关于todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 想知道的人很多,那么,就有必要说一下了,to do不定式怎样作主语,作宾语,作补语?说表语。做目的状语。和“to do”不定式在句子中的成分及用法是什么?todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 的内容,方便您深入了解常用to do不定式作宾语的动词要选择同一,来了解了解。
todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 :动词不定式做宾补跟to do的
后接不定式作宾补的动词
admit(承认),advise(建议),allow(允许), ask(请求), beg(请求), bribe(行贿),cause(导致),compel(迫使), command(命令),encourage(鼓励),expect(期望), forbid(禁止), force(迫使),get(使得),hate(憎恨),help(帮助),implore(恳求),induce(劝说),instruct(吩咐), invite(邀请),like(喜欢),oblige(强迫), order(命令),permit(允许), persuade(说服), remind(提醒), report(报告), request(要求), show(表现), teach(教), tell(告诉),tempt(诱惑), urge(敦促), want(想要),warn(警告),wish(希望)
He advised me to buy a computer. 他建议我买台电脑。
We expected him to arrive in time. 我们希望他及时到。
I usually help Mum do the housework on Saturdays. 星期六,我通常帮助妈妈做家务。
Please tell her not to make so much noise. 请告诉她别弄出那么多的响声。
另外,使役动词let, make, have和感官动词see, hear, feel, smell, listen to, notice, watch以及find等,后接不带to的不定式作宾补。
todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 :后接todo不定式作宾语的动词有哪些;后接动名词作宾语的动词有哪些越细越好最好是初二的
直接给你网址,里边有你想要的解释,

todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 :to do不定式怎样作主语
to do有名词词性又可以做非谓语所以能作主、宾、表、补、状。放在不同位置,做不同成分。
如To see is to believe. 主、表都可以。
I come here to help you. 表目的(也是补语)
就不一一举例了,知道词性,可以当什么成分就一目了然了。

todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 :todo都有什么用法
1. 不定式的用法------1.1 不定式作主语
不定式作主语,往往用it作形式主语,真正的主语不定式放至句子的后面。
例如:It's so nice to hear your voice. 听到你的声音真高兴。
It's necessary for you to lock the car when you do not use it.不用车的时候,锁车是有必要的。
It's very kind of you to help us. 他帮助我们,他真好。
It seemed selfish of him not to give them anything. 他不给他们任何东西,这显得太自私了。
但是,用不定式作主语的句子中还有一个不定式作表语时,不能用It is… to…的句型。另外,这样的句子,不能用动名词作表语。例如:
(对)To teach is to learn.
(错)It is to learn to teach.
(错)To teach is learning.
(错)Teaching is to learn.
典型例题
The chair looks rather hard, but in fact it is very comfortable to ___.
A. sit B. sit on C. be seat D. be sat on
答案:B. 如果不定式为不及物动词,其后应有必要的介词。当动词与介词连用时,常位于"形容词+动词不定式"结构的末尾。
1.1.1 不定式做主语 It's for sb/It's of sb to do sth
这样的句子中,由于表语形容词性质的不同,导致了不定式逻辑主语标志用for或of的区别。
1)for sb. 句型中的形容词一般为表示事物的特征特点,表示客观形式的形容词,如easy, hard, difficult, interesting, impossible等:例如:
It's very hard for him to study two languages. 对他来说学两门外语是很难的。
2)of sb句型中的形容词一般为表示性格,品德,心智能力,表示主观感情或态度的形容词,如good, kind, nice, clever, foolish, right。例如:
It's very nice of you to help me. 你来帮助我,你真是太好了。
1.2 不定式作宾语
1) 有些及物动词用不定式作宾语,结构为动词+不定式。例如:
afford aim agree arrange ask decide
bother care choose demand desire determine
elect endeavor hope fail help learn
long 渴望 mean manage offer plan pretend
refuse tend undertake expect hate intend
例如:
The driver failed to see the other car in time. 司机没能及时看见另一辆车。
He offered to help me. 他表示愿意帮助我。
2)有些动词除了可以用不定式作宾语,还用不定式作补语,即有动词+宾语+不定式的结构。例如:
ask choose expect help beg intend
like/love need prefer prepare want wish
例如:
I like to keep everything tidy. 我喜欢每件东西都保持整洁。
I like you to keep everything tidy. 我喜欢你使每件东西都保持整洁。
I want to speak to Tom. 我想和汤姆谈话。
I want you to speak to Tom. 我想让你和汤姆谈话。
3) 有些动词或动词词组可以用动词+疑问词+不定式的结构作宾语。例如:
decide know consider forget learn remember
show, wonder find out tell inquire explain
例如:
Please show us how to do that. 请演示给我们如何去做。
There are so many kinds of tape-recorders on sale that I don't knowwhich to buy.
有这么多的录音机,我都拿不定主意买哪一种。
1.3 不定式作表语
不定式可放在be动词后面,形成表语。例如:
My work is to clean the room every day. 我的工作是每天清扫房间。
His dream is to be a doctor. 他的梦想是成为一名医生。
1.4 不定式作定语
不定式做定语通常要放在被修饰的词后,往往表示未发生的动作。例如:
I have a lot of work to do. 我有许多事要做。
There was nothing to bring home that morning. 那天早上(他回家时)两手空空。
1.5 不定式作状语
1)目的状语
常用结构为to do , only to do(仅仅为了), in order to do, so as to do, so(such)… as to…(如此…以便…)。例如:
He ran so fast as to catch the first bus. 他飞快地跑以便赶上第一班车。
I come here only to say good-bye to you. 我来仅仅是向你告别。
2)作结果状语,可以表示没有预料到的或事与愿违的结果,不定式要放在句子后面。
I awoke to find my truck gone. 我醒来发现箱子不见了。
He searched the room only to find nothing. 他搜索了房间,没发现什么。
3)表原因
I'm glad to see you. 见到你很高兴。
She wept to see the sight. 她一看到这情形就哭了。
4)表示理由和条件
He must be a fool to say so.
You will do well to speak more carefully.
1.6 不定式作补语
1) 有些有动词+宾语+不定式的结构。例如:
动词 宾语 不定式
He reminded me to buy some eggs.
THAT-从句
He reminded me that I had to buy some eggs.
advise allow cause challenge command compel
drive 驱使 enable encourage forbid force impel
induce instruct invite like/love order permit
make let have want get warn
persuade request send tell train urge
例如;
Father will not allow us to play on the street. 父亲不让我们在街上玩耍。
The officer ordered his men to fire. 长官命令士兵开火。
注意:有些动词如make,have,get,want等可用不定式作做宾补,也可用分词作宾补。现在分词表达主动,也表达正在进行,过去分词表达被动。
2) 有些有动词+宾语+不定式的结构,不定式的动词往往是be,不定式一般可以省去。例如:
consider find believe think declare(声称) appoint
guess fancy(设想) guess judge imagine know
例如:
We believe him to be guilty. 我们相信他是有罪的。
We know him to be a fool. 我们知道他是个笨蛋。(to be 不能省去)
典型例题
Charles Babbage is generally considered ___ the first computer.
A. to invent B. inventing C. to have invented D. having invented
答案:C. 一般没有consider+宾语+be以外不定式的结构,也没有consider+宾语+doing的结构,排除A、B、D。consider用动词be以外的不定式作宾补时,一般要求用不定式的完成式,故选C。
3) 有些动词可以跟there +to be的结构。例如:
believe expect intend like love mean
prefer want wish understand
例如:
We didn't expect there to be so many people there. 我们没料到会有那么多人在那里。
You wouldn’t want there to be another war. 你不至于想让另外一场战争发生吧。
1.7 动词不定式的否定式
在不定式标志to前加上not。例如:
Tell him not to shut the window。让他别关窗。
She pretended not to see me when I passed by. 我走过的时候,她假装没看见。
典型例题
1)Mrs. Smith warned her daughter ___ after drinking.
A. never to drive B. to never driver C. never driving D. never drive
答案:A warn sb to do sth. 的否定形式为warn sb not to do sth. 此处用的是否定词never.
2)The boy wanted to ride his bicycle in the street,but his mother told him ____.
A. not to B. not to do C. not do it D. do not to
答案:A not to 为not to do it 的省略形式。可以只用to这个词,而不必重复整个不定式词组。及物动词do后应有宾语,因此也B,D不对。
2. 省略不定式符号“to”的情况
1) 情态动词 ( 除ought 外) 后。
She can't speak to you.
He should give her some money.
Shall I talk to him?
Would you like a cup of coffee?
I might stay another night in the hotel.
They must leave before 10.00 a.m.
2) 使役动词 let, have, make后,感官动词 see, watch, look at, notice , observe, hear, listen to, smell, feel, find 等后。
注意:被动语态中不能省去to。例如:
I saw him dance. 我看见他跳舞。
=He was seen to dance.
The boss made them work the whole night. 老板让他们整夜干活。
=They were made to work the whole night.
He saw her fall from the cliff.
We heard them close the door.
They saw us walk toward the lake.
She felt the spider crawl up her leg.
3) 使役动词 let, have, make后
Her parents let her stay out late.
Let's go to the cinema tonight.
You made me love you.
Don't make me study that boring grammar book!
4) would rather,had better句型后
We had better take some warm clothing.
She had better ask him not to come.
You'd better not smile at a crocodile!
We had better reserve a room in the hotel.
You'd better give me your address.
They had better work harder on their grammar!
5) Why… / why no…句型后
6) help 后可带to,也可不带to, help sb (to) do sth:
7) but和except后。but前是实义动词do时,后面出现的不定式不带to。
比较:He wants to do nothing but go out. 他只想出去玩。
He wants to believe anything but to take the medicine. 除了吃这药,他什么都信。
8) 由and, or和than连接的两个不定式,第二个to 可以省去:
9) 通常在discover, imagine, suppose, think等词后作宾补时,可以省去to be。例如:
He is supposed (to be) nice. 他应该是个好人。
典型例题
1) ---- I usually go there by train.
---- Why not ___ by boat for a change?
A. to try going B. trying to go C. to try and go D. try going
答案:D. why not 后面接不带to 的不定式,因此选D。
2) Paul doesn't have to be made ___. He always works hard.
A. learn B. to learn C. learned D. learning
答案:B. make后接不带to 的动词不定式,当其用于被动时,to 不可省略。
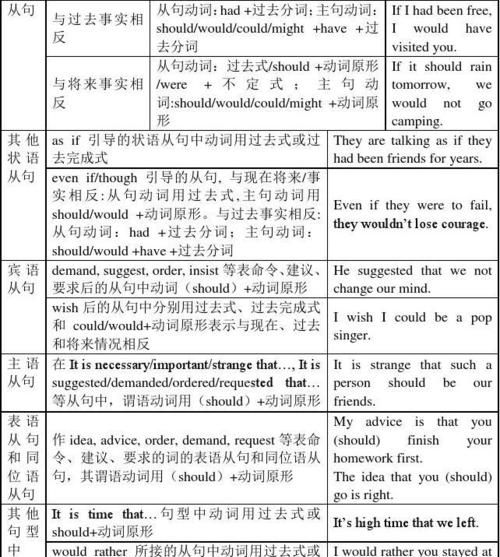
3. 不定式的时态和语态
1) 一般式表示的动词,有时与谓语动词表示的动作同时发生,有时发生在谓语动词的动作之后,例如:
He seems to know this. 他似乎知道这事。
I hope to see you again. = I hope that I'll see you again. 我希望再见到你。
2) 完成式:完成式表示的动作发生在谓语动词表示的动作之前,比如to have broken, to have seen, to have saved. 例如:
Someone must have broken the window and climbed in.
I would like to have seen the Taj Mahal when I was in India.
He pretended to have seen the film.
If I'd seen the ball I would have caught it.
3) 进行式表示动作正在进行,与谓语动词表示的动作同时发生。例如:
I'd really like to be swimming in a nice cool pool right now.
You must be joking!
I happened to be waiting for the bus when the accident happened.
4) 完成进行式表示动作从过去开始并延续至说话的时候: (to) have been + 现在分词 例如:
to have been crying
to have been waiting
to have been painting
The woman seemed to have been crying.
You must have been waiting for hours!
He pretended to have been painting all day.
5) 不定式的被动语态: (to) be + 被动式, 例如 to be given, to be shut, to be opened 例如:
I am expecting to be given a pay-rise next month.
These doors should be shut.
This window ought to be opened.
4. 不定式的特殊句型------4.1 too…to…
1)too…to 太…以至于…。例如:
He is too excited to speak. 他太激动了,说不出话来。
---- Can I help you ? 需要我帮忙吗?
---- Well, I'm afraid the box is too heavy for you to carry it, but thank you all the same.
不用了。这箱子太重,恐怕你搬不动, 但还是谢谢你。
2)如在too前有否定词,则整个句子用否定词表达肯定,too 后那个词表达一种委婉含义,意 为"不太"。例如:
It's never too late to mend. 改过不嫌晚。(谚语)
3)当too 前面有only, all, but时,意思是:非常… 等于very。例如:
I'm only too pleased to be able to help you. 能帮助你我非常高兴。
He was but too eager to get home. 他非常想回家。
4.2 so as to
1) 表示目的;它的否定式是so as not to do。例如:
Tom kept quiet about the accident so as not to lose his job.汤姆对事故保持沉默是为了不丢掉他的工作。
Go in quietly so as not to wake the baby.轻点进去,别惊醒了婴儿。
2) 表示结果。例如:
Would you be so kind as to tell me the time? 劳驾,现在几点了。
4.3 Why not
"Why not +动词原形"表达向某人提出建议,翻译为:"为什么不……?" "干吗不……?"。例如:
Why not take a holiday? 干吗不去度假?
以上就是关于todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 ,常用to do不定式作宾语的动词要选择同一的全部内容,以及todo不定式作宾语的固定搭配 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

