本文目录
高中定语从句详解PPT绝对经典课件
定语从句是高中阶段的重点,大家要记住相关的语法规则,并且需要通过以后的练习来逐渐透彻掌握。学习中肯定会遇到一些困难,不好弄懂的知识点一定要结合例句细心多看几遍。下面为大家带来高中定语从句详解,希望能帮到你!
Ⅰ.概念:
(1) 定语从句:在主从复合句中用作定语的从句叫定语从句。定语从句一般紧接在先行词后面。
(2) 先行词:被定语从句修饰的成份。先行词可以为一个词,短语,或整个主句。
(3) 引导定语从句的词叫关系词,分为关系代词和关系副词。
关系词的作用:
1) 引导定语从句,连接主句和从句,相当于一个连词;
2) 必在从句中作某个句子成份(可以做主语,宾语,表语,定语,状语)
常用的关系代词: that、 which、 who、whom、as , 在从句中作主语,宾语,whose在从句中作定语)
常用的关系副词(在从句中只作状语): when、why、 where
The student who answered the question was John.
I know the reason why he was so angry.
The boy (whom) you are talking to is my brother.
I'd like a room whose window looks out over the sea.
定语从句三步:
第一找出先行词;
第二看先行词在定语从句中的语法的功能(做主语、宾语或状语);
第三选择合适的'关系词。
Ⅱ. 几个关系代词的基本用法:
●that: 可指人或物;在定语从句中作主语,宾语,表语。(指人时,相当于who或 whom;指物时,相当于which)(不用于非限制性定语从句; 不可置于介词后作宾语) 如:
1. Do you know the gentleman that/who spoke just now?
2. You can take anything ( that) you like.
3. What is the question (that/which) they are talking about?
4. Here is the man ( who/whom/that ) you want to see.
5. She's no longer the girl ( that) she used to be before.
●which: 指物;在定语从句中作主语,宾语,表语,定语。如:
1. The bookwhich/that was on the desk was bought by my father.
2. The book (which/that) I bought yesterday is very interesting.
3. The factory in which his father works is far from here.
●who, whom, whose:
who: 主格, 在从句中作主语,在口语或非正式用法中作宾语; 只可指人
whom: 宾格,在从句中作宾语; 只可指人
whose: 属格,在从句中作定语,可指人也可指物。
1. I like the students who/that work hard.
2. All who heard the story were amazed.
(代词如he, they, any, those, all, one等后多用who.)
3. He's a man from whom we should learn.
= He's a man (whom/who/that) we should learn from.
4. A child whose parents are dead is called an orphan.
5. I'd like a room whose window faces south.
=I'd like a room of which the window faces south.
=I'd like a room the window of which faces south.
关系代词作介词宾语: (介词+ whom / which)
关系代词在定语从句中用作介词宾语时, 介词可放于从句之首, 也可放于从句之末. 但以放于句首较为正式.(介词前置,必须注意不影响动词词组的含义。)
1. This is the book for which you asked. =This is the book (that/which) you asked for.
2. Do you know the person with whom I shook hands?
= Do you know the person (whom/who/that) I shook hands with?
3. Is this the factory to which you paid a visit last week?
4. Is this factory the one to which you paid a visit last week?
5. This is the girl whom they are looking after. (介词after与look构成固定词组,不可前置。look at, look for, look after, take care of等)
●as 的用法:(as 引导定语从句, 在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语)
①如为限制性的,多用于the same …as ; the same as;such …as …; as many/much as;so …as等结构中。
1. I have the same book as you (have). 我有一本和你的一样的书。
2. .---Why didn't you mention that in face of the police just now?
--- I thought it was such a minor detail as was hardly worth mentioning.
3. Don't do such things as you are not sure about.
比较:I live in the same house that he used to live in.
I'm wearing the same shirt as you wore yesterday.
比较:Here is so big a stone as no one can lift. (定语从句)
Here is so big a stone that no one can lift it.(结果状语从句)
②如为非限制性的,多单独引导一个定语从句,这种定语从句可置于句首,句中或句尾,译为"正如,这一点"。(动词常为know, see, expect, point out, etc.)
As we all know, smoking is harmful to one's health . (as 作宾语)
=As is known to all, smoking is harmful to one's health . (as 作主语)
=It's known to all that smoking is harmful to one's health .
=Smoking is harmful to one's health, as we all know .(as 作宾语)
=Smoking, as we all know, is harmful to one' health.
He was a foreigner, as I knew from his accent. (宾语, 先行词是前面整个句子)
Ⅲ. 关系副词引导的定语从句:
●When 指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语。其先行词是表时间的名词(如:time, day, week, tear, month, etc.)
He came last night when I was out.
We will put off the picnic until next week, when the weather would be better.
注意:先行词为"时间名词",可用when引导定语从句,when在定语从句中作状语;还可以用which或that 引导,which或that在从句中作主语或宾语。
比较:1. I still remember the day when /on which my brother joined the army.(作状语)
2. I still remember the days which/that we spent together. (作宾语)
3. I shall never forget the day when Shen Zhou Ⅴ was launched, which has a great effect on my life.
●Where 指地点,在定语从句中作地点状语。其先行词是表示地点的名词,如:place, school, factory, room, etc.
This is the place where I was born.
I live in the room where /in which he used to live.
注意:先行词是"地点名词",定语从句可用where引导,还可用which或that引导,which/that 在从句中作主语或宾语。
比较: ※1. This is the factory where /in which he worked last year. (作状语)
2. I think you have got to the point where a change is needed, or you would fail.
3. He's got himself into a dangerous situation where he's likely to lose control of the plane.
4. This is the park which/that they visited last year. (作宾语)
●Why 指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语。先行词为reason 时,可用for which指代;当关系词在从句中作主语或宾语时,则用which或that 引导。如:
1. The reason why / for which / (that) he didn't attend the meeting was that he was ill.
2. I don't believe the reason (that/which) he gave me. (作宾语)
3. Have you asked him the reason that may explain his success? (作主语)
当先行词为way时,the way在从句中作状语时,定语从句常用that, in which,或how引导,that常可以省略。
the way在从句中作主语或宾语时,则用which或that 引导。如:
This is the way (that) /in which I do such things.
比较: Please do the experiment in the way (that/which)I have shown you.
Ⅳ. 限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别:
1. 形式上,非限制性定语从句往往用逗号隔开。
2. 语法上,非限制性定语从句一般不用that.
3. 语义上,限制性定语从句与先行词关系紧密,起限定作用,如果去掉了这个定语从句,整个句子就不完整或者会改变意思;而非限制性定语从句与先行词关系不是很紧密,对先行词起补充说明或描述的作用。
This is the book I like best. 这就是我最喜欢的那本书。
Beijing, which has been China's capital for more than 800 years, is rich in cultural and historic relics. 北京是中国八百年之久的古都,它有着丰富的文化和历史遗产。
4. 翻译时,限制性定语从句可译为一句(较短的一般译为"的"字结构);而非限制性定语从句可译为两句。(见上句翻译)
比较: He has a sister, who is a musician.
He has a sister who is a musician.
引导非限制性定语从句的关系代词,指人时用who, whom, whose , 指物时用which , whose; 关系副词when,where, why, etc.
1. He studied hard at school when he was young, which leads to his success in his later life.
2. Tom's father, who arrived just now, is a famous scientist.
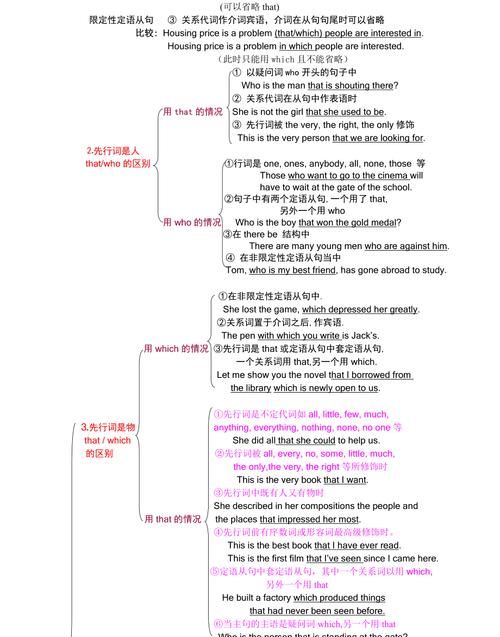
Ⅴ. 几个易混淆的关系代词的比较:
●that & which:
在定语从句中,which 和that 在指代事物时,一般可以互换使用,但并非在任何情况下都是这样,这里介绍宜用that, 而不宜用which 的情况.
①先行词为不定代词,all, much, something, everything, anything, nothing, none, the one等,
1.We should do all that is useful to the people .
2.There's nothing that can be said about it .
3.Do you mean the one that was bought yesterday?
②先行词被only, any, few, little, no, just, very, one of等词修饰时。
1.The only thing that we could do was to wait.
2.That's the very word that is wrongly used.
3. The last place (that) we visited was the chemical works.
比较 *This is one of the best novels that were published last year.
This is the only one of the best novels that was published last year.
③先行词是序数词时或被序数词修饰时。
1.When we talk about Wuxi, the first that comes into mind is Tai Lake.
2.This is the third film that has been shown in our school this term.
④先行词是最高级或被最高级修饰时。
1.This is the best that can be done now.
2.The most important thing that should be done right now is how to stop him from going on.
⑤先行词既有人又有物,用which和who都不适合,这时宜用that.
1.The writer and his novel that you have just talked about is really well known .
2.The rider and his bike that had run over an old woman were held up by the police.
⑥被修饰词为数词时.
1.Yesterday I caught two fish and put them in a basin of water .Now you can see the two that are still alive .
⑦如果有两个从句,其中一个关系代词已用which ,另一个关系代词宜用that,以避免语言的单调或重复。
Edison built up a factory which produced things that had never been seen before.
⑧疑问词是who或which,关系代词宜用that,以避免重复。
1. Which is the book that you like best?
2. Who is the man that is standing at the gate?
⑨主句是There be 结构,修饰其主句的定语从句宜用that 作关系代词. 如:
1. There is still a seat in the corner that is still free.
⑩被修饰成分为表语时,或者关系代词本身是定语从句的表语时,该关系代词宜用that .
1. That's a good book that will help you a lot.
2. My home village is no longer the place ( that ) it used to be .
定语从句中宜用which而不宜用that 的情况:
①当关系代词的前面有介词时.
1.A zoo is a park in which many kinds of animals are kept for exhibition.
2.Is this the room in which Mr. White lives?
②在非限制性定语从句中.
1.Crusoe's dog, which was are now very old, became ill and died .
2.More and more people are beginning to learn English, which is becoming popular in our country. (which指代主句)
③在一个句子中有两个定语从句,其中一个定语从句的关系代词用了that, 另一个宜用which .
1. Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the library which was newly open to us.
④当关系代词后面带有插入语时.
1. Here's the English grammar which, as I have told you, will help improve your English.
⑤先行词本身是that, 宜用which .
What's that which she is looking at?
⑥先行词是those+复数名词.
A shop should keep a stock of those goods which sell best.
●who & that:
who 和 that 指代人时,有些情况宜用who, 而不宜用that
①先行词为anyone, anybody, those, all, one, ones, they, he, people时. 如:
1.The person I want to learn from is the one who studies hard and works well.
2.Anyone who (=Whoever) failed to come to the meeting yesterday must give his reason .
3.Those who are not fit for their work should leave office at once.
②在There be 结构中,修饰主语的定语从句宜用关系代词who 指代人. 如:
1.There is a gentleman who wants to see you .
2.There are several students in our class who are still not sure about the use of attributive clauses.
③当先行词有较长的后置定语时. 如:
1. I met a foreigner in the park yesterday afternoon who could speak Chinese very well.
●as & which:
as & which 引导非限制性定语从句的区别:
①位置的不同:
which 引导的定语从句只置于所限制的句子后;as 位置较灵活,也就是说as可置于所限制的句子前面;插在句子中或放在句子后。如:
1. He was late again, which made his teacher very angry.
2. Jack, as you know, is an honest man. 或Jack is an honest man , as you know.
或As you know, Jack is an honest man.
②先行词的不同:
as引导非限制性定语从句时,其先行词多为一个句子;
which引导非限制性定语从句时,其先行词可以是一个词,一个短语或一个句子。
1. She was very patient towards the children, which her husband seldom was.
2. He was proud, which I dislike very much.(先行词是一个句子)
3. He is an honest man, as is known to all.
③as 一般译为"正如""就像","这一点"
as we all know;as you know; as is known to all; as you see; as we can see; as has been expected; as we have imagined.
定语从句宾语从句表语从句思维导图
to
cope with physical privation. They
lived apart from the men and
went to war in their own
regiments. The tales tell us that
they conquered men on the field
of battle. Amazons occur in Greek
literature in the Iliad of Homer,
for example, in 600 B.C.
高中定语从句的讲解视频
定语从句,一个句子跟在一名词或代词(先行词)后进行修饰限定,就叫做定语从句。
通俗来讲,从句在整个句子中做定语,这个从句就叫做定语从句。从句在主句中充当定语成分。 被修饰的词叫先行词。定语从句不同于单词作定语的情况,它通常只能放在被修饰的词(即先行词)之后。
定语从句由关系词(关系代词、关系副词)引导,关系代词、关系副词位于定语从句句首。
定语从句=先行词+关系词+从句

扩展资料:
1)who, whom, that
这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中所起作用如下:
Is he the man who/that wants to see you?
他就是想见你的人吗?(who/that在从句中作主语)
He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday.
他就是我昨天见的那个人。(whom/that在从句中作宾语)
2) Whose 用来指人或物,(只用作定语, 若指物,它还可以同of which互换), 例如:
They rushed over to help the man whose car had broken down.
那人车坏了,大家都跑过去帮忙。
Please pass me the book whose (of which) cover is green.
请递给我那本绿皮的书。
3)which, that
它们所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可作主语、宾语等,例如:
A prosperity which / that had never been seen before appears in the countryside.
农村出现了前所未 有的繁荣。(which / that在从句中作主语)
The package which / that you are carrying is about to come unwrapped.
参考资料:定语从句-百度百科
定语从句的思维导图
定语从句的思维导图
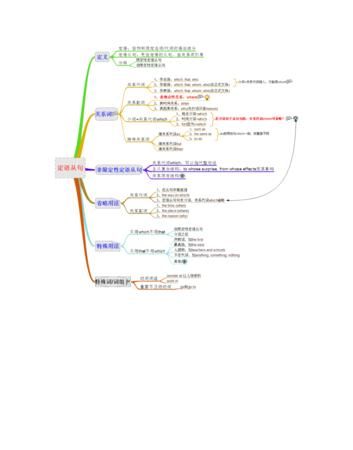
一、定语从句的概念
在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。被修饰的名词或代词叫先行词,定语从句一般放在先行词的后面。
二、定语从句的关系词
引导定语从句的关系词有关系代词和关系副词,常见的关系代词包括that, which, who(宾格whom,所有格whose)等,关系副词包括where, when, why等。关系代词和关系副词放在先行词及定语从句之间起连接作用,同时又作定语从句的重要成分。
三、定语从句的分类
根据定语从句与先行词的关系,定语从句可分为限制性定语从句及非限制性定语从句。限制性定语从句紧跟先行词,主句与从句不用逗号分开,从句不可省去,非限制性定语从句主句与从句之间有逗号分开,起补充说明作用,如省去,意思仍完整。
限制性关系从句
从语义上看,限制性关系从句主要起限定作用,修饰特定的人或事物,如果去掉限制性定语从句,整个句子表意会不完整甚至不通顺;从结构上看,限制性关系从句常紧跟先行词,并且同先行词之间一般不加逗号分隔(但不是绝对的)。
限制性关系从句的关系词包括:that, which, who, whom, whose, as, than等。
非限制性关系从句
从语义上看,非限制性关系从句主要起补充说明的作用,有时相当于一个并列分句或状语从句,可以表达原因、目的、结果、条件、让步等意义。
例如:Dr Lee, who had read through the instructions carefully before doing his experiments, did not obtain satisfactory results. (非限制性关系从句表示让步的意义,相当于though Dr Lee had read through the instructions...)
非限制性定语从句的关系词包括:which, who, whom, whose, as等,另外that在非限制性关系从句中并非绝对不可使用。
四、关系代词的用法
1. that 既可以用于指人,也可以用于指物。在从句中作主语或宾语,作主语时不可省略,作宾语可省略。例如:
Mary likes music that is quiet and gentle.玛丽喜欢轻柔的音乐。(that作主语)
The coat (that) I put on the desk is blue.我放在桌子上的那件外套是蓝色的'。(that作宾语)
2.which用于指物,在句中作主语或宾语,作主语不可省略,作宾语可省略。例如:
The building which stands near the train station is a supermarket.位于火车站附近的那座大楼是一家超市。(作主语)
The film (which) we saw last night was wonderful. 我们昨天晚上看的那部电影很好看。(作宾语)
3.who, whom用于指人,who 用作主语,whom用作宾语。在口语中,有时可用who代替whom,也可省略。例如:
The girl who often helps me with my English is from England.经常在英语方面帮助我的那个女孩是英国人。(作主语)
Who is the teacher (whom) Li Ming is talking to?正在与李明谈话的老师是谁?(作宾语)
注意:(1)当定语从句中含有介词,介词放在句末时,who, that, which可省略,但介词在关系代词前时,只能用“介词+which/whom”结构。例如:
This is the house in which we lived last year.这是我们去年居住的房子。
Please tell me from whom you borrowed the English novel.请告诉我你从谁那借的这本英文小说。
(2)含有介词的固定动词词组中,介词不可前置,只能放在原来的位置上。例如:
This is the person whom you are looking for. 这就是你要找的那个人。
(3)that 作介词的宾语时,介词不能放它的前面,只能放在从句中动词的后面。例如:
The city that she lives in is very far away.她居住的城市非常远。
(4)关系词只能用that的情况:
a. 先行词被序数词或形容词最高级所修饰,或本身是序数词、基数词、形容词最高级时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
He was the first person that passed the exam. 他是第一个通过考试的人。
b.被修饰的先行词为all, any, much, many, everything, anything, none, the one等不定代词时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
Is there anything that you want to buy in the shop?你在商店里有什么东西要买吗?
c.先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last, little, few 等词修饰时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
This is the same bike that I lost.这就是我丢的那辆自行车。
d. 先行词里同时含有人或物时,只能用that, 而不用which.例如:
I can remember well the persons and some pictures that I saw in the room.我能清楚记得我在那个房间所见到的人和一些照片。
e.以who或which引导的特殊疑问句,为避免重复,只能用that.例如:
Who is the girl that is crying? 正在哭泣的那个女孩是谁?
f.主句是there be 结构,修饰主语的定语从句用that,而不用which.例如:
There is a book on the desk that belongs to Tom. 桌子上那本书是汤姆的。
(5)关系词只能用which,而不用that 的情况:
a.先行词为that, those时,用which, 而不用that.例如:
What’s that which is under the desk? 在桌子底下的那些东西是什么?
b.关系代词前有介词时,一般用which,而不用that.例如:
This is the room in which he lives. 这是他居住的房间。
c.引导非限制性定语从句,用which, 而不用that.例如:
Tom came back, which made us happy. 汤姆回来了,这使我们很高兴。
五、关系副词的 用法
(1)when指时间,其先行词表示时间,在句中作时间状语。例如:
This was the time when he arrived.这是他到达的时间。
(2)where指地点,其先行词表示地点,在句中作地点状语。例如:
This is place where he works.这是他工作的地点。
(3)why 指原因,其先行词是原因,起原因状语作用。例如:
Nobody knows the reason why he is often late for school. 没人知道他为什么上学总迟到。
六、关系构成
关系从句的句法功能主要是充当定语。在英语中,关系从句通常位于它所修饰的词(组)之后。被关系从句修饰的词(组)叫做先行词(英语:antecedent),引导关系从句的词称为关系词,关系词指代先行词并在关系从句中充当一定的成分。
例如:This is the book which interests me.(“which interests me”是关系从句,修饰先行词“book”,而关系词“which”指代先行词“book”并在关系从句中充当主语。这句话可以拆分为两个句子来理解:“This is the book.”和“The book interests me.”)
七、特殊的关系从句
名词性关系从句
名词性关系从句(英语:nominal relative clause)又叫自由关系从句(英语:free relative clause),名词性关系从句在结构上不含有先行词,它的关系词同时扮演了关系词和先行词的角色,因此名词性关系从句的关系词又叫缩合连接代词。
例如:I like what I see.(“what I see”是名词性关系从句,它没有先行词,与此同时缩合连接代词“what”又直接充当了“like”的宾语。)
缩合连接代词“what”可以根据语义解释为“the thing(s) that”或“the person(s) that”。
嵌入式关系从句
嵌入式关系从句(英语:embedded relative clause)是一种较复杂的关系从句,它既是先行词的后置定语,又是另一结构的宾语。
例如:She has an adopted child who she says was an orphan. (关系从句修饰“an adopted child",同时又是“she says”的宾语)
双重关系从句
双重关系从句(英语:double relative clause)是指两个关系从句修饰同一个先行词的语法现象。
例如:You can easily find us;just look for a house whose windows need washing andwhosefence needs repairing!

以上就是关于定语从句思维导图高中 ,高中定语从句详解PPT绝对经典课件的全部内容,以及定语从句思维导图高中 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
