提起初中阶段的宾语从句 想必大家一知半解。今天就给家解读一下。和初中宾语从句讲解初中阶段的宾语从句 的内容,让您更清楚知道初中宾语从句,一起深入了解。
初中阶段的宾语从句 :初中英语宾语从句语法专项讲解
一般情况下:
连接词如果与谓语在一起,表示连接词在从句中作为主语。通常的这类接词有:whowhat等。连接词、名词、谓语在一次,表示连接词在从句中做主语的定语。这类连接词有how much等。连接词、主语、谓语在一起,表示连接词在从句中作宾语、状语或者表语。这类连接词有when等。连接词、名词、主语、谓语在一起,表示连接词在从句中作宾语或者表语的定语。这类连接词有how等。
当由陈述性语句来充当宾语从句时,可以使用that来引导,但是that无词义。而在口语或者非正式文体中that通常会省略。如果由一般性疑问句来充当宾语从句,可以使用if或whether引导,意思为“是否”。
特殊情况下:
但是在一些特殊的情况下只能用whether:
首先是在具有选择意义时,或者是有or或or not时,特别是直接与or not连用时,语句往往用whether(if…or not也可以使用)。
其次是在在介词之后用whether;在不定式前用whether;当whether置于句首时,句子不能换用if;如果引导主语从句和表语从句,那么适宜使用whether。
最后如果用if会引起歧义时,那么可以使用whether。
我们通常遇到的宾语从句都可以通过简化来实现复合句转变为简单句。如果主句谓语动词是hope,wish,choose,promise等词汇,同时宾语从句的主语和主句主语相同时,我们可以将宾语从句简化为不定式结构;如果主句谓语动词是learn,forget,tell等动词,同事主句主语和从句主语相同时,我们可以将宾语从句简化为疑问词+不定式结构。如果主句的谓语动词是require等时,同时主句和从句的主语不相同时,我们可以将宾语从句简化为名词(代词)+不定式结构;如果某些动词后是宾语从句,我们可以用介词加动名词(短语)等其他形式来简化。
初中英语宾语从句在初中英语学习过程中算是一个比较难的知识点了,但是大家要相信:付出总会有回报,功夫不负有心人的道理。只要带着心去学,带着脑去用,再难的问题也一定会克服的。

初中阶段的宾语从句 :初中英语“宾语从句”的常见重点知识点有哪些
宾语从句的主要考点是引导词、语序和时态。若主句的主语和从句的主语相同,常可转换成“疑问词+动词不定式”。
初中阶段的宾语从句 :初中宾语从句讲解
变成宾语从句(直接英语变间接引语)对这两个题来说都是“去掉引号”
初中在这个语法上主要有两个考点(当然还有人称和连接词):
1.
时态(1)引号外是过去时(2)引号外不是过去时
(1)引号外是过去时
(引号外面句子时态决定引号中句子时态)(有特殊情况,此处不说了)
例:''Do
you
speak
English?
''
he
asked
me.
-------->
He
asked
me
if
I
spoke
English.
(引号外
he
asked
me
是过去时,所以''Do
you
speak
English?
''
去引号时,
Speak
也
要
变成过去时
spoke)
例:The
student
asked
Mary,''where
do
you
live?''
The
student
asked
Mary
where
she
lived.(
引号外
The
student
asked
Mary是过去时,所''where
do
you
live?''去引号时,live
也
要
变成过去时
lived)
例:He
said,"His
mom
will
go
to
Paris."--------->
He
said
his
mom
would
go
to
Paris.(
引号外
He
said是过去时,所以"His
mom
will
go
to
Paris."去引号时,will
也
要
变成过去时
would)
(2)引号外不是过去时(去引号时,引号中句子时态不变)
''Do
you
speak
English?
''
he
often
asks
me.--------->
He
often
asks
me
if
I
speak
English.(去引号
句子仍然是一般现在时)
''Did
you
know
him
in
2010?
''
he
often
asks
me.--------->
He
often
asks
me
if
I
knew
him
in
2010.(去掉引号
仍然是一般过去时)
2.
语序(要用陈述语序)
(陈述语序就是
把一般疑问句变成陈述句)
如:Did
you
speak
English?——>
you
spoke
English.
where
did
you
live?——>
where
you
lived.
另外
Are
they
good
at
PE?——>
they
are
good
at
PE.
Can
he
swim?
——>
He
can
swim.

初中阶段的宾语从句 :关于初中英语的宾语从句
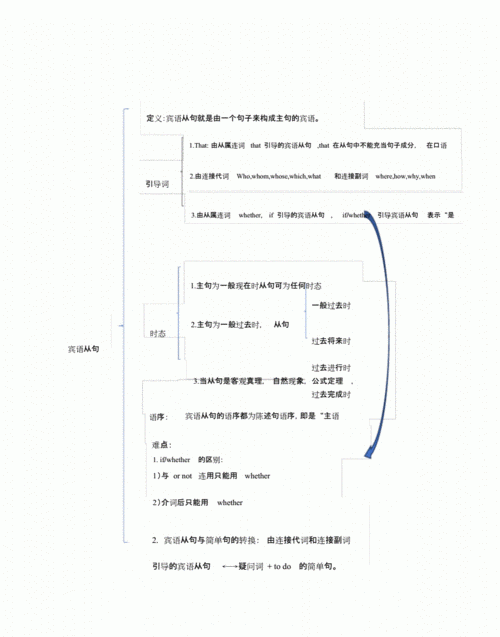
一. 宾语从句的种类
宾语从句是一种名词性从句,在句中作及物动词的宾语,或介词的宾语,或
形容词的宾语。根据引导宾语从句的不同连词,宾语从句可分为三类。
1. 由that引导的宾语从句。That只有语法作用,没有实在的意义,在口语
和非正式文体中可以省略。例如:
He said (that) he wanted to stay at home.
She doesn’t know (that) she is seriously ill.
I am sure (that) he will succeed.
2. 由连接代词who, whom, whose, what, which和连接副词when, where, why, how引导的宾语从句。这些连接代词和连接副词在宾语从句中充当某个成分。例如:
Do you know who (whom) they are waiting foe?
He asked whose handwriting was the best.
Can you tell me where the No.3 bus stop is?
I don’t know why the train is late.
3. 由if或whether引导的宾语从句。If和whether在句中的意思是“是否”。例如:
I want to know if (whether) he lives there.
He asked me whether (if) I could help him.
二. 宾语从句的语序
宾语从句的语序应为陈述句的语序。例如:
I hear (that) physics isn’t easy.
I think (that) you will like this school soon.
Can you tell me how I can get to zoo?
Please tell me when we’ll have the meeting.
三. 宾语从句的时态
1. 如果主句的时态是一般现在时,宾语从句该用什麽时态就用什麽时态。
如:
I don’t think (that) you are right.
Please tell us where he is.
Can you tell me how I can get to the railway station?
2. 如果主句的时态是一般过去时,宾语从句只能用相应的过去时态(一般过去时, 过去进行时, 过去将来时,过去完成时)。例如:
He asked what time it was.
He told me that he was preparing for the sports meet.
He asked if you had written to Peter.
He said that he would go back to the U.S. soon.
3. 如果宾语从句所陈述的是客观真理,其时态常用一般现在时。例如:
Our teacher said that January is the first month of the year.
Scientists have proved that the earth turns around the sun.
【中考范例】
1 Miss Green didn’t tell us _______ in 2009.
A. where does she live B. Where she lives
C. where did she live D. where she lived
【解析】答案:D。该题考查的是宾语从句的语序和时态。宾语从句应用陈述句的语序和时态,所以应选D。
2.Would you please tell me ________?
A. when did he come home
B. where he would play football
C. if he had seen the film
D. why he didn’t watch the game
【解析】答案:D。该题考查的是宾语从句的语序和时态。主句用的实际上是现在时,宾语从句在这个句子里应用陈述句的语序和一般过去时。
3.I don’t know when __________.
A. will the train leave B. the train will leave
C. would the train leave D. the train leave
【解析】答案:B。该题考查的是宾语从句的语序和时态。只有B在语序和时态上符合要求。
4.---We don’t know _____________.
---It is said that he was born in Sweden.
A. what he is B. if he lives here
C. where he comes from D. which country is he from
【解析】答案: C。该题考查的是宾语从句的语序。按照他们谈论的话题可知:他们说的是某人是哪里人。A和B可以排除掉。D的语序不对,只有C正确。
动词的语态
动词的语态---表示谓语与主语之间的关系的动词形式叫做语态,分为主动语态和被动语态。
主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者
一、被动语态
结构:1.行为动词的被动语态: 助动词be + 及物动词的过去分词.
be有人称.时态.数的变化,其变化规则与be作为连系动词时完全一样.
一般现在时 am/is/are+及物动词的过去分词 一般过去时 was/were +及物动词的过去分词
一般将来时 will +be +及物动词的过去分词 现在完成时 have/has+been+及物动词的过去分词
2.情态动词的被动语态: 情态动词 + be +及物动词的过去分词
否定式:是在助动词 be 或情态动词后加not构成
疑问式:是把上述助动词或情态动词提到主语之前,句尾加问号构成.
用法: 1.不知道动作的执行者是谁,或没有必要或不想指出谁是动作的执行者.
eg. The window was broken yesterday. Is English taught in your school? 2.强调或突出动作的承受者,此时如想同时指出动作的执行者,可用“by +动作执行者(宾格)来表示.
eg.The red dress was made by her mother. The letter must be written by me.
注 意点: 1.只有及物动词能构成被动语态, 不及物动词不能构成被动语态.
2.某些不及物动词与介词.副词搭配构成短语动词,带有宾语时,则有了动作的承受者,这时应把它们看作一个整体,变为被动语态,不能丢掉其中的介词,常用的有look after,take care of,cut down, laugh at,talk about,turn on等 eg.Catherine always takes care of the little girl.→The little girl is always taken care of by Carherine.
3.有些动词短语本身即是被动语态的形式, 不要再加by 短语,常用的有
be covered with be surprised at be interested in be worried about be made of/from be known to
4.某些动词形式是主动语态,但含有被动的意思. eg. This dictionary sells well.
This kind of car drives fast. The woolen sweater costs $ 88.
5.主动语态与被动语态的相互变化关系
主动句: 主语 + 谓语 + 宾语(动作执行者) (动作承受者)
被动句: 主语 +谓语动词的被动形式+ by + 动作执行者 (动作承受者)
1)主动句如何变为被动句
a.找到动作的承受者(常为主动句的宾语)作被动句的主语.b.找到谓语变为be + 过去分词的结构.
c.找到动作的执行者(常为主动句的主语)作 by 的宾语.若不必指出动作的执行者,可省去 by 短语. d.确定be动词的时态.数. 例如: She makes the beautiful kites.
The beautiful kites are made by her. (被动句)
2)被动句如何变为主动句. a.找到动作的执行者(常为被动句的宾语)作主动句的主语.
b.找到be+过去分词结构还原为及物动词原形.
c.找到动作的承受者(常为被动句的主语)作主动句的宾语.
d.确定及物动词的时态.数(注意)在以上转换中,代词作主语用主格, 代词作宾语用宾格.
6.主动语态中有些动词如:make,see,listen, watch,feel后常跟不带to的动词不定式作宾语补足语,变为被动语态要带上to
He made the boy work for him. →The boy was made to work for him.
7.主动语态中若有双宾语,变为被动语态时, 通常把指人的间接宾语变为被动语态的主语. His uncle gave him a dictionary yesterday.→He was given a dictionary by his uncle yesterday.
G:现在完成时枣表示到目前为止已经完成,并对现在留下某种后果和影响的动作。
结构:助动词have/has + 动词的过去分词
用法:
1.表示过去发生的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果,常与一些时间状语,如:already, yet, ever, never, just, before, once,twice等连用,也可以和包括现在在内的时间状语,如these days,today,this year,so far等连用.eg.I have already posted the letter. (信已经不在我这儿了)
2.表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,一直持续到现在,也许还将继续下去,可以和表示从过去某一时刻延续到现在的一段时间的状语连用,即for +时间段,since+时间点/从句, in the last ten years等,谓语只可用延续性动词.
解析: 1.英语动词根据词义可分为两种,一种是延续性的,一种是终止性的,终止性动词(也可称为非延续性动词,瞬间动词,或点动词),如begin,start,die,buy,leave, come等,表示动作的发生与结束于一瞬间完成,不能再延续,所以它的现在完成时不能和表示延续的时间状语连用,即不能与表示一段时间的状语,for+时间段, since+时间点/从句连用,也不能用在how long引导的特殊疑问句中.
eg. I've left Shanghai for three days.(×) I've been away from Shanghai for three days.( √ ).
I left Shanghai three days ago. ( √ ) It is /has been three days since I left Shanghai.( √ )
2.初中英语课本中常见终止性动词有:leave, go, come, arrive, begin, buy, borrow, die, join, become等.终止性动词要表示持续时, 可用以下方法:
⑴.将时间状语改为时间段 + ago,句中谓语动词用一般过去时.
eg.我弟弟参军两年了. My brother joined the army two years ago.
⑵.若保留for+时间段,since+时间点/从句, 或用在 how long 句型中,则需将终止性动词改为相应的状态动词或延续性动词
常见终止性动词与延续性动词(或状态动词)的对应关系如下
come/go/arrive/get/reach/move------be in/at open-----be open
die------be dead close----be closed become---be borrow---keep begin/start-----be on put on----wear
leave-----be away (from) buy-----have fall asleep----be asleep
end/finish-----be over catch a cold-----have a cold
join the army----be in the army be a soldier join the Party----be in the Party be a Party member
→My brother has been in the army for two years. →My brother has been a soldier for two years.
3.现在完成时中been to,gone to和been in/at been to去过某地,表示某人的一种经历,可以和once,twice,already,ever,never等连用. eg. She has been to Shanghai twice. (表示目前人在这里)
gone to 去某地了,说话时某人已离开此地,在去某地的途中或已在某地,
eg. She has gone to Shanghai。 (表示现在她人不在这里)
been in/at 逗留在某地(已经一段时间).常和for ten days,since I came here等连用.
eg. She has been in Shanghai since she moved there.
4.现在完成时和一般过去时的区别
现在完成时所表明的是过去发生的动作对现在的影响,强调的是现在的情况,不可以和表示过去的时间状语yesterday,in 1991,three days ago last time,last night等连用一般过去时表明的是过去发生的事实,和现在不发生关系.
5.现在完成时中的 for 与 since
for + 时间段 与延续性动词的现在完成时连用 since + 时间点/从句
I have kept the library book for a week.= I have kept the library book since a week ago.
6. It is /has been +一段时间 + since 从句.自从某事发生已有一段时间了. eg. It is /has been two years since my brother joined the army. 注意:1.since 引导的从句中动词用过去时
2.when 引导 的特殊问句不与现在完成时连用.
3.have got,has got 虽然是现在完成时,但have got=have has got==has

以上就是关于初中阶段的宾语从句 ,初中宾语从句的全部内容,以及初中阶段的宾语从句 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
