本文目录
高中英语语法总结-名词性从句
首先,名词性从句中宾语从句与其他三个不同,在that;
whether
和if
等的用法上。
其次,要搞明白做的是哪种名词性从句。我用的一个笨办法是让学生往前看:没东西了,自然是主语从句,要不就是前面有一个形式主语it,前面是及物动词或介词是宾语从句,前面是系动词是表语从句,前面是一个名词是同位语从句。要关注引导词的细微差别。
最后,扎实的基本知识:从句并不总是老老实实地跟在前面说的那些词的后面,注意颠倒顺序的情况和中间插入其他内容的情况。
其他的可以看语法书讲解:看从句中是否缺成分,弄明白各种引导词的用法和含义。
英语语法名词性从句思维导图
英语中 不乏大量的名词性从句。名词性从句是由名词和动词组成的一组单词。
名词是人的名字、动物、地点、事物或者一种状态,比如快乐hapiness或者兴奋excitement。
换句话说,名词就是某人或某物的称呼。
名词意味着名字
代词it, she, you, him, this等等可以取代名词。如果发现用一个代词可以取代一组单词,那么这组单词即为名词短语。我们来看下几个例子:
 名词从句可以在句子中作主语、宾语或者补语。
名词从句可以在句子中作主语、宾语或者补语。
做主语:Whatever Taylor Swift sings becomes a hit.
It becomes a hit.
作宾语:Did you know that Taylor Swift is only twenty-five?
Did you know this?
作主语补足语:
Taylor Swift’s beauty and talent are what many girls dream of.
Taylor Swift’s beauty and talent are this.
名词从句通常可以通过对句子剩余部分提问来辨认。
比如说:
What becomes a hit? 答案即是whatever Taylor Swift sings
What did I know? 答案为:that Taylor Swift is only twenty-five?
What are Taylor Swift’s beauty and talent? 答案是:what many girls dream of.
明白了吗?
名词性从句很容易辨认,通常由以下词引导
that, if, whether,
what, when,how, where, 还有:
whatever,whenever, however.
You can tell me when it’s over if the high was worth the pain. 这句话里如何用this或it来替代句子成分呢?
这句话里包含了2个名词从句
1 You can tell me when it’s over
2. You can tell me if the high was worth the pain.
You can tell me ‘this’
待续。请继续关注Jason老师
想过你为什么没学好英语吗?
因为你没有真正的掌握英语学习的方法!
学英语不能输在起跑线上,
关注我们微信Jason-English8,学习别人不会告诉你的英语学习方法,真正的进入英语世界!
六年级上册英语语法知识点归纳
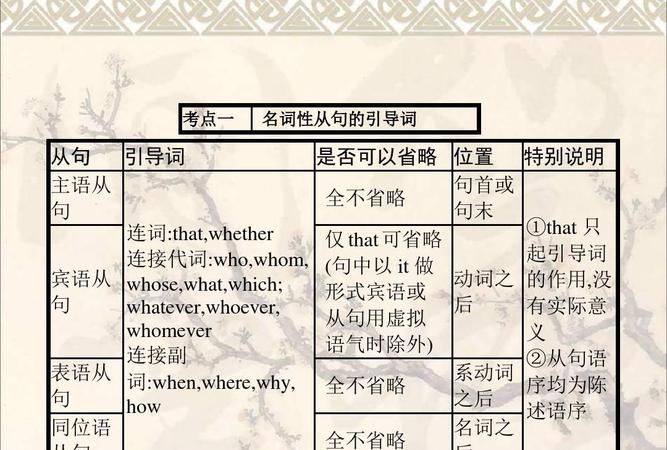
名词性从句相当于名词,可分别作主句的主语、表语、宾语和同位语。因此,名词性从句可分为主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句和同位从句。
一、引导名词性从句的连接词
1. 连接代词:who, whose, whom, what, which.有词义,在从句中担任成分,如主语、表语、宾语、或定语等。
2. 连接副词:when, where, why, how.有词义,在从句中担任成分,作状语。
3. 连接词:that, whether, if, as if.that 无词义,在从句中不担任成分,有时可省略;if (whether), as if虽有词义,但在从句中不担任成分。
注意:连接代词与连接副词在句中不再是疑问句,因而从句中谓语不用疑问式。连接代词与连接副词在从句充当句子成分,连接词whether 和if(是否),as if(好像)在从句中不充当句子成分,只起连接作用。根据句义,如果连接代词与连接副词,whether、if 和as if都用不上时,才用that作连接词(that本身无任何含义)。
二、主语从句
1. 主语从句在复合句作主语。
e.g. Who will go is not important.
2. 用it作形式主语,主语从句放在句末。
e.g. It doesn‘t matter so much whether you will come or not.
3. that引导主语从句时,不能省略。
e.g. That he suddenly fell ill last week made us surprised.
三、表语从句
1. 表语从句在复合句中作表语,位于系动词之后。
e.g. The question was who could go there.
2. 引导表语从句的连接词that有时可省去。
e.g. My idea is (that) we can get more comrades to help in the work.
四、宾语从句
1. 宾语从句在复合句中作宾语。引导宾语从句的连词that一般可省略。
e.g. I hope (that) everything is all right.
2. 介词之后的宾语从句,不可用which或if连接,要分别用what或 whether.
e.g. I’m interested in whether you‘ve finished the work……
I’m interested in what you‘ve said.
3. whether与if都可以引导宾语从句,常可互换。但下面情况不能互换。
(1)宾语从句是否定句时,只用if,不用whether.
e.g. I wonder if it doesn’t rain.
(2)用if 会引起误解,就要用whether.
e.g. Please let me know whether you want to go.(此句如果把whether改成if,容易当成条件句理解)
(3)宾语从句中的whether 与or not直接连用,就不能换成if;不直接连用,可换。
e.g. I don‘t know whether or not the report is true.
I don’t know whether/ if the report is true or not.
(4)介词后的.宾语从句要用whether引导。whether 可与不定式连用。whether也可引导主语从句、表语从句、同位语从句,还可引导让步状语从句,以上均不能换成if.但引导条件从句时,只能用if,而不能用whether.
e.g. It depends on whether we have enough time.
They don‘t know whether to go there.
Please come to see me if you have time.
五、同位语从句
同位语从句在句中作某一名词的同位语,一般位于该名词(如:news, fact, idea, suggestion, promise等)之后,说明该名词的具体内容。
e.g. I have no idea when he will be back.
The fact that he had not said anything surprised everybody.

英语什么是名词性从句
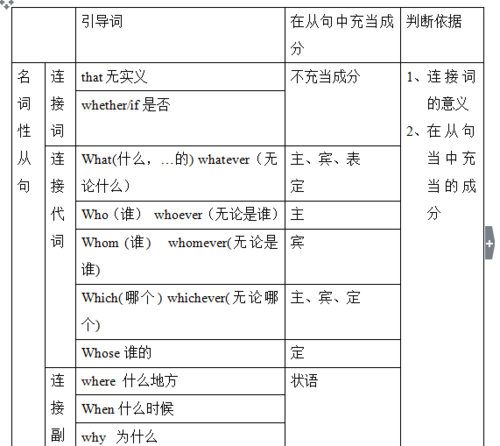
名词性从句
名词性从句:其功能相当于名词,根据其在句中充当的成分可分为主语,宾语,表语和同位语从句.名词性从句必须用陈述语序.
常见引导词:
1. that 无意义,在名词性从句中不充当成分;
2. whether/if “是否” , 在从句中不充当成分;
3. who “谁”,在从句中作主语, 口语中可作宾语, 表语;
4. whom “谁”,在从句中作宾语, 表语;
5. whose “谁的”,在从句中作定语,表语;
6. what “什么”,“…的”,在从句中作主语,宾语, 表语, 定语,含义没有明确的范围;
7. which “哪个,哪些”,在从句中作主语,宾语, 表语, 定语,含义有明确的范围;
8. when “何时”,在从句中作时间状语,表语;
9. where“何地”,在从句中作地点状语,表语;
10. why “为什么”,在从句中作原因状语,表语;
11. how “怎样,怎么”在从句中作方式状语,表语。 由how组成的短语也可引导名词性从句, 在从句中作状语,如how many, how long , how soon, how often, how far…
12. because “因为”,在从句中作原因状语;
13. as if/as though “好像,似乎”,在从句中不充当成分;
14. whoever “无论谁”,在主句和从句中都可作主语,宾语,表语;
15. whomever “无论谁”,在主句和从句中都可作宾语,表语;
16. whatever “无论什么”,在主句和从句中都可作主语,宾语,表语,定语;
17. whichever “无论哪个”,在主句和从句中都可作主语,宾语,表语,定语,含义有明确的范围;
一、主语从句
用作主语的从句。
常见引导词:that, whether, who, whom, whose, what, which, when, where, why, how, how much, how many, how long, how far, how soon, how often, whoever, whomever, whatever, whichever;
1. ________ the teacher said today was quite right.
2. _______ they are badly in need of help is quite clear.
3. ________ they will sell the house is not yet decided.
4. _________ was said here must be kept secret.
5. _________ makes mistakes must correct them.
6. It is a pity ______ she has made such a mistake.
7. ______ we will start is not decided yet.
8. ______ surprised me most was his manner.
9. ______ he was chosen monitor is clear.
10. _______ he has gone is still unknown.
注: 1、主语从句做主语,谓语用单数;但两个以上的从句做主语,谓语用复数;
What he says and what he does disagree.
2、可用“it”做形式主语,把主语从句放在后面;
主要有下列句型:
1) It +v.+ adj. / n. +从句
It is a shame that we missed the last train.
It is important that we should learn a foreign language.
It’s a pleasure that we’re going to have a party.
注:It is important /necessary/ natural/ a pity/strange/ impossible that sb. / sth. (should) do…
It is necessary that you not sleep in class.
2) It +不及物动词+从句
It seems/appears that he is from the USA.
It happened that his parents were out when he called.
3) It + be +过去分词+从句
It is said that... 据说……
It is known to all that... 众所周知……
It is reported that... 据报道……
It is believed that... 据信……;人们相信……
It is suggested that... 有人建议……
It is hoped that… 人们希望… …
It must be pointed out that... 必须指出……
It has been proved that... 已证明…….
It is said that Tom once studied in the USA.
It is reported that a storm is on the way.
It has been proved that the theory is correct.
3、在主语从句中,“that”放在句首时不能省略,若“it”做形式主语,“that”从句放在后面在口语中,可以省略“that”;
二、宾语从句
放在某个动词,介词或形容词后做宾语。
常见引导词:that, whether, if, who, whom, whose, what, which, when, where, why, how, how much, how many, how long, how far, how soon, how often, whoever, whomever, whatever, whichever;
1. I think ________ a healthy diet should contain a lot of green vegetables and fruit.
2. I wonder ________ you can do me a favor.
3. It depends on _________ the manager will agree to the plan or not.
4. The teacher asked little Tom _______ first discovered America.
5. He asked me ________ pronunciation was the best in our class.
6. He told me ________ had happened on his way to school.
7. Do you think _______ team will win the match?
8. You can do ____________ you like.
9. I’ll give the job to ___________ has much work experience.
10. I don’t know __________ he will leave for America.
注:1. 含宾补时,常用下面句型:
主语+动词+it+宾补+宾语从句;
I find it necessary that we should ask him for advice.
2. 介词后常接wh-词引导的从句,很少接that引导的(介词but, except, in 除外), 若介词后的从句由 that引导,则须用it作形式宾语
After what seemed a long time, he returned home.
You may depend on it that they will support you.
She was fortunate in that she had friends to help her.
3. 在“be+adj.”后,常可接that引导的宾语从句,也可把其称为原因状语从句.
I’m afraid that I can’t accept your invitation.
She’s happy that her daughter had passed the exams.
4. 否定转移:“think, believe, suppose, guess, expect, imagine”等词所接的宾语从句若为否定式,常把否定词提前到在主句中。
He doesn’t believe we have finished our work.
I don’t think he cares about it, does he?
5. “that”引导的宾语从句做某动词或形容词宾语时,“that”可省略,但若有两个并列的“that”从句,后一个“that”不可省略;
I hear Tom is good at soccer and that he joined the club last week.
6. 宾语从句的时态特点
①主句若用现在时(含一般现在时,一般将来时,现在完成时),从句根据情况可用任何相应时态;
I hear they will be back in a week.
Do you know why he left without a word?
I’m not sure whether he has been to the Great Wall before.
②主句用过去式时,从句要用相应的过去时态(包括一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时,过去完成时);
She hesitated whether she would take our advice.
He told me his son was watching TV.
He said that he had been in London for two days.
注:当从句表示“真理,格言,谚语,科学事实”时,从句用现在时态;
My grandpa told me that the earth is round.
三、表语从句
表语从句放在系动词后,如be, seem, look等,用来说明,解释主语,使其具体化;
常见引导词:that, whether, who, whom, whose, what, which, when, where, why, how, how much, how many, how long, whoever, how far, how soon, how often, whomever, whatever, whichever, because, as if/as though;
1. What she wants to know is _______ computer she should buy.
2. The problem was ______ could do the work.
3. What I want to know is _________ answers are right.
4. He is late for school today; it is ________ he missed the first bus.
5. It seems _________ he is from the USA.
6. The trouble is _______ he has no work experience.
7. The question is ________ we should ask them for help.
8. He missed the first bus today; that is ________ he was late for school.
9. This is ________ you made the mistakes.
10. The problem is _______ he can get food and clothing.
注:1. 引导词通常不省略;
2. 当“reason”做主语时,表语从句用 “that”引导;
The reason for his illness is that he was caught in a heavy rain.
3. The truth/fact is that…
The trouble/difficulty/problem is that…
The fact is that he has never been there before.
The trouble is that we are short of money and technology.
四、同位语从句
同位语从句放在某名词后,对其进一步解释,说明该名词的具体内容。
常见引导词:that, when, where, whether, why, who, whom, whose, how…
同位语从句常放在下列名词后: news, word, idea, fact, truth, reason, thought, doubt, belief, hope, promise, possibility, order, proposal, advice, suggestion, demand…
There was little hope that they would survive.
Word came that our team had won.
I have no idea why she left.
They had the question whether he could pass the final exam.
He didn’t take my advice that we should set off earlier.
以上就是关于名词性从句 英语 ,高中英语语法总结-名词性从句的全部内容,以及名词性从句 英语 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

