本文目录
英语名词性从句思维导图
主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句在复合句中起名词的作用,这四种从句合称名词性从句。它们在主句中充当主语、表语、宾语或同位语,都不能用逗号与主句分开。(注:句中划线部分为从句)
■主语从句
1、定义:先找到句子的谓语,主句的谓语前面的从句,叫做主语从句。
Why he left wasn't important.(wasn't是主句的谓语动词,why he left做主语从句)
That she became an artist may have been due to her father's influence.(may have been due是主句的谓语动词,that she became an artist做主语从句)
2、借助形式主语it,主语从句放在后面
①由that引导的主语从句可以放在主语的位置,这时that不可以省略。例如:That prices will go up is certain.
that主语从句放在句首的情况不是很常见,绝大部分主语从句都借助形式主语it,主语从句放在后面。
It is strange that he knows nothing about it.
It is a pity that he can't swim.
It happened that he wasn't in that day.
It is said that there has been an earthquake in India.
在口语中,用it做形式主语时,主语从句的that可以省略。
②wh-疑问词引导的主语从句,可以放在句首(第一组),也可以借助形式主语it(第二组)。
第一组:When he'll be back depends much on the weather.
How it was done was a mystery.
Whether we'll succeed remains to be seen.
第二组:It is uncertain whether the game will be held.
It's a puzzle how life began.
It doesn't matter much where we live.
Is it known where he went?
■宾语从句
1、定义:及物动词(第一组)和介词(第二组)的后面可以接从句做宾语,叫做宾语从句。
第一组I guess(that) we'll leave soon.
He asked when we would be in London.
She informed me (that) she was to send for it the next day.(that可以省略)
I'll tell you what I read in today's paper.
第二组
I'll find out whether she's interested in going.
Can you give us a description of what has happened.
She was shocked by what she had seen.
2、借助形式宾语it,that引导的宾语从句放在后面。I've heard it said that you have won a scholarship.
分析:it在句中做形式宾语,said做宾语补足语,that you have won a scholarship是真正的宾语。She has seen to it that all the children are well taken care of.
分析:it在句中做形式宾语,that all the children are well taken care of是真正的宾语。
■表语从句
1、定义:系动词的后面可以接句子做表语,叫做表语从句。
The fact is that she never liked him.
That is not what I meant.
The question is who is responsible for what has happened.
She is no longer what she used to be.
2、注意:
①The reason Hollywood was a good place for making movies was that the sun shines there every day.
分析:the reason做主语时,表语从句用that引导。
②引导表语从句的that一般不省略。
■同位语从句
1、定义:有些名词的后面可以跟that引导的从句,说明这个名词的内容,这样的从句叫做同位语从句。所以,只有可以有内容的名词才可以接同位语从句,例如:fact,message,idea,possibility,conclusion,thought,news,order,report,rumor等等。
that在从句中不做成分,但是不能省略。
He had the feeling that he would not see her again.I've come to the conclusion that it won't be wise to do so.
2、有时为了保持句子的平衡,同位语从句有时和前面的名词分开。
The rumor spread that a new school would be built here.
that引导的同位语从句修饰the rumor,但是主句The rumor spread太短,如果把后面的同位语从句放在the rumor后面,主语太长,给人头重脚轻的感觉。
3、在少数情况下,名词性从句的其他关联词也可以引导同位语从句。但if不可以引导同位语从句。
You have no idea how worried I was.
I have no idea why she left.
There is some doubt whether John will come on time.
在学习名词性从句时注意下面四点:
一、名词性从句要用陈述语序,也就是说:①名词性从句的关联词做主语的话,关联词后面接谓语动词;②名词性从句的关联词不做主语的话,关联词后面接从句的主语和谓语。
①I don't know who broke the window.(宾语从句中关联词who做主语,broke是谓语动词)
②The little boy told his mother where he found the coin.(宾语从句中关联词where不做主语,where后面接主谓部分he found)
二、感叹句做名词性从句时语序不做变化
Don't you know how excited I was then?
三、时态的呼应
某些从句(特别是宾语从句)中的动词时态,常受主句谓语时态的制约。
①如果主句谓语动词为现在时或将来时,从句中的谓语可以不受影响。例如:
Has he told you when he received the gift?
Will you tell me how you two are getting along?
②如果主语谓语动词为过去时,从句谓语一般要跟着改为相关的过去时。
I didn't know where they lived.He thought he was working for the people.asked him how long he had been waiting.
③但是,当宾语从句表示永恒真理时谓语可以不变:This proved that the earth is round.
四、当and连接两个that引导的宾语从句时,and后面的that不可以省略
She promised (that) she would come and see him sometimes and that she would never forget him.句中的第一个that可以省略,为了清楚地表示出第二个that引导的是宾语从句,第二个that不省略。

名词性从句题目及答案解析
在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词从句 (Noun Clauses)。 名词从句的功能相当于名词词组, 它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
一、高考焦点指南在复合句中起名词作用的从句叫做名词性从句。它包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。名词性从句是中学阶段的一个重要语法项目,在历年的高考中几乎都涉及到,并且每年的命题各有变化。分析历届高考试题名词性从句考查的焦点主要有以下六个方面
1. 考查名词性从句的语序问题
高考真题例示:
例1. The photographs will show you ____.(MET1989)
A. what does our village look like B. what our village looks like
C. how does our village look like D. how our village looks like
例2. Someone is ringing the doorbell. Go and see ___________. (NMET2000)
A. who is he B. who he is C. who is it D. who it is
例3. Can you make sure ______ the gold ring? (NMET1990)
A. where Alice had put B. where did Alice put
C. where Alice has put D. where has Alice put
例4. He asked ________ for the violin. (NMET1991)
A. did I pay how much B. I paid how much
C. how much did I pay D. how much I paid
2. 考查引导词that与what的区别
高考真题例示:
例1. ______we can’t get seems better than ______we have. (NMET1996)
A. What; what B. What; that C. That; that D. That; what
例2. No one can be sure _____ in a million years. (MET1991)
A. what man will look like B. what will man look like
C. man will look like what D. what look will man like
例3. _______ you have done might do harm to other people. (MET 1987)
A. That B. What C. Whether D. How
例4. _______ you don't like him is none of my business. (上海1992)
A. What B. Who C. That D. Whether
3. 考查it在名词性从句中作形式主语或形式宾语的用法
高考真题例示:
例1. _____ is a fact that English is being accepted as an international language. (NMET1995)
A. There B. This C. That D. It
例2. It worried her a bit ______her hair was turning grey.
A. while B. if C. that D. for
例3. I hate _____when people talk with their mouths full. (NMET1998)
A. it B. that C. this D. them
例4. Does _______ matter if he can't finish the job on time? (MET 1991)
A. this B. that C. he D. it
4. 考查whether与if的区别
高考真题例示:
例1. _____we’ll go camping tomorrow depends on the weather. (NMET1996)
A. If B. Whether C. That D. Where
例2. What the doctors really doubt is _____my mother will recover from the serious disease soon. (上海2001)
A. when B. how C. whether D. why
例3. _____ the 2000 Olympic Games will be held in Beijing is not known yet. (MET1992)
A. Whenever B. If C. Whether D. That
5. 考查名词性从句中的疑问词+ever引导的名词性从句与no matter+疑问词引导的状语从句的区别
高考真题例示:
例1. It is generally considered unwise to give a child _____he or she wants. (NMET1997)
A. however B. whatever C. whichever D. whenever
例2. ______leaves the room last ought to turn off the lights. (MET1988)
A. Anyone B. The person C. Whoever D. Who
例3. Sarah hopes to become a friend of ______shares her interests. (上海1995)
A. anyone B. whomever C. whoever D. no matter who
6. 考查名词性从句的虚拟语气问题
高考真题例示:
例1:It is necessary that a college student ______at least a foreign language. (上海1993)
A. masters B. should master C. mastered D. will master
二、语法要点剖析
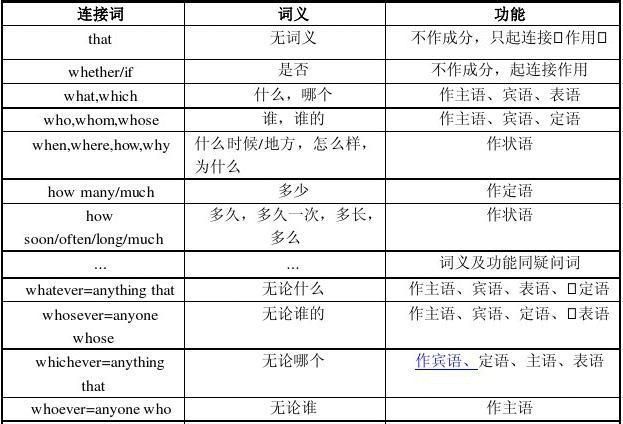
一、名词性从句
主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句,在整个句子中所起的作用,相当于一个名词。因此,这四种从句通称为名词性从句。
引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类:
连接词:that, whether, if (不充当从句的任何成分)
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, which.
连接副词:when, where, how, why
1. 主语从句
作句子主语的从句叫主语从句。主语从句通常由从属连词that,whether,if和连接代词what,who,which,whatever, whoever以及连接副词how,when,where,why等词引导。that在句中无词义,只起连接作用;连接代词和连接副词在句中既保留自己的疑问含义、又起连接作用,在从句中充当从句的成分。例如:
What he wants to tell us is not clear. 他要跟我们说什么,还不清楚。
Who will win the match is still unknown. 谁能赢得这场比赛还不得而知。
It is known to us how he became a writer. 我们都知道他是如何成为一名作家的。
Where the English evening will be held has not yet been announced. 英语晚会将在哪里举行,还没有宣布。
有时为避免句子头重脚轻,常用形式主语it代替主语从句作形式主语放于句首,而把主语从句置于句末。主语从句后的谓语动词一般用单数形式。常用句型如下:
(1) It + be + 名词 + that从句
(2)It + be + 形容词 + that从句
(3)It + be + 动词的过去分词 + that从句
(4)It + 不及物动词 + that 从句
另注意在主语从句中用来表示惊奇、不相信、惋惜、理应如此等语气时,谓语动词要用虚拟语气“(should) +do”,常用的句型有:
It is necessary (important, natural, strange, etc.) that …
It is a pity (a shame, no wonder, etc.) that…
It is suggested (requested, proposed, desired, etc.) that…
2. 宾语从句
名词句用作宾语的从句叫宾语从句。引导宾语从句的关联词与引导主语从句表语从句的关联词大致一样,在句中可以作谓语动词或介词及非谓语动词的宾语。
1. 由连接词that引导的宾语从句
由连接词that引导宾语从句时,that在句中不担任任何成分,在口语或非正式的文体中常被省去,但如从句是并列句时,第二个分句前的that不可省。例如:
He has told me that he will go to Shanghai tomorrow. 他已经告诉我他明天要去上海。
We must never think (that) we are good in everything while others are good in nothing. 我们决不能认为自己什么都好,别人什么都不好。
注意:在demand、order、suggest、decide、insist, desire, demand, request, command等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,宾语从句常用“(should)+ 动词原形”。例如:
I insist that she (should) do her work alone. 我坚持要她自己工作。
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once. 司令员命令部队马上出发。
2. 用who,whom, which, whose, what, when, where, why, how, whoever, whatever, whichever等关联词引导的宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,应注意句子语序要用陈述语序。例如:
I want to know what he has told you. 我想知道他告诉了你什么。
She always thinks of how she can work well. 她总是在想怎样能把工作做好。
She will give whoever needs help a warm support. 凡需要帮助的人,她都会给予热情的支持。
3. 用whether或if引导的宾语从句,其主语和谓语的顺序也不能颠倒,仍保持陈述句语序。此外,whether与if 在作“是否”的意思讲时在下列情况下一般只能用whether,不用if:
a. 引导主语从句并在句首时;b. 引导表语从句时;c . 引导从句作介词宾语时;d. 从句后有“or not”时;e. 后接动词不定式时。例如:
Whether there is life on the moon is an interesting question. 月球上有没有生命是个有趣的问题。
The question is whether she should have a low opinion of the test?
Everything depends on whether we have enough money. 一切要看我们是否有足够的钱。
I wonder whether he will come or not. 我想知道他来还是不来。
Can you tell me whether to go or to stay? 你能否告诉我是去还是留?
4. 注意宾语从句中的时态呼应,当主句动词是现在时,从句根据自身的句子情况,而使用
不同时态。例如:
he studies English every day. (从句用一般现在时)
he studied English last term. (从句用一般过去时)
I know (that) he will study English next year. (从句用一般将来时)
he has studied English since 1998. (从句用现在完成时)
当主句动词是过去时态(could, would除外),从句则要用相应的过去时态,如一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时等;当从句表示的是客观真理,科学原理,自然现象,则从句仍用现在时态。例如:
The teacher told us that Tom had left us for America.
5. think, believe, imagine, suppose等等动词引起的否定性宾语从句中,要把上述主句中的动词变为否定式。即将从句中的否定形式移到主句中。例如:
We don’t think you are here. 我们认为你不在这。
I don’t believe he will do so. 我相信他不会这样做。
3. 表语从句
在句中作表语的从句叫表语从句。引导表语从句的关联词与引导主语从句的关联词大致一样,表语从句位于连系动词后,有时用as if引导。其基本结构为:主语 + 系动词 + that从句。例如:
The fact is that we have lost the game. 事实是我们已经输了这场比赛。
That’s just what I want. 这正是我想要的。
This is where our problem lies. 这就是我们的问题所在。
That is why he didn’t come to the meeting. 那就是他为什么不到会的原因。
It looks as if it is going to rain. 看上去天要下雨了。
需要注意的,当主语是reason时,表语从句要用that引导而不是because。例如:
The reason why he was late was that he missed the train by one minute this morning
4. 同位语从句
同位语从句说明其前面的名词的具体内容。同位语从句通常由that引导,可用于同位语从句的名词有advice、demand、doubt、fact、 hope、idea、information、message、news、order、problem、promise、question、 request、suggestion、truth、wish、word等。例如:
The news that we won the game is exciting. 我们赢得这场比赛的消息令人激动。
I have no idea when he will come back home. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
The thought came to him that Mary had probably fallen ill. 他想到可能玛丽生病了。
同位语从句和定语从句的区别:
that作为关系代词,可以引导定语从句,充当句子成分,在从句中作宾语时可以省略; that引导同位语从句时,起连词的作用,没有实际意义,不充当句子成分,一般不能省略。
试比较下面两个例句:
I had no idea that you were here.(that引导同位语从句,不能省略)
Have you got the idea(that)this book gives you of life in ancient Greece?(that引导定语从句,作宾语,可以省略)
三、高考热点透视
1. ___ is a fact that English is being accepted as an international language. (NMET 1995)
A. There B. This C. That D. It
答案D。当名词从句在句中作主语时,为避免句子头重脚轻,常用it作形式主语置于句首,而将真正的主语从句放在句尾。此时it只起先行引导作用,本身无实义。此句也可以改写为:That English is being accepted as an international language is a fact.
2.A computer can only do ____ you have instructed it to do.(NMET2001)
A.how B.after C.what D.when
答案C。从句子结构可知,句子的空白处应该填引导宾语从句的连词,做主句谓语动词do的宾语,同时该连接词还是从句中的do的宾语,因此,此处的连接词应该用what。
3. He asked ____ for a violin.(MET1992)
A. did I pay how much B. I paid how much
C. how much did I pay D. how much I paid
答案:D。宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,句子语序要用陈述语序。
4. What the doctors really doubt is my mother will recover from the serious disease soon.(上海2001年春季招生)
A. when B. how C. whether D. why
答案C。这是一个表语从句。根据 doubt一词可知,所怀疑的应是是否能治好病,所以要填whether。这句话的意思是“医生真的怀疑我妈妈是否能很快从重病中恢复过来。”
5.It is generally considered unwise to give a child _____he or she wants. (NMET1997)
A. however B. whatever C. whichever D. whenever
答案B。根据句意“一般认为孩子要什么就给什么是不好的。”可以看出后面的从句应是一个宾语从句,而从句中wants缺少宾语,A. however 和D. whenever是不能作宾语的;排除A和D,whichever表示“无论哪一个,无论哪些”,应表示一定范围内的人或物,此处没有涉及事物的范围,所以应选 B.whatever,表示“无论什么”。
6. ______leaves the room last ought to turn off the lights. (MET1988)
A. Anyone B. The person C. Whoever D. Who
答案C。本题句子的意思是:无论谁最后离开房间一定要把灯关掉。本题考查连接代词whoever引导的名词性从句,连接代词whoever可以引导名词性从句,并在从句中作主语,相当于any person who或The person who, 意为“一切……的人”。而anyone和the person均非连词,不能引导从句,况who leaves the room last意为“某个最后离开房间的人”,与题意不符,如果要选A. Anyone或B. The person,都必须在它们后面再加上引导定语从句的关系代词who。如果要选D. Who就体现不出“无论谁”的含义了。
7. Sarah hopes to become a friend of ______shares her interests. (Shanghai1995)
A. anyone B. whomever C. whoever D. no matter who
答案为C。本题句子的意思是:Sarah希望跟自己有共同爱好的人交朋友。疑问词+ever引导的名词性从句与no matter+疑问词引导的从句的区别是:前者既可以引导名词性从句也可以引导让步状语从句;后者只能引导让步状语从句。首先排除A和D,从句中需要的是主语,所以whomever也不行。
8. ---- I drove to Zhuhai for the air show last week.
---- Is that ______ you had a few days off ? ( NMET1999)
A. why B. what C. when D. where
答案A。根据语境,甲说上周驱车去珠海观看航模展览。乙据此来询问甲这是否是请几天假的原因,故答案是A。答案B,C, D均与该题语境不符。根据上句提供的语境,下句应该问“那就是你为什么离开几天的原因吗?”
9. I still remember ______ this used to be a quiet village. ( NMET1993)
A. when B. how C. where D. what
答案A。根据从句中缺少的句子成分是状语,排除D.what,而答案C, D均与题意不符,所以应选A.when。used to be表示一种过去存在的状态,本句的意思是“我仍然记得这里在什么时候是个宁静的地方。”
10.I read about it in some book or other,does it matter ____ it was?(2001春季招生)
A.where B.what C.how D.which
答案D。这是一个主语从句。主语从句中缺少表语。从上句的意思分析,应是哪本书,所以要填which,这句话的意思是“我在某本书中读到过有关这方面的内容,是哪一本书重要吗?”。
11. Information has been put forward ____ more middle school graduates will be admitted into universities.
A. while B. that C when D. as (2001年上海)
答案B。该题考查that引导的同位语从句。同位语从句通常由that引导,接在fact, news, promise, possibility, information, doubt, message名词后,用来解释或说明名词的内容。
12. —I think it is going to be a big problem.
—Yes, it could be.
—I wonder ______ we can do about it. (北京 2002春季)
A、if B、how C、what D、that
答案C。本题考察名词性从句的连接词的用法。wonder后面应跟宾语从句,而从句中的谓语动词do是及物动词,可见从句缺少一个代替宾语的成分,我们可以用排除法排除不作成分的if和that,再排除引导方式状语的how,答案是C,句子的意思是“我们能就此做些什么”。
四、专项考点练习
1. ________that they found an unusual plant in the forest.
A. It is said B. They are said C. It said D. It says
2. _____ caused the accident is still a complete mystery.
A. What B. That C. How D. Where
3. It worried Mary a lot _____ she would pass the college entrance examination.
A. whether B. if C. that D. how
4. Shanghai has taken on a new look. It isn’t like _____ it used to be .
A .what B. how C. that D. which
5. ____ is no possibility ______ Bob will win the first prize in the match.
A. There, that B. It, that C. There, whether D. It, whether
6. Little Tommy was reluctant to tell the schoolmaster ____ he had done the day before.
A .that B. how C .what D. where
7. The old man smiled when he saw how pretty _____ up to be during the past few years.
A. had his daughter grown B. would his daughter grow
C. his daughter would grow D. his daughter had grown
8. Have you seen Mary lately? My boss wants to know _______.
A. how she is getting along B. how is she getting along
C. what she is getting along D. what is she getting along
9. ____surprised me most was _____such a little girl of seven could play the violin so well.
A. That; what B. What; that C. That; that D. What; what
10. These wild flowers are so special I would do ______ I can to save them.
A. whatever B. which C. that D. whichever
11. _____ helped to save the drowning girl is worth praising.
A. Who B. Anyone C. Whoever D. The person
12. Eat _____ you like and leave the others for _____ comes in late.
A. any; who B. every; whoever C. whichever; whoever D. either; whoever
13. ____ she couldn’t understand was _____ fewer and fewer students showed interest in her lessons.
A. What; why B. That; why C. What; because D. Why; that
14. It was ____ he said ___ disappointed me.
A. What; that B. That; that C. What; what D. That;what
15. It was ordered that all the soldiers _______to the front.
A. should send B. must be sent C. should be sent D. must go
16. The true value of life is not in ______, but _______.
A. which we get; what give we B. what we get; what we give
C. which do we get; what do we give D. how we get; that we give
17. We are all for your proposal that the discussion _______.
A. be put off B. was put off C. should put off D. is to be put off
18. Go and get your coat.It's ____ you left it.
A. where B. there C. here where D. where there
19. Sarah hopes to become a friend of ______ shares her interests.
A. anyone B. whomever C. whoever D. no matter who
20. You can’t imagine ______ when they received these nice Christmas presents.
A. how they were excited B. how excited they were
C. how excited were they D. they were how excited
Keys: 1---5 A A ABA 6---10 CDABA 11----15 CCAA C 16---20 BAACB

英语语法名词性从句思维导图
英语语法:名词性从句最详分析
名词性从句是由if, whether, that 和各种疑问词充当连接词所引导的从句,其功同名词一样。

一、主语从句
主语从句是在复合句中充当主语的从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾。
1. It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
It 作形式主语代替主语从句,主要是为了平衡句子结构,主语从句的连接词没有变化。而it引导的强调句则是对句子某一部分进行强调,无论强调的是什么成分,都可用连词that。被强调部分指人是也可用who/whom。例如:
It is a pity that you didn't go to see the film.
It doesn't interest me whether you succeed or not.
It is in the morning that the murder took place.
It is John that broke the window.
2. 用it 作形式主语的结构
(1) It is +名词+从句
It is a fact that …事实是…
It is an honor that…非常荣幸
It is common knowledge that…是常识
(2) it is +形容词+从句
It is natural that…很自然…
It is strange that…奇怪的是…
(3) it is +不及物动词+从句
It seems that…似乎…
It happened that…碰巧…
(4) it +过去分词+从句
It is reported that…据报道…
It has been proved that…已证实…
3. 主语从句不可位于句首的五种情况
(1) if 引导的主语从句不可居于复合句句首。
(2) It is said , (reported) …结构中的主语从句不可提前。例如:
It is said that President Jingo will visit our school next week. (right)
That President Jiang will visit our school next week is said. (wrong)
(3) It happens…, It occurs… 结构中的主语从句不可提前。例如:
It occurred to him that he failed in the examination. (right)
That he failed in the examination occurred to him. (wrong)
(4) It doesn't matter how/whether …结构中的主语从句不可提前。例如:
It doesn't matter whether he is wrong or not. (right)
Whether he is wrong or not doesn't matter. (wrong)
(5) 含主语从句的复合句是疑问句时,主语从句不可提前。例如:
Is it likely that it will rain in the evening? (right)
Is that will rain in the evening likely? (wrong)
4. What 与that 在引导主语从句时的区别
What 引导主语从句时在句时在从句中充当句子成分,如主语.宾语.表语,而that 则不然。例如:
1) What you said yesterday is right.
2) That she is still alive is a consolation.
二、宾语从句
宾语从句就是在复合句中作宾语的名词性从句,通常放在主句谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。
1. 作动词的宾语
(1) 由that引导的宾语从句(that 通常可以省略),例如:
I heard that be joined the army.
(2) 由what, whether (if) 引导的宾语从句,例如:
1) She did not know what had happened.
2) I wonder whether you can change this note for me.
(3) 动词+间接宾语+宾语从句。例如:
She told me that she would accept my invitation.
2. 作介词的宾语
例如:Our success depends upon how well we can cooperate with one another.
3. 作形容词的宾语
例如:I am afraid (that) I've made a mistake.
That 引导的从句常跟在下列形容词后作宾语:
Anxious, aware, certain, confident, convinced, determined, glad, proud, surprised, worried, sorry, thankful, ashamed, disappointed, annoyed, pleased, hurt, satisfied, content 等。也可以将此类词后的that 从句的看作原因状语从句。
4. It 可以作为形式宾语
It 不仅可以作为形式主语,还可以作为形式宾语而真正的宾语that 从句则放在句尾,特别是在带复合宾语的句子中。 例如:
We heard it that she would get married next month..
5. 后边不能直接跟that 从句的动词
这类动词有Allow, refuse, let, like, cause, force, admire, condemn, celebrate, dislike, love, help, take, forgive等。这类词后可以用不定式或动名词作宾语,但不可以用that引导的宾语从句。例如:
I admire their winning the match. (right)
I admire that they won the match. (wrong)
6. 不可用that从句作直接宾语的动词
有些动词不可用于“动词+间接宾语+that从句“结构中,常见的有Envy, order, accuse, refuse, impress, forgive, blame, denounce, advise, congratulate等。例如:
He impressed the manager as an honest man. (right)
He impressed the manager that he was an honest man. (wrong)
7. 否定的转移
若主句谓语动词为Think, consider, wuppose, believe, expect, fancy, guess, imagine等,其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,一般要把否定词转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。例如:
I don't think this dress fits you well.(我认为这件衣服不适合你穿。)
三、表语从句
表语从句在复合句中作表语的名词性从句,表语是用来说明主语的身份、性质、品性、特征和状态的,表语常由名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式、动词的-ing、从句来充当,它常位于系动词(be, become, appear, seem,look,sound,feel,get,smell等词)之后。
引导表语从句的词有连词that, whether,连接代词和连接副词,关系代词型what,以及as if, as though, because等连词。
1. 由that引导
The fact is that he doesn’t really try. 事实是他没有做真正的努力。
The trouble is that I have lost his address. 麻烦的是我把他的地址丢了。
My suggestion is that we should tell him. 我的建议是我们应该告诉他。
His sole requirement was (is) that the system work. 他唯一的要求是这个制度能起作用。
My idea is that we should start making preparations right now. 我的意见是我们马上就开始做准备工作。
【连词that的省略问题】
引导表语从句的that通常不省略,但在口语或非正式文体中有时也可省略:
My idea is (that) we should do it right away. 我的意见是我们应该马上干。
The trouble is (that) he is ill. 糟糕的是他病了。
2. 由whether引导
The question is whether the film is worth seeing. 问题是这部电影是否值得看。
【注意】whether 可引导表语从句,但与之同义的if却通常不用于引导表语从句。
3. 由连接代词引导
You are not who I thought you were. 你已不是我过去所想像的人。
The problem is who we can get to replace her. 问题是我们能找到谁去替换她呢。
The question is who (m) we should trust. 问题是我们应当相信谁。
What I want to know is which road we should take. 我想知道的是我们应走哪条路。
4. 由连接副词引导
The problem is how we can find him. 问题是我们如何找到他。
That was when I was fifteen. 这是我15岁时发生的事。
That’s where I first met her. 那就是我第一次遇见她的地方。
That’s why he didn’t come. 这就是他没有来的缘故。
That’s why I object to the plan. 这就是我反对这个计划的原因。
That’s where you are wrong. 这就是你不对的地方。
5. 由关系代词型what引导
That’s what I want to stress. 这是我想强调的。
That’s what we are here for. 我们来这里就为了这个。
Fame and personal gain is what they’re after. 他们追求的.是名利。
He is no longer what he was. 他已经不是以前的他了。
6. 由as if / as though引导
It isn’t as if you were going away for ever. 又不是你离开不回来了。
Now it was as though she had known Millie for years. 现在好像她认识米莉已有好多年了似的。
It is not as though we were poor. 又不是我们家里穷。
7. 由because引导
It is because I love you too much. 那是因为我太爱你了。
That’s because you can’t appreciate music. 这是因为你不能欣赏音乐。
If I’m a bit sleepy, it’s because I was upall night. 如果我有点困,是因为一夜没睡。
It's because I passed a slip of paper for John to Helen in class. 这是因为我在上课中替约翰传纸条给海伦。
【注意】because 可引导表语从句,但与之同义的since, as, for等也不用于引导表语从句。
四、同位语从句
同位语从句指的是在复合句中充当同位语的从句,属于名词性从句的范畴,同位语从句用来对其前面的抽象名词进行解释说明,被解释说明的词和同位语在逻辑上是主表关系。
引导同位语从句的词语通常有连词that,whether,连接代词和连接副词等。
1. 由that引导
We heard the news that our team had won. 我们听到消息说我们队赢了。
They were worried over the fact that you were sick. 他们为你生病发愁。
The news that we are having a holiday tomorrow is not true. 明天放假的消息不实。
I’ve come to the conclusion that it was unwise to do that. 我得出结论这样做是不明智的。
The fact that the money has gone does not mean it was stolen. 那笔钱不见了这一事实并不意味着是被偷了。
He referred to Copernicus’ statement that the earth moves round the sun. 他提到了哥白尼关于地球绕太阳转的说法。
【注意1】 在某些名词(如demand, wish, suggestion, resolution等)后面的同位语从句要用虚拟语气。 如:
They were faced with the demand that this tax be abolished. 他们面对废除这个税的要求。
They expressed the wish that she accept the award. 他们表示希望她接受这笔奖金。
There was a suggestion that Brown should be dropped from the team. 有一项建议是布朗应该离队。
The suggestion that the new rule be adopted came from the chairman. 采纳新规则的建议是主席提出的。
The resolution that women be allowed to join the society was carried. 允许妇女参加这个协会的决议通过了。
I can understand their eagerness that you should be the main speaker. 我理解他们希望你作主要发言人的殷切心情。
【注意2】 引导同位语从句的连词that通常不省略,但在非正式文体中也可以省去。 如:
He gabbed his suitcase and gave the impression he was boarding the Tokyo plane. 他拿起了手提箱,给人的印象是他要登上飞往东京的飞机了。
2. 由whether引导
There is some doubt whether he will come. 他是否会来还不一定。
Answer my question whether you are coming. 你回答我的问题:你来不来。
The question whether it is right or wrong depends on the result. 这个是对还是错要看结果。
We are not investigating the question whether he is trustworthy. 我们不是在调查他是否可以信任的问题。
【注意】 whether 可引导同位语从句,但if不能引导同位语从句。
3. 由连接代词引导
Have you any idea what time it starts? 你知道什么时候开始吗?
From 1985-90 I was an instructor at the regional party headquarters. After that I went back to work in a factory. Then I had no idea what a casino was. 从1985年到1990年我是地方党部的教员。随后我回到一家工厂工作。当时我不知道赌场是什么样的地方。
4. 由连接副词引导
I have no idea when he will come back. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
It is a question how he did it. 那是一个他如何做的问题。
He had no idea why she left. 他不知道她为什么离开。
You have no idea how worried I was! 你不知道我多着急!
【关于分离同位语从句】
有时同位语从句可以和同位的名词分开。 如:
The story goes that he beats his wife. 传说他打老婆。
The news got about that he had won a car in the lottery. 消息传开说他中彩得了一辆汽车。
The rumour spread that a new school would be built here. 谣传这里要盖一所新学校。
Report has it that the Smiths are leaving town. 有传言说史密斯一家要离开这座城市。
The thought came to him that maybe the enemy had fled the city. 他想到可能敌人已逃离这座城市。
The order soon came that all citizens should evacuate the village. 不久命令下来,所有居民都必须撤出村子。
;高中英语名词性从句和定语从句的语法总结详细一点吗
名词性从句是由if, whether, that 和各种疑问词充当连接词所引导的从句,其功同名词一样.
一.主语从句
主语从句是在复合句中充当主语的从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾.
1. It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
It 作形式主语代替主语从句,主要是为了平衡句子结构,主语从句的连接词没有变化.而it引导的强调句则是对句子某一部分进行强调,无论强调的是什么成分,都可用连词that.被强调部分指人是也可用who/whom.
2. 用it 作形式主语的结构
(1) It is +名词+从句
(2) it is +形容词+从句
(3) it is +不及物动词+从句
(4) it +过去分词+从句
3. 主语从句不可位于句首的五种情况
(1) if 引导的主语从句不可居于复合句句首.
(2) It is said , (reported) …结构中的主语从句不可提前.
(3) It happens…, It occurs… 结构中的主语从句不可提前.
(4) It doesn’t matter how/whether …结构中的主语从句不可提前.
(5) 含主语从句的复合句是疑问句时,主语从句不可提前.
4. What 与that 在引导主语从句时的区别
What 引导主语从句时在句时在从句中充当句子成分,如主语.宾语.表语,而that 则不然.
定语从句也称为关系从句或形容词性从句,由关系代词(who, whom, whose, which, that)或关系副词(as, when, where, why)等引导.关系词除了起引导作用外,还在从句中指代前面的先行词,并在从句中担任一定的成分.
一、限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句
定语从句就其与先行词的关系而言,可分为限定性定语从句和非限定性定语从句.限定性定语从句和先行词之间没有逗号,表示对先行词起修饰限制作用;而非限定性定语从句和先行词之间有逗号分开,是对先行词进行补充说明,相当于并列句.如:
He is the man who has strong personality. 他是个个性很强的人.(限定性定语从句)
My brother, who works abroad, is coming next week. 我哥哥在国外工作,他下周将回来.(非限定性定语从句)
注:1. 非限定性定语从句不能用that来引导,一般用which,as或who(指人).用which或as引导时,既可以修饰主句的部分内容,也可修饰主句的全部内容.如:
He spoke confidently, which impressed me most. (which指代整个主句,在从句中作主语)
2. as引导的非限定性定语从句既可以放在主句之前,也可以放在主句之后,但which或who引导的非限定性定语从句不能放在主句之前.如:
As we all know, the moon is a satellite of the earth.
The large area is covered with thick snow, which affects people's life greatly.
3. 在限定性定语从句中,关系代词作宾语时可以省略;但在非限定性定语从句中,关系代词作宾语时不能省略.如:
The film (which) I saw last night is about a young teacher. (which可以省去)
She introduced me to her husband, whom I hadn’t met before. (whom不能省去)
二、通常只用关系代词that,不用 which,who或whom的几种情况
1. 当先行词是all, everything, nothing, something, anything, little, much, none, few等时.如:
All that you want are here.
2. 当先行词被all, no, some, any, every, a few, a little, much, only, very等修饰时.如:
There is no person that doesn’t make mistakes.
3. 当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时.如:
This is the best film that I have ever seen.
4. 当出现两个或两个以上的先行词,并同时兼指人和物时.如:
We are talking about the people and countries that we have visited.
5. 当主句是以which 或 who 开头的特殊疑问句时.如:
Who is the person that is standing over there?
6. 当定语从句为there be 句型时,关系代词只能用that,但经常可以省略.如:
I know the difference (that) there is between you.
7. 当关系代词在从句中作表语时,常用that.如:
He does not seem to be the man that he was. 他似乎和过去不一样了.
三、as 与其他词连用引导的定语从句
as 引导定语从句时,可指人也可指物,通常与the same,such,so等连用,形式为:the same… as,such… as,as …as,so… as.As在定语从句中可作主语、宾语、表语等.如:
She knew he felt just the same as she did. 她知道他的感觉与她自己的一样.(as代替事,作宾语)
I lend you such books as will interest you. 我借给你使你感兴趣的书.(as代替物,作主语)
注:the same… as 和the same… that的用法不同.as引导的定语从句表示其内容与主句所讲的事物“相似”,指同类事物;that引导的定语从句表示其内容与主句所讲的事物是“同一个”,指同一事物.如:
This is the same pen as I lost yesterday. 这和我昨天丢的笔一样.(类似的笔)
This is the same pen that I lost yesterday. 这支笔就是我昨天丢的那支.(同一支笔)
四、“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
在“介词+which/whom”结构中,介词的选择取决于三种情况:
1.定语从句中谓语动词或表语的搭配.如:
This is the college in which I am studying.
He is the man about whom we are talking.
2.先行词与介词的习惯搭配.如:
The speed at which the machine operates is shown on the meter. 仪表上显示出这台机器运转的速度.
3.当定语从句为最高级时只能用of which; 否则用其他介词.如:
I have five dictionaries of which Longman Dictionary is the best.
I have five dictionaries among which Longman Dictionary is published in UK.
注:不可拆分的动词短语介词不能提前,如put up with;有的短语可能有不同的介词搭配,此时需要根据上下文来确定.如:be familiar with/to,compare with/to等.
有时为表意清楚,还可以在关系副词where/ when前加介词from, to等.如:
China is the birthplace of kites, from where kite flying spread to Japan, Korea, Thailand and India. 中国是风筝的故乡,从这里,放风筝的运动传到了日本、韩国、泰国和印度.
以上就是关于名词性从句的变化规则 ,英语名词性从句思维导图的全部内容,以及名词性从句的变化规则 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

