一说起倒装句语序结构 网上有很多解释,那么,就有必要说一下了,倒装句是什么结构?和倒装句英语结构是什么?倒装句语序结构 的内容,让大家更深入了解倒装句详解,来了解了解。
倒装句语序结构 :倒装句英语结构
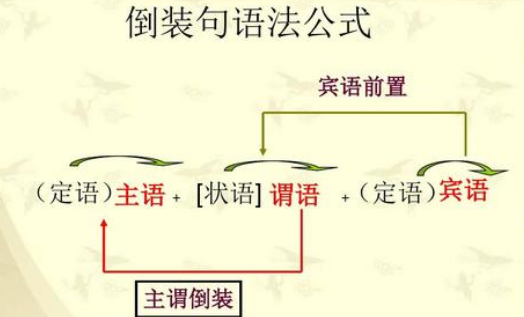
构成:主语和谓语是句子的核心,它们之间有两种语序:主语在谓语之前称为自然语序(Natural Order);主语在谓语之后则称为倒装语序(Inverted Order)。而倒装语序中又有完全倒装(Full Inversion)和部分倒装(Partial Inversion)。
在现实的语言实践中,由于语法结构的要求,或是由于修辞的需要,往往要改变句子的自然语序,把一些本应置于主语之后的句子成分提到主语之前。称这种语序的变化为“倒装语序”这样的倒装语序可能使句子的内在含义产生细微的、甚至明显的改变。
只有注意观察引起倒装的原因,才能更准确地理解句子的含义。为了使句子的某成分突出,我们还会使用强调,而倒装语序大多都用于强调。
英语句子的倒装一是由于语法结构的需要而进行的倒装,二是由于修辞的需要而进行的倒装。前一种情况,倒装是必须的,否则就会出现语法错误;后一种情况,倒装是选择性的,倒装与否只会产生表达效果上的差异。
倒装句语序结构 :倒装句的结构是什么
英语句子表达的基本语序是“主语+谓语”。但在实际应用中,因语法结构的需要,或是为了强调,常把谓语移到主语之前,称为倒装。

倒装句语序结构 :倒装句英语结构是什么
倒装语序分为全部倒装和部分倒装,全部倒装结构是谓语动词提前至主语之前,部分倒装结构是助动词或情态动词提至主语之前,而谓语动词位置不变。
具有“地点”意义的副词、时间意义的副词,以及能表移动方向的副词放在句首,句子的主语是名词,谓语是连系动词或表示“位置移动”的单个不及物动词时,该动词放在主语前面。
具有“方位”意义的介词短语或副词短语在句中作状语或表语放在句首,谓语是连系动词be,以及表示“位于、存在”或“位置移动”的单个不及物动词时,该动词放在主语前面。

一、全部倒装:
谓语动词提前至主语之前为全部倒装。
1、当首句为方位或时间副词,谓语动词为go,come等时通常用全部倒装。
2、如果句首出现了地点状语,句子也可以进行全部倒装。
3、当句子中出现分词结构的时候,可以把现在分词或过去分词和地点状语联系在一起放在句首,把be动词留在中间当作谓语动词,主语放在后面。
二、部分倒装:
助动词或情态动词提至主语之前,谓语动词位置不变,即为部分倒装。
1、当句首状语为否定词或带有否定意义的词语时,这个句子就需要部分倒装。
2、当句首为only加状语的时候,这个句子需要部分倒装。
3、so.....that结构中的so位于句首时,常引起部分倒装。
4、句子开头的as处在第二个单词的位置上,表示虽然的意思时,用部分倒装。
5、常见的固定搭配结构中需要用倒装的情况。
倒装句语序结构 :倒装句详解
一、部分倒装
否定副词位于句首时的倒装 在正式文体中,never, seldom, rarely, little, hardly, scarcely, no sooner, no longer, nowhere 等含有否定意义的副词若位于句首,则其后要用部分倒装:
I shall never forgive him. / Never shall I forgive him. 我永远不会宽恕他。
He seldom goes out for dinner. / Seldom does he go out for dinner. 他很少出去吃饭。
She hardly has time to listen to music. / Hardly does she have time to listen to music. 她几乎没时间听音乐。
He little realizes how important this meeting is. / Little does he realize how important this meeting is. 他不甚明白这个会议的重要性。
We had no sooner reached the airport than the plane took off. / No sooner had we reached the airport than the plane took off. 我们刚到机场,飞机就起飞了。
【注意】
(1) 对于not…until句型,当not until…位于句首时,其后的主句要用倒装语序:
He didn’t leave the room until the rain stopped. / Not until the rain stopped did he leave the room. 雨停了之后他才离开这房间。
(2) 某些起副词作用的介词短语,由于含有否定词,若位于句首,其后要用部分倒装:
On no accounts must this switch be touched. 这个开关是绝不能触摸的。
In [Under] no circumstances will I lend money to him.无论如何我也不会再借钱给他了。
但是,in no time(立即,马上)位于句首时,其后无需用倒装语序:
In no time he worked out the problem. 他马上就算出了那道题。
“only+状语”位于句首时的倒装 当一个状语受副词only的修饰且置于句首时,其后用部分倒装语序:
Only then did he realize that he was wrong. 到那时他才意识到他错了。
Only in this way are you able to do it well. 你只有用这种方法才能把它做好。
Only when he returned home did he realize what had happened. 当他回到家里时,才知道出了什么事。
“so+adj. / adv.”位于句首时的倒装 副词so后接形容词或副词位于句首时,其后用部分倒装:
So cold was the weather that we had to stay at home. 天气太冷,我们只好呆在家里。
So fast does light travel that we can hardly imagine its speed. 光速很快,我们几乎没法想像它的速度。
So sudden was the attack that we had no time to escape. 袭击来得非常突然,我们来不及逃跑。
“so+助动词+主语”倒装 当要表示前面提出的某一肯定的情况也同样适合于后者,通常就要用“So+助动词+主语”这种倒装结构:
You are young and so am I. 你年轻,我也年轻。
She likes music and so do I. 她喜欢音乐,我也喜欢。
If he can do it, so can I. 要是他能做此事,我也能。
【注意】
(1) 若前面提出某一否定的情况,要表示后者也属于同样的否定情况,则应将其中的so改为neither或nor:
You aren’t young and neither am I. 你不年轻,我也不年轻。
She hasn’t read it and nor have I. 她没有读它,我也没有读。
(2) 注意该结构与表示强调或同意的“so+主语+特殊动词”结构的区别:
"It was cold yesterday." "So it was." “昨天很冷。”“的确很冷。”
"Father, you promised." "Well, so I did." “爸爸,你答应过的。”“嗯,是答应过。”
由not only…but also引出的倒装 当not only…but also位于句首引出句子时,not only 后的句子通常用部分倒装形式:
Not only is he a teacher, but he is also a poet. 他不仅是一位教师,而且是一位诗人。
Not only did he speak more correctly, but he spoke more easily. 不仅他讲得更正确,也讲得更不费劲了。
虚拟条件句的省略与倒装 当if引导的虚拟条件从句中含有had, were, should等时,如将if省略,则要将had, were, should等移到主语前,构成倒装句:
Had you come yesterday, you would have seen him.若你昨天来,你就会见到他了。
Should you require anything give me a ring. 如果需要什么,可以给我打电话。
Were it not for your help, I would still be homeless. 要不是你帮助,我会仍然无家可归。
【注意】省略if后提前的had不一定是助动词:
Had I money, I would buy it. 假若我有钱,我就会买它。
二、完全倒装
here 和there位于句首时的倒装 表示地点的here和 there位于句首时,其后用完全倒装形式。这类倒装句的谓语通常是动词be和come, go等表示移动或动态的不及物动词:
Here’s Tom. 汤姆在这里。
There’s Jim. 吉姆在那儿。
Here comes the bus. 公共汽车来了。
There goes the bell. 铃响了。
There goes the last train. 最后一班火车开走了。
【注意】
(1) 以上倒装句中的谓语动词come和go不能用进行时态,即不能说 Here is coming the bus。
(2) 若主语为代词,则不倒装:
Here I am. 我在这儿。/ 我来了。
Here it comes. 它来了。
(3) 其中的动词有时也可能是stand, lie, live等表示状态的动词(表示存在):
There stood a desk against the wall. 靠墙放着一张书桌。
Once upon a time there lived a man known by the name of Beef. 从前有个人名叫比夫。
away和down等位于句首时的倒装 地点副词away, down, in, off, out, over, round, up 等位于句首时,其后用完全倒装语序。这类倒装句的谓语通常表示动态的不及物动词:
Away went the runners. 赛跑选手们跑远了。
Round and round flew the plane. 飞机盘旋着。
The door opened and in came Mr Smith. 门开了,史密斯先生进了来。
Down came the rain and up went the umbrellas. 下雨了,伞都撑起来了。
【注意】 若主语为人称代词,则不能用倒装:
Away he went. 他跑远了。
Down it came. 它掉了下来。
状语或表语位于句首时的倒装 为了保持句子平衡或使上下文衔接紧密,有时可将状语或表语置于句首,句中主语和谓语完全倒装:
Among these people was his friend Jim. 他的朋友吉姆就在这些人当中。
By the window sat a young man with a magazine in his hand. 窗户边坐着一个年轻人,手里拿着一本杂志。
【注意】 在表语置于句首的这类倒装结构中,要注意其中的谓语应与其后的主语保持一致,而不是与位于句首的表语保持一致。
比较: In the box was a cat. 箱子里是一只猫。 In the box were some cats. 箱子里是一些猫。
分词和不定式置于句首的倒装 有时为了强调,可将谓语部分的现在分词、过去分词或不定式置于句首,从而构成倒装:
Buried in the sands was an ancient village. 一个古老的村庄被埋在这沙土之中。
Standing beside the table was his wife. 站在桌旁的是他的妻子。
To be carefully considered are the following questions. 下列问题要仔细考虑。
涉及only的倒装及考题分析
按英语习惯同,当“only+状语”位于句首时,其后句子要用部分倒装。
如: Only then did he realize that he was wrong. 到那时他才意识到他错了。
Only in this way are you able to do it well. 你只有用这种方法才能把它做好。
Only in this way can our honour be saved. 只有这样,才能保住我们的荣誉。
Only then did I understand what she meant. 只有到那时我才明白她的意思。
Only after her death was I able to appreciate her. 只有到她死后我才认识到她的价值。
Only when he returned home did he realize what had happened. 当他回到家里时,才知道出了什么事。
Only in this way can we learn English. 只有这样才能学会英语。
The pilot reassured the passengers. Only then did I realize how dangerous the situation had been. 飞机驾驶员要乘客们放心,这时我才明白刚才的情况有多危险。
Only by shouting was he able to make himself heard. 他只有叫喊才能让别人听到他。
Only when we landed did we see how badly the plane had been damaged. 我们只是在着陆之后才看到飞机损坏的严重程度。
Only on one point do I agree with you. 只有一点,我同意你的说法。
【典型考题】
(答案分别为DC)
1. Only then _________ how much damage had been caused.
A. she realized B. she had realizedC. had she realized D. did she realize
2.Only after my friend came _________.
A. did the computer repaired B. be repaired the computer
C. was the computer repaired D. the computer was repaired
特别说明:有时命题者不是利用位于句首的“only+状语”来考查倒装,而是倒过来,利用给定的倒装结构来考查对only的选择。
如下面一题(答案选A): _________ by keeping down costs will Power Data hold its advantage over other companies.
A. Only B. Just C. Still D. Yet
涉及副词so的两类常考倒装
这类倒装主要见于以下两种情形:
1. 当副词so后接形容词或副词位于句首时,其后要用部分倒装。
如: So cold was the weather that we had to stay at home. 天气太冷,我们只好呆在家里。
So fast does light travel that we can hardly imagine its speed. 光速很快,我们几乎没法想象它的速度。
So sudden was the attack that we had no time to escape. 袭击来得非常突然,我们来不及逃跑。
2. 当要表示前面提出的某一肯定的情况也同样适合于后者,通常就要用“So+助动词+主语”这种倒装结构。
如: You are young and so am I. 你年轻,我也年轻。
She likes music and so do I. 她喜欢音乐,我也喜欢。
If he can do it, so can I. 要是他能做此事,我也能。
【典型考题】(答案分别为BBA)
1. So difficult _________ it to work out the problem that I decided to ask Tom for advice.
A. I did find B. did I find C. I have found D. have I found
2. _________ about wild plants that they decided to make a trip to Madagascar for further research.
A. so curious the couple was B. So curious were the couple
C. How curious the couple were D. The couple was such curious
3. —It’s burning hot today, isn’t it?—Yes. _________ yesterday. A. So was it B. So it was C. So it is D. So is it
特别说明:
(1) 若前面提出某一否定的情况,要表示后者也属于同样的否定情况,则应将其中的so改为neither或nor。
如: You aren’t young and neither am I. 你不年轻,我也不年轻。 She hasn’t read it and nor have I. 她没有读它,我也没有读。
请看考题(答案选D): Mary never does any reading in the evening, _________.
A. so does John B. John does too
C. John doesn’t too D. nor does John
(2) 注意“So+助动词+主语”与表示强调或同意的“So+主语+助动词”的区别。
如: “It was cold yesterday.” “So it was.” “昨天很冷。”“的确很冷。”
请看考题(答案分别为CD):
1. — Maggie had a wonderful time at the party. —_________, and so did I.
A. So she had B. So had she C. So she did D. So did she
2.—Father, you promised! —Well, _________. But it was you who didn’t keep your word first.
A. so was I B. so did I C. so I was D. so I did
倒装句中的主谓一致
在“副词here, there, now, then, up, down, in, out, away等、作状语或表语的介词短语或分词短语+谓语动词+主语”的倒装结构中,谓语动词的数由动词后面的主语决定
如: On the wall hang two maps. 墙上挂着两张地图。
On the wall hangs a world of map. 墙上挂着一张世界地图。
Here is your coat. 这是你的外套。
Here are your running-shoes. 这是你的跑鞋。
Such is the result. 结果就是这样。
Such are the results. 这就是结果。
副词后的倒装
here 和 there 之后以及诸如 back, down, off, up 等一类的副词小品词之后,名词主语一般置于谓语之后。这类副词常与诸如 come 和 go 等转移动词一起连用。
如: Here comes a taxi! There goes the last train! 有辆出租车来了! 最后一班火车开走了! (注意这里不可用进行时)
Down came the rain and up went the umbrellas. 下雨了,伞都撑了起来。
当我们给人东西或确定位置时,这种倒装常用在be之后(主语往往是复数)。
如: Here’s a cup of tea for you. 给你一杯茶。(给东西)
Here’s your letters. 这儿有你的信。(给与或指明)
There’s (重读) Johnny smith. 约翰尼·史密斯在那儿。(确定位置)
主语如是代词则不倒装。
如: Here it comes. 它来了。
There she goes. 她走了。
Up it went. 它上去了。
Here you are. 给你。
There she is. 她在那儿。

以上就是关于倒装句语序结构 ,倒装句详解的全部内容,以及倒装句语序结构 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
