本文目录
语法填空情态动词
had better(常简略为'd better)是一固定词组,had better"最好",用于表示对别人的劝告、建议或表示一种愿望。其用法有以下几点:
一、had better后面必须跟动词原形。
had better后跟动词原形(即不带to的不定式),构成had better do sth.句型。
这里的had不能用have来替换。如:
You'd better go to hospital at once.你最好立即去医院看病。
Tom, you'd better go there today.汤姆,你最好今天去那儿。
二、主语不论是第几人称,句子不论是什么时态,都要用had better的形式。如:
Now you(he,we) had better listen to the teacher.你(他,我们)现在最好听老师讲。
三、had better可用于的时态。
1.had better用于指现在。如:
Now you had better listen to the radio.你现在最好听收音机。
You had better be quiet.你最好安静一些。
2.had better用于指将来。如:
You had better start tomorrow.你最好明天动身。
We had better buy the more expensive one. It will last much longer and so it will be cheaper in the end.我们最好还是买贵些的,它更经久耐用,所以到头来,它还是更便宜些。
3.had better用于进行式,表示讲话人提出建议时,动作正在进行。如:
We had better be watching the TV play.我们最好现在就看到电视剧。
We had better be starting back now.我们最好现在就动身回去。
4.had better + have + V-ed可表示"本该做而没有做的事"。如:
You had better have done it .如果你把那件事办妥就好了。(但实际上你没有那样做)
You had better have stayed with us .要是当时你和我们呆在一起多好啊。(实际上没有)
四、had better的否定式。如:
常用的否定形式是将否定副词not直接放在had better的后面。如:
You had better not miss the last bus.你最好不要错过末班公共汽车。
You had better not leave for Nanjing the day after tomorrow.你最好后天不要动身去南京。
注意:否定副词not绝不能放在had的后面。如:不能说:You hadn't better go.而应该说:You had better not go.
五、had better的疑问式。
had better通常不以普通疑问句的形式出现。但有时用于否定疑问句,常用Hadn't+主语+better...?结构,作为一种劝告形式,比肯定形式的语气更婉转一些。如:
Hadn't you better take an umbrella?你不认为该带一把伞吗?
Hadn't you better ask him first?你不认为该先问问他吗?
六、had better在反意疑问句中。
在反意疑问句中,疑问部分一般用"had+主语?",但有时可用"will you?"表示一种请求或建议。如:
You'd better not go out today, had you? 今天你最好不要外出,好吗?
I must stay at home this afternoon. You had better come to my house, will you?今天下午我必须留在家里,你最好来我家,好吗?
七、在祈使句中,had有时可以省略。如:
Better not do it .最好别做那事。
Better not wait for them.最好不要等他们。
八、had better的被动式。
You had better do it.->It had better be done.
You had better have done it.->It had better have been done.
九、had better在间接引语中的用法。
在直接引语变为间接引语的过程中,had better同第一人称或第三人称连用时,保持不变;had better同第二人称连用时,可以保持不变,也可用advise+宾语+不定式(宾补)来表示。如:
He said, "Ann had better hurry."->He said (that) Ann had better hurry.
He said, " I had better hurry."->He said (that) he had better hurry.
He said to me," You had better hurry." ->He said (that) I had better hurry.->He advised me to hurry.
十、had better在表示对别人劝告、建议时,不宜用于与陌生人、长辈及上级的交谈中。
对长辈说话时,最好不用had better。比较有礼貌的说法是:It might be better for you...;
It would be better for you...。如:
It might be better for you to help me,Grandpa.爷爷,您最好能帮我一下。
[练习]
下列各句都有一处错误,请改正。
1.You'd better to wait for me at the school gate.
2.I have better write to him now.
3.You had not better go there.
参考答案:1.去掉to。2.have应改为had。3.将not置于better后面。

初一英语情态动词专项训练
第六章 情态动词
一.概念:
情态动词是表示能力,义务,必须,猜测等说话人的语气或情态的动词.
二.相关知识点精讲:
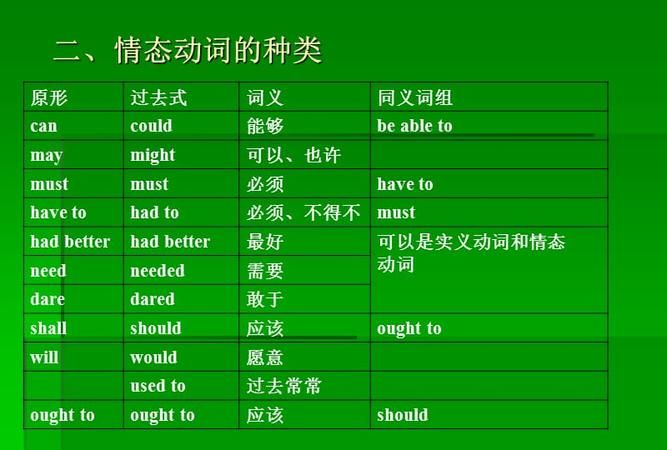
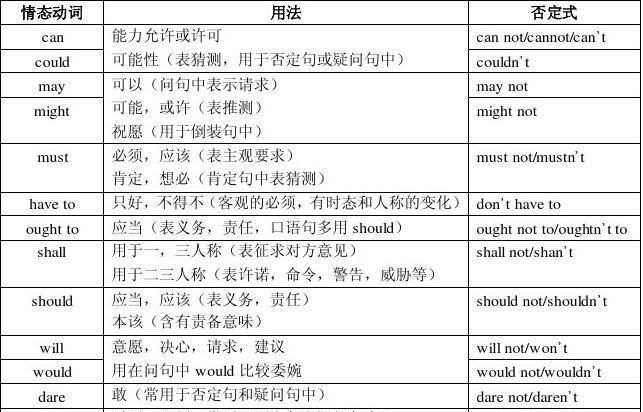
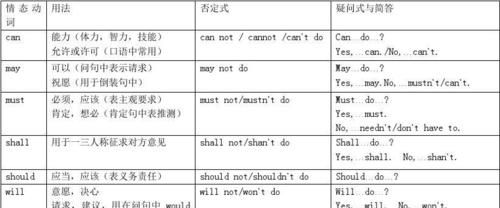
1.can
1)表能力
can表能力时意味着凭体力或脑力或技术等可以无甚阻力地去做某事。
I can climb this pole. 我能爬这根杆子。
He is only four , but he can read. 他只有4岁,但已认得字了。
Fire can’t destroy gold. 火烧不毁金子。
因为can不能和其他助动词连用,所以表示将来式时用will be able to
You will be able to skate after you have practiced it two or three times.
你练习两三次后就会溜冰了。
2)表可能性
多用于否定与疑问结构中,但也可用在肯定句中。
Can the news be true? 这消息可能是真的吗?
It can’t be true. 它不可能是真的。
What can he possibly mean? 他可能是什么意思?
can 用在肯定句中表示理论上的可能性(一时的可能)。
A horse in the center of London can cost a lot of money.
Attending the ball can be very exciting.
The road can be blocked. 这条路可能会不通的。
may 在肯定句中表示现实的可能性。
The road may be blocked. 这条路可能不通了。
3)表示允许(和may意思相近)常见于口语。
Can (May) I come in ? 我能进来吗?
Can I smoke here ? 我可以在这里抽烟吗?
2.could的用法
1)表过去的可能和许可,(多用于间接引语中)
At that time we thought the story could not be true.
那时我们认为所说的事不可能是真的。
Father said I could swim in the river.
爸爸说我可以在河里游泳。
2)表过去的能力
I could swim when I was only six.
我刚六岁就能游泳。
Could在肯定句中表示过去的能力时,常表抽象的一般的能力。
He could be very naughty when he was a child.
他小时候会是很顽皮的。
3)表“允许”。可表示委婉客气的提出问题或陈述看法
Could I use your bike?
Yes, you can.
他会记得那时吗?
I’m afraid I couldn’t give you an answer today.
恐怕我今天不能回答你。
The teacher said you could go to the store for sweets.
老师说你可以去商店买糖。
3)Could/can+have done 结构表示对过去发生的事情的“怀疑”或“不肯定”。 could 加完成式还用于肯定句时一般表过去可能完成而却未完成的动作。
Can they have won the basketball match?
他们赢了那场篮球赛吗?
What you referred to just now can have made her very sad.
你刚刚所谈到的可能令他很伤心。
You could have completed the task a little earlier.
你本来能早点完成任务的。(但事实上并没有提前完成任务)
I could have passed my examination easily but I made too many stupid mistakes.
我本可以轻易通过考试,但我犯了太多不该犯的错误。
如表具体做某一件事的能力时,则须用 be able to .
He was able to translate the article without a dictionary.
他可以不用词典翻译那篇文章。
Can表示一贯的能力 ,be able to表示客观能力和通过努力可以达到的能力
I can’t swim. But I am sure I will be able to swim through more practicing.
The fire spread through the hotel, but everyone was able to get out
When the boat sank he was able to swim to the bank
3.may 的用法
1)表示请求、可以、允许。
You may drive the tractor. 你可以开那台拖拉机。
2)当回答由may 引起的问题时,否定答语要用must not,表示“不许可”、“不应该”、“不行”。
May I come in?
Yes, you may.
No,you can’t
No, you may not .
No ,you mustn’t
No ,you’d better not.
3) may /might 推测性用法 可能
He may be right.
He may not come today (可能不)
He may /might come tomorrow.
, 注意: 1只用于肯定和否定句中,不用于疑问句中。
2 might 比may可能性更小
He might get a job.
He may get a job.
3 may no 可能不 can not不可能
He may not come
He can’t come
3)表建议(可和as well 连用)
You may(might)as well stay where you are.
你还是原地待着好。(may as well 有“还是……的好”的含义)
4)表祝愿
May you be happy!
might
1)表过去的“可能”和“允许”多用于间接引语。
She said that he might take her dictionary.
她说他可以拿她的词典去用。
除在间接引语中外,might一般不表示过去的“可能”与“许可”。表过去的“可能”可用could,表过去的“许可”可用were (was) allowed to。
2)表现在的“可能”,其可能性要比may小。
Electric irons could be dangerous; they might give you a severe shock.
电熨斗会有危险,它可能电着人。
3)may (might) + have +done 表示对过去发生行为的推测,含有“想必”、“也许是”的意思。
It may have been true. 这事也许是真的。
He might not have settled the question. 他可能尚未解决那个问题。
4.must 的主要用法。
1)表示必须、必要
We must do everything step by step .我们必须按部就班地做一切事情。
Why must you always bother me? 为什么你偏要打扰我呢。
2)must be + 表语的结构,通常表示猜测,含有“一定”之意。(只用在肯定句中)
He must be an honest boy. 他一定是个诚实的男孩。
This must be your room. 这一定是你的房间。
3)must 的否定式有两个:当回答由must引起的问题时,否定答复要用needn’t或don’t have to 表示“不必”、“无须”、“用不着”、“不一定”的意义。当表示“不应该”、“不许可”、“禁止”时,就用must not。
Must I go tomorrow?明天我必须去吗?
Yes, please.是的,请吧!
No , you needn’t. 不,你不必去。
4)must +have +过去分词的结构,常用在肯定句中,表示对过去发生行为的推测,含有“一定”、“准是”的意思。否定和疑问句用can。
She must have studied English before.她以前一定学过英语。
5.have to的含义与must是很接近的,只是have to 比较强调客观需要,must着重说明主观看法。
I must clean the room.(主观想法)
I have to clean the room.(客观需要)
另外,have to 能用于更多时态:
We had to be there at ten .我们得在十点钟到那里。
We will have to reconsider the whole thing.
这一切我们将不得不重新加以考虑。
have to 的否定式:don’t have to do 表示“不必做……”之意。
6.ought to 的用法
Ought to 后接动词原形,表义务,但不及must 那样具有信心,如:
You don’t look well. You ought to go to see the doctor.
你气色不好,应该去看病。
Ought to 用于否定句,其否定形式可缩略为oughtn’t ,如:
You oughtn’t to smoke so much. 你不应该抽这么多烟。
也可以用于疑问句,如:
Ought you to smoke so much?你应该抽这样多烟吗?
Ought to 在间接引语中表过去时形式不变,如:
He said you ought to tell the police.
他说你应该去报告警察。
7.shall的用法
1)用于第一人称征求对方的意见,如:
What shall I wear on the journey? 我路上穿什么好呢?
Shall we dance? 我们跳舞好吗?
2)shall 用于第二、三人称时表允诺,警告,命令,威胁(现已少见),如:
She shall get her share. 她可以得到她的一份。
You shall have it back tomorrow.你明天可以将它拿回。
情态动词should一般不应被认为是情态动词shall的过去式,主要用法有:
1)用于第一人称疑问句中询问对方的意愿,但语气较委婉温和,如:
What should we do now? 我们现在该怎么办?
2)表示应该、必须,常与must 换用。例如:
We should (must) master a foreign language at least.
我们应当至少掌握一门外语。
3)“should+be+表语”的结构,表示推测或惊奇。例如:
They should be back by now. 他们现在应该回来了吧。
I am sorry that she should be so careless. 我感到遗憾她竟会那样粗心。
4)“should+have+过去分词”的结构,表示过去该做而实际上尚未做的动作或行为;其否定则表示发生了不应该发生的行为。其同义结构“ought to have +过去分词”,表示过去“早应该”、“本当”之意,语气较强。例如:
I should have thought of that. 这一点我是应当想到的。(但没想到)
They should not have left so soon.他们不应当走得这么早。(但已走了)
5) 在“It is natural (strange, natural, necessary, surprised, impossible, important ) that……”句型中,主语从句中的谓语动词要用should +动词原形”表示“理所当然”、“奇怪”、“必要”、“惊异”等的意思。在lest(以免)、for fear (that) (以防)、in case(以备万一)等之后也要用should+动词原形;在advise, sugest, order, demand, request 等的从句中should+do”例如:
It is necessary that he(should) be sent there at once.
有必要马上派他到那里去。
It is strange that he should say so. 他会说这样的话真是奇怪。
Let us go at once lest we should be late for the train.
我们马上走吧,以免赶不上火车。
8..will和would的用法
1)表示意志,决心或愿望。例如:
Surely we will support all the people in the world in their struggle for peace.
我们一定要支持全世界人民争取和平的斗争。
He would not let me try it . 他不肯让我去试。
2)will表示经常性、习惯性、倾向性,would表示过去的习惯行为。
He will sit there hour after hour looking at the traffic go by.
他会经常一连几个小时坐在那儿观看来往的车辆。
He would come to see me when he was in Beijing.
他在北京时,常来看望我。
3)用于第二人称作主语的疑问句中,表示对对方的请求,would的语气比will委碗
Would/will you kindly tell me the way to the station? 请问到火车站怎么走?
4)表可能性
This will be the book you are looking for.
这可能就是你要找的书。
She eould be about 60 when she died.
他死时大概60岁。
9. need和dare的用法
情态动词need 实义动词 need
现 You need (not) do You (don’t) need to do
在
时 He need (not) do He needs (doesn’t need) to do
过 You needed (didn’t need) to do
去
时 He needed (didn’t need) to do
将 You need (not) do You will (not) need to do
来
时 He need (not) do He will (not) need to do
句型 时态 动词
情态动词dare 实义动词 dare
肯定句 现在时 dare to 少用 dare/dares to do
过去时 dare to 少用 dared to do
否定句 现在时 daren’t/dare not do do/does not dare (to) do
过去时 dared not do did not dare (to) do
疑问句 现在时 Dare he do? Do you/Does he dear (to) do?
过去时 Dared he do? Did he dare (to) do
needn’t have v-ed 表示过去做了某事,但没有做的必要, 意为“本没必要…”。例如:
You needn’t have waken me up; I don’t have to go to work today
10.表推测的情态动词句子的反意疑问句
He must/may be in the room, isn’t he?
He can’t be in the room, is he?
He must have finished the work, hasn’t he?
He may have done the work last night, didn’t he?
:情态动词+行为动词进行式
情态动词+行为动词进行式(即情态动词+ be + v-ing形式),表示推测或评论某动作现在是否正在进行。例如:
1)He must be playing basketball in the room.
2)She may be staying at home.
11.情态动词+行为动词完成进行式
情态动词+行为动词完成进行式(即情态动词+ have been + v-ing 形式),表示推测或评论过去某动作是否正在进行或一直在进行。例如:
1)They should have been meeting to discuss the problem.
2)He may / might have been buying stamps in the post office when you saw him.
12.used to +v, be used to +v-ing和be used to +v
(1)used to +v意为“过去常常”,“过去一直”;be used to +v-ing / n(名词)意为“习惯于”;be used to +v意为“被用来(做某事)”。
(2)used to只表示过去,而be used to +v-ing / n可表示现在、过去或将来。例如:
1)He used to smoke. Now he doesn’t.
2)He’s quite used to hard work / working hard.
3)The knife is used to cut bread.
13.用作情态动词的其他短语
would rather, would sooner, would (just) as soon, had rather, had better, had sooner, can not but, may (just) as well等可用作情态动词。例如:
1)The soldier would sooner die than surrender.
2)The brave soldier would as soon die as yield to such an enemy.
3)I’d rather walk than take a bus.
4)If you don’t like to swim, you may just as well stay at home.
注:这些短语后一般直接跟动词原形.would (had) rather, would (had) sooner, would (just) as soon后可跟that 引导的从句,that 常省去,从句要用虚拟语气。对现在和将来的假设用过去时,对过去的假设用过去完成时。例如:
1)I would rather you came on Sunday.
2)I would sooner you hadn’t asked me to speak yesterday.
初中英语中的情态动词
介词有in, on ,out ,with, without, beside, beyond, behind, 之类的
情态动词有can, could, may, might, must, should, ought to ,would will
初一学的情态动词有哪些
您好,这个问题的正确答案是must can could might may,如果您有任何问题可以追问我,如果没有问题,请采纳,谢谢!
以上就是关于初一的情态动词有哪些 ,语法填空情态动词的全部内容,以及初一的情态动词有哪些 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
