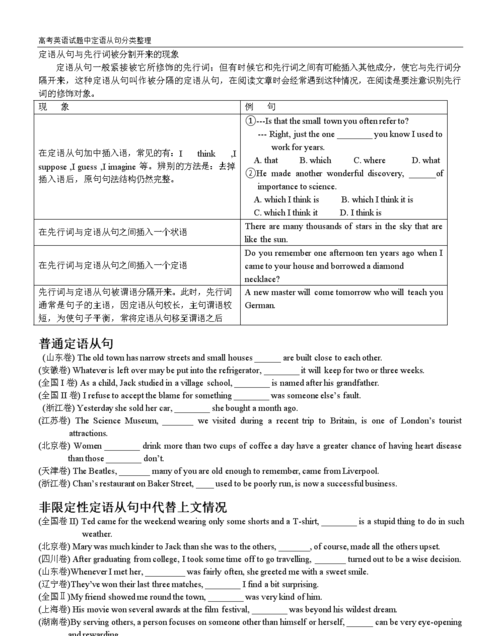
1)当先行词是all,anything,everything,something,nothing等不定代词或先行词前有first,last,any,few,much,some,no,only以及形容词最高级修饰时,只能用关系代词that引导从句。
That is all that I've heard from him.
He's the first person that I'm going to interview this afternoon.
2)关系代词的省略
在从句中作宾语的关系代词常可省略。关系代词紧跟介词,作介词宾语时不可用that,只可用which或whom引导从句,并且不可省略,但当介词位于宾语从句句末时,作为介词宾语的关系代词仍可用that,也可省略。
This is one of those things with which we have to put up.
This is one of those things (whichthat) we have to put up with.
3)引导定语从句的关系副词有when,where,why等。关系副词在从句中作状语,意义上相当于一个“介词+which”的结构。
Even in comic books where(=in which) there are no words,the stories are fully expressed through the drawings.
No one knows the reason why(=for which) he was so angry that day.
5.定语从句
*非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句既可修饰先行词,也可修饰整个主句,起补充说明作用,与主句之间有逗号隔开,若省去,原句意思不受影响。不可用that引导非限制性定语从句。关系词不可省略。
Every object has a gravitational pull,which is rather like magnetism.
*“介词+whichwhomwhose”引导的定语从句
“介词+whichwhomwhose”可引导限制性定语从句,也可引导非限制性定语从句,该结构中介词的选择取决于从句谓语动词的固定搭配,或先行词的习惯搭配。
This is the computer on which he spent all his savings
It is written by a person with whom we are all familiar.
*as引导的定语从句
as引导的定语从句主要用于“such...as”及“the same...as”的结构中,代替先行词是人或物的名词。as引导非限制性定语从句时,代替整个主句,从句可位于主句之前、之后或中间。
These are not such problems as can be easily solved.(as代替先行词problems)
As is mentioned above,no single company or group can control what happens on the Internet.(as代替主语)
英语八类状语从句的用法归纳
一、概说
状语从句即指在主从复合句用作状语的从句。按照其意义,状语从句可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句等。状语从句是高中英语学习中的一个语法重点,也是历年高考重点考查的内容之一。学习状语从句主要应注意引导状语从句的从属连词的用法与区别,以及从属连词在一定的语言环境中的意义与用法。
二、时间状语从句
1.引导时间状语从句的从属连词很多,常见的有before,after,when,while,as,since,till,until,assoonas等。
2.表示“当…时候”的while,when,as的用法区别是:while从句中的谓语动词必须是延续性动词;表示带有规律性的“每当”或当主、从句谓语动词的动作发生有先后时,只能用when;当表示“一边…一边…”或“随着”时,只能用as。另外,用于此义的as所引导的时间状语从句谓语只能是动作动词,不能是状态动词。如下面一道高考题的答案是B而不能是A:
“I’mgoingtothepostoffice.”“_____you’rethere,canyougetmesomestamps?”
A.As B.While C.Because D.If
3.until在肯定句中通常只连用延续性动词,表示相应动作结束的时间;在否定句中通常连用非延续性动词,表示相应动作开始的时间,意为“直到…才”。如:
Hewaiteduntilshewasabouttoleave.他等着一直到她准备离开。
Ididnotbegintoworktillhehadgone.他走了后我才开始工作。
4.表示“一…就”除用assoonas外,还可用theminute,thesecond,theinstant,immediately,directly,instantly,nosooner…than,hardly…when等。如:
Icameimmediatelyyoucalled.你一来电话我就来了。
Hardlyhadshearrivedwhenitbegantosnow.她刚到就下起雪来了。
ThemomentIhavefinishedI'llgiveyouacall.我一干完就给你打电话。
5.everytime,eachtime,(the)nexttime,(the)lasttime,bythetime,thefirsttime,anytime等以time结尾的词语也可用作连词,引导时间状语从句。如:
Nexttimeyoucomein,pleaseclosethedoor.下次你进来,请关门。
Hedidn’ttellmeanythingthelasttimeIsawhim.上次我见到他时他什么也没告诉我。
BythetimeIgothome,shehadalreadygonetobed.我到家时她已睡觉了。
三、条件状语从句
1.引导条件状语从句的从属连词主要有if,unless,as[so]longas等。如:
Don’tcomeunlessItelephone.除非我打电话,否则你别来。
Ifyouwatchcarefullyyouwillseehowtodoit.如果你仔细瞧你会看出该怎样做。
Aslongasyoudoyourbest,we’llbehappy.只要你尽力,我们就满意了。
2.incase也可引导条件状语从句,其意为“如果”、“万一”。如:
IncaseIforget,pleaseremindmeaboutit.如果我忘了,请提醒我。
四、让步状语从句
1.引导让步状语从句的从属连词主要有although,though,however(=nomatterhow),evenif(即使),whether…or(不论…还是)等连词。如:
Thespeechisgood,thoughitcouldbebetter.这次演讲不错,虽然还可以再好一点。
Hewentouteventhoughitwasraining.尽管下雨,他还是出去了。
2.as也可引导让步状语从句,但要将名词、形容词或副词等提到as前,若提前的是单数可数名词,要省略a/an。如:
Teacherasheis,hecan’tknoweverything.虽然是老师,他也不可能什么都懂。
3.连词while有时也可表示“尽管”、“虽然”,引导让步状语从句。如:
Whilewedon’tagreewecontinuetobefriends.尽管我们意见不同,我们还是朋友。
4.whatever,whoever,however,whenever,wherever等引导让步状语从句。如:
Don’tloseheartwhateveryoudo.不管你做什么,都不要灰心。
Whoeveryouare,youcan’tpassthisway.不管你是谁,你都不能从这里通过。
注:表示“虽然”的though,although不可与but连用,但可与yet,still连用。
五、原因状语从句
1.引导原因状语从句的从属连词主要有because,as,since,seeing(that),now(that)等:
Theycan’thavegoneoutbecausethelight’son.他们不可能出去了,因为灯还亮着。
Sinceyouaregoing,Iwillgo.既然你去,我也去。
Nowthatwearealone,wecanspeakfreely.现在我们单独在一起,可以随便谈了。
2.除以上提到的大家比较熟悉的引导原因状语从句的从属连词外,when有时也可引导原因状语从句,其意“既然”。如:
Ican’ttellyouwhenyouwon'tlisten.既然你不想听,我就不告诉你了。
3.有关原因状语从句还应注意以下几点:
(1)as与since,nowthat一样表示双方都知道的原因,通常位于主句前,且均不可用于强调结构被强调。
(2)当表示直接的因果关系,回答why时,或有only,just,all,partly,not,but等副词修饰时,或用在强调结构中都只能用because。
(3)for有时也可引出表示原因的分句,但它只能位于后面,对前一分句加以解释或推断。
(4)不要受汉语意思影响将表示“因为”的连词与表示“所以”的so连用。
六、地点状语从句
引导地点状语从句的从属连词主要有where(在…的地方),wherever(无论什么地方),everywhere(每个…地方),anywhere(任何…地方)。如:
I’mnotlivingwhereIwas.我不在原处住了。
Youcan’tcampwhere[wherever,anywhere]youlikethesedays.如今你可不能随便在哪儿宿营。
EverywhereIgo,Ifindthesamething.不管我走到哪里,我都发现同样情况。
2.有的同学认为地点状语从句在平时见得不多,误认为考试不会涉及,但恰恰相反,地点状语从句却是英语考试经常考查的一个知识点。请看以下考题:
(1)Whenyoureadthebook,you’dbettermakeamark_____youhaveanyquestions.
A.atwhich B.atwhere C.theplacewhere D.where
(2)Afterthewar,anewschoolbuildingwasputup_____therehadoncebeenatheatre.
A.that B.where C.which D.when
(3)Youshouldmakeitaruletoleavethings_____youcanfindthemagain.
A.when B.where C.then D.there
(4)Shefoundhercalculator______shelostit.
A.where B.when C.inwhich D.that
以上四题均选where,其意为“在…的地方”,用以引导地点状语从句。
七、目的状语从句
1.引导目的状语从句的从属连词主要有inorderthat,sothat,incase,forfear等。如:
IhiredaboatsothatIcouldgofishing.我租了一条船去钓鱼。
Takeyourcoatincaseitrains(shouldrain).带着雨衣以防下雨。
Hestudiedhardinorderthathecouldpasstheexam.他努力学习,是为了能通过考试。
2.引导目的状语从句的sothat有时可省so或that,即单独用so或that来引导目的状语从句。如:
Checkcarefully,soanymistakewillbecaught.仔细检查,以便任何错误都可检查出。
BringitcloserthatImightseeitbetter.拿近些,使我能看得清楚些。
八、结果状语从句
引导结果状语从句的从属连词主要有sothat,so…that,such…that等。如:
Hewassoangrythathecouldn'tspeak.他气得话都说不出来。
Heshutthewindowwithsuchforcethattheglassbroke.他关窗子用力很大,结果玻璃震破了。
注:so…that和such…that中的that有时(尤其在口语中)可省略。
英语八大从句类型与用法总结高中
根据从句语法功能的不同可分为:主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句、定语从句和状语从句6类。
1、主语从句
主语从句就是作主语的从句。它的连接词有连词、连接副词、连词代词。主语从句放在句首时,句子显得很笨重,因此常用it作形式主语,而将真正的主语后置,比如:
It is a pity that you have missed such a wonderful concert.
真遗憾你错过了这么精彩的一场音乐会。
2、表语从句
表语从句就是作表语的从句。它的连接词有连词、连接副词、连词代词等。
比如:
My idea is that we meet at the bus stop.
我的想法是我们在公共汽车站会面。
3、宾语从句
宾语从句就是作宾语的从句。它的连接词有连词、连接副词、连词代词等。
比如:
She said that she would drop maths.
她说她要放弃数学。

4、同位语从句
同位语从句就是作同位语的从句,它的连接词有连词、连接副词等。
The fact that everyone loves beauty is common sense.
人人爱美是常识。
5、定语从句
定语从句就是作定语的从句。定语从句主要修饰、限定、描绘名词,有时修饰代词,放所修饰词后边。
比如:
The girl who wears a new dress is my daughter.
那个穿新衣服的女孩是我的女儿。
6、状语从句
状语从句就是作状语的从句。在复合句中修饰主句中的谓语动词、形容词或副词,起状语作用的从句叫作状语从句。
比如:
Soon after he jumps his parachute will open.
他跳伞之后,降落伞就会打开。
以上就是关于定语从句的八种类型及例句 ,定语从句的例句的全部内容,以及定语从句的八种类型及例句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
