本文目录
英语动词有多少种形式
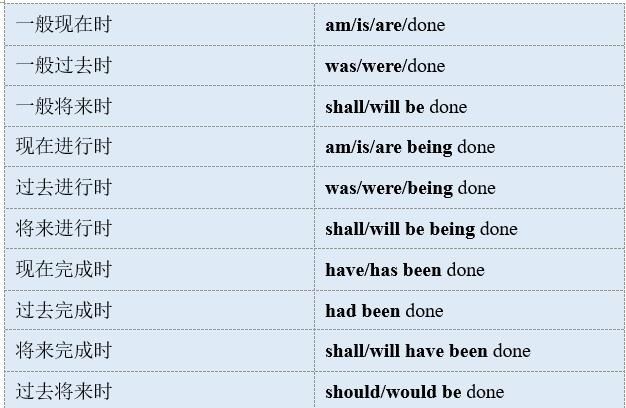
英语中总共有16个时态:
现在式:一般时(例:he works hard表示他工作努力)进行时(例:he is reading表示他正在阅读)完成时(例:he have finished it表示他已完成了)完成进行时(例:he have been writting it for two hours表示他已经写了两个小时了)
过去式:一般时(例:he worked hard表示他过去工作很努力)进行时(例:he was reading last night表示他昨晚在阅读)完成时(例:he had finished it since you arrived.表示在你到达之前他已完成)完成进行时(例:he had been writting it表示他过去就已经在写了)
将来式:一般时(例:he will work hard表示他将努力工作)进行时(例:he will be reading表示他将会阅读的)完成时(例:he will have finished it by the time of tomorrow表示明天之前他将完成)完成进行时(例:he will have been staying there for ten years by the time of next month表示到下个月,他将呆在那儿十年了)
过去将来式 一般时(例:he would work hard表示他过去工作努力)进行时(例:he would be working hard表示他过去一段时间在努力工作着)完成时(例:he would have finished it by the last month表示他到上个月为止就将完成任务)完成进行时(例:he would have been staying there for ten years by the time of last month表示到上个月为止,他在那里差不多呆了十年之久)区别与联系:现在一般时与现在完成时1.I come from Shanghai(上海人)I have come from Shanghai(从上海来)2.You read very well. (强调能力)Youve read very well. (强调一次刚完成的动作)3.I forget.(一时想不起来了)I have forgotten.(仍没想起来,可能已回忆起来了现在一般时与现在进行时1.He works hard.(强调始终如一)He is working hard.(强调现在)2.What do you do? (干什么工作的)What are you doing?(在干什么)3.Here comes the bus! (表高兴和欣慰) The bus is coming.(汽车到来的情景)现在完成时与过去一般时1.Ive seen him this morning.(还在上午的时间里)I saw him this morning.(时间已不在上午了)2.Whos opened the window? (窗户还在开着)Who opened the window? (与现在无关,窗户可能已关上)3.Have you ever heard him sing? (他可能不是爱唱歌)Did you ever hear him sing?(你曾听过他唱歌吗,他可能是歌唱家)过去完成时与过去一般时1.I came here after I finished middle school.(两个动作每间隔)I came here after I had finished middle school.(两个动作有间隔,强调先后概念)2.I waited till I saw him.I waited till I had seen him. (这两个句子差不多,过去完成时更普遍)3.We hoped he would come.(我们希望他来)We had hoped he would come.(我们本希望他来的)过去进行时与过去一般时1.I read a book yesterday. (书已看完)I was reading a book yesterday.(书尚未看完)2.The guests arrived.(客人已到)The guests were arriving.(客人陆续到达)3.He woke from a dream. (表示全醒)He was waking from a dream.(表示初醒)将来一般时与现在进行时1.Will he come? Is he coming?(时间发生的比较近)2.Shell have a baby. (表示肯定)Shes going to have a baby.(表示推测,计划)3.Ill see him this evening.(表示意愿)Im seeing him this evening.(表示打算,已有安排)现在一般时与过去一般式1.Do you wish to see me?Did you wish to see me?(表示婉转客气)2.Thats all I have to say.(我的话就这些)Thats all I had to say.(我要说的就这些)3. How do you like the film? (看电影过程中)How did you like the film?(看完电影后)现在完成时与现在完成进行时1.Someone has phoned you.(打了电话)Someone has been phoning you.(一直在打电话)2.Ive read the novel.(已读完)Ive been reading the novel.(还没读完)3.He has lived here for six weeks.He has been living here for six weeks. (区别不大,后者更口语化)现在一般时与过去完成时1.I hope that hell come.I had hoped he would come.(与事实相反)(经常这样用的词有:expect, think, intend, mean, suppose)
请采纳
动词的时态和语态课件
动词的时态:
1、动词的时态主要有:
一般现在时、现在进行时、现在完成时、现在完成进行时、一般过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、一般过去将来时、一般将来时、将来进行时和将来完成时等。
2、一般将来时的表达方式:
(1)一般将来时表示未来的动作或状态,常与表示将来的时间状语,如:tomorrow, next day, soon, in a month, in the future, next Sunday等连用。有时句中无时间状语,时间关系由上下文暗示。
(2)will do还表示临时的决定。
(3)在if, unless, before, after, until等引导的条件或时间状语从句中,从句用一般现在时代替一般将来时,而主句用一般将来时。
(4)“be going to+动词原形”表示打算、计划、决定要做的事或有迹象表明即将发生的动作或状态。
(5)“be+V-ing形式”表示按计划、安排即将发生的动作,这一结构常用于以下动词,如:come, go, leave, arrive, return, fly, meet, see, do, have, get等。
(6)“be about to+动词原形”表示打算或安排即将发生的动作。它一般不与表示时间的副词或其他时间状语连用。
(7)“be to+动词原形”表示按计划、安排即将发生的动作。
(8)一般现在时表示按时刻表或根据规定将要发生的动作,这一结构常用于表示位移的动词,如:come, go, leave, start, begin, take off, set off等。

动词的语态:
1、一般现在时的被动语态:
is/am/are+V-ed。例如:English is widely spoken all over the world.
2、一般过去时的被动语态:
was/were+V-ed。例如:The underground was built five years ago.
3、一般将来时的被动语态:
①will/shall be+V-ed。例如:
The decision will be made at the meeting tomorrow.
We shall be punished if we break the rule.
②be going to be+V-ed。例如:The problem is going to be discussed at the meeting tomorrow.
③be to be+V-ed。例如:The sports meet is to be held on April 20.
英语中动词的时态有哪些
英语中不同时间和方式发生的动作或状态要用谓语动词的不同形式来表示,这种表示动作或状态发生时间和方式的动词形式称作动词时态。时间主要有四个主要部分,即现在、过去、将来和过去将来。动作方面也有四种,即一般、完成、进行和完成进行。把这些时间和动作方面结合在一起就构成16种动词时态。(以play为例)具体表述如下:
1、一般现在时(We
play);
2、一般过去时(We
palyed);
3、一般将来时(We
will
play);
4、一般过去将来时(We
would
play);
5、现在进行时(We
are
playing);
6、过去进行时(We
were
playing);
7、将来进行时(We
will
be
playing);
8、过去将来进行时(We
would
be
playing);
9、现在完成时(We
have
played);
10、过去完成时(We
had
played);
11、将来完成时(We
will
have
played);
12、过去将来完成时(We
would
have
played);
13、现在完成进行时(We
have
been
playing);
14、过去完成进行时(We
had
been
playing);
15、将来完成进行时(We
will
have
been
playing);
16、过去将来完成进行时(We
would
have
been
playing)。
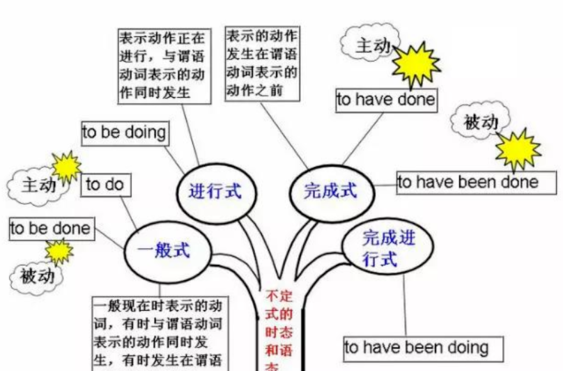
其实是英语动词的时和体.时有现在,过去,将来和过去将来;体有一般,完成,进行和完成进行.而语态有2种,即主动和被动.
动词的时态与语态
1、表示的意思不同:时态是一种动词形式,不同的时态用以表示不同的时间与方式。 是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式;
语态表示动作与执行者和承受者之间的关系.语态与动作的时间没有关系。
2、分类不同:语态分主动和被动,时态有现在时,过去时,将来时,完成时等16种。
3、用法不同:时态是在各种时间条件下的动词形式;语态是用以说明主语与谓语动词之间的关系。
扩展资料
时态的转换
方式
一般过去时与现在完成时的转换
请看:
A. He joined the League two years ago.
B. He has been in the League for two years.
C. It is two years since he joined the League.
D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
一般现在时与现在进行时的转换
Peter is at work,but Mike is at play.
Peter is working,but Mike is playing.
现在进行时与一般将来时的转换
请看:
The train is leaving soon.
The train will leave soon.
规则
英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
一般过去时与现在完成时的转换
在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能。但是,可用别的表达方式:
1、瞬间动词用于“一段时间 + ago”的一般过去时的句型中;
2、瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用;
3、瞬间动词用于“It is + 一段时间 + since + 一般过去时”的句型,请看:
A. He joined the League two years ago.
B. He has been in the League for two years.
C. It is two years since he joined the League.
D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
一般现在时与现在进行时的转换
在一般现在时中,at加上名词表示“处于某种状态”,如at work(在工作),at school(上学、上课)等。此短语可与进行时态转换。请看:
Peter is at work,but Mike is at play.
Peter is working,but Mike is playing.
现在进行时与一般将来时的转换
在现在进行时态中go,come,leave,start,arrive等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作。如:I am coming,Mum! 意为“我就来,妈妈!”请看:
The train is leaving soon.
The train will leave soon.
“be going to+动词原形”与“will(shall)+动词原形”结构的转换
“be going to+动词原形”、表示打算、计划要做的事;将来时“will(shall)+动词原形”结构在书面语中,当主语为第一人称时,常用助动词shall。在口语中,所有人称都可以用will。请看:
We are going to visit the Great Wall next Sunday.
We shall visit the Great Wall next Sunday.
参考资料来源:百度百科-时态语态
参考资料来源:百度百科-时态
以上就是关于动词时态和他们的形式 ,英语动词有多少种形式的全部内容,以及动词时态和他们的形式 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
