本文目录
在什么情况下用动词不定式呢
在英语中,用到动词不定式的情况有很多:
在语法中,动词不定式是指动词的一种不带词形变化从而不指示人称、数量、时态的形式。它被叫做不定式,是因为动词不被限定,或者说不被词形变化所局限。不定式属于非谓语动词。
如果动词不定式的逻辑主语是这个不定式所表示的动作的承受者,不定式一般要用被动语态形式。如:
It's a great honour to be invited to Mary's birthday party.不定式作主语是被动语态to be invited是被邀请
It was impossible for lost time to be made up.不定式作主语
I wish to be sent to work in the country.不定式作宾语
Can you tell me which is the car to be repaired?不定式作定语
He went to the hospital to be examined.不定式作状语
在There be结构中,修饰主语的不定式可用被动,也可用主动如:There are still many things to take care of (to be taken care of).但有时两种形式表达的意思不同,如:There is nothing to do now.( We have nothing to do now.) There is nothing to be done now.(We can do nothing now.)
形式
1) 现在式:一般现在时表示的动词,有时与谓语动词表示的动作同时发生,有时发生在谓语动词的动作之后。
He seems to know this.
I hope to see you again. = I hope that I'll see you again. 我希望再见到你。
完成式:表示的动作发生在谓语动词表示的动作之前。
I'm sorry to have given you so much trouble.
He seems to have caught a cold.
进行式:表示动作正在进行,与谓语动词表示的动作同时发生。
He seems to be eating something.
完成进行式:
She is known to have been wreaking on the problem for many years.
一般在表示情绪的动词后加to do也表将来
疑问词
疑问词who,what,which,when,where,whether,how后可接不定式构成不定式短语,在句中作主语、宾语、表 语等。如:
When to leave for London has not been decided yet. 不定式在句子中做主语Mr. Smith didn't know whether to leave or stay there. 不定式在句子中做宾语
I asked Professor Xu how to learn English well. 不定式在句子中做直接宾语
The question was where to get the medicine needed. 不定式在句子中表语)
以上例句中疑问词+不定式部分,均可转换为相应的从句形式。如:When we shall leave…③…how I could learn……
经常在这种结构中使用的动词有:consider,decide,discover,explain,find out,forget,hear,know,learn,observe,understand,wonder等。
作主语
动词不定式作主语时,句子的谓语动词常用单数,其位置有以下两种:
把不定式置于句首。如:
To get there by bike will take us half an hour.
骑自行车到那儿将花费我们半个小时。
To make up for lost time is not possible.
要弥补失去的时光是不可能的。
To lean out of the window is dangerous.
身子探出窗外很危险。
To save money now seems impossible.
现在好像不可能存钱。
用it作形式主语,把真正的主语不定式置于句后,常用于下列句式中。如:
It+be+名词+to do
It's our duty to take good care of the old.
照顾老人是我们的责任。
It takes sb+some time+to do
How long did it take you to finish the work?
你花了多少时间来完成这项工作?
It+be+形容词+for sb+to do
It is difficult for us to finish writing the composition in a quarter of an hour.
我们难以在四分之一小时内完成这篇作文。
It is stupid of you to write down everything (that) the teacher says.
你把老师说的所有东西都记下来的行为是很愚蠢的。
It is an offence to drop litter in the street.在
马路上乱丢废物是违章的。
It seems(appears)+形容词+to do
It seemed impossible to save money.
在句型③中,常用表示客观情况的形容词,如:difficult,easy,hard,important,impossible,necessary 等;
在句型④中,常用careless,clever,good,foolish,honest,kind,lazy,nice,right,silly,stupid,wise等 表示赞扬或批评的词。
在不定式前的sb,可看作其逻辑主语。这一句式有时相当于Sb is+形容词+to do句式 ,如:It's kind of you to help me with my English.=You are kind to help me with my English.
It + 不定式结构可位于believe/consider/discover/expect/find/think和wonder之后
He thought it would be safer to go by train.
他认为乘火车比较安全。
He will find it is hard to make friends.
他会感觉到交朋友困难。
不定式的完成式也可作句子的主语
eg:
To have made the same mistake twice was unforgivable.
两次犯同样的错误是不可原谅的。
It is better to have loved and lost than never to have loved at all.
爱过而后失去了爱,比从未爱过要好。
不定式作为句子成分时,动词用单数形式。
当不定式作主语的句子中又有一个不定式作表语时,不能用It is… to…的句型(对)To see is to believe. 眼见为实 < 正确 >
It is to believe to see. < 错误 >
作宾语
以下动词后,只能跟不定式作宾语
afford (付得起),agree(同意),aim(力求做到),appear(显得),arrange(安排),ask(要求),attempt (试图),care(想要),choose(决定),claim(声称),condescend(屈尊),consent(准许),decide(决定),demand(要求),determine(决心),endeavor(竭力),expect(期待),fail(未履行),help(帮助),hesitate(犹豫),hope(希望),learn(学会),manage(设法),neglect(疏忽),offer(主动提出),plan(计划),prepare(准备),pretend(假装),proceed(接着做),promise(答应),prove(证明),refuse(拒绝),resolve(解决),seem(觉得好像),swear(发誓),tend(往往会),threaten(预示),undertake(承诺),volunteer(自愿做),vow(发誓),want(想要),wish(希望)
eg:
The driver failed to see the other car in time.
司机没能及时看见另一辆车。
I happen to know the answer to your question.
我碰巧知道你那道问题的答案。
动词+疑问词+ 不定式
decide,know,consider forget,learn,remember,show,understand,see,wonder,hear,find out,explain,tell
eg:
Please show us how to do that. 请演示给我们如何去做。
There are so many kinds of tape recorders on sale that I can't make up my mind which to bu.有这么多的录音机,我都拿不定主意买哪一种。
注意:疑问词带不定式在句中作成分时,谓语动词用单数。
The question is how to put it into practice.
问题是怎样把它付诸实施。
3)当复合宾语中的宾语是不定式时,先用形式宾语it代替不定式,把不定式置于补语之后,即:主语+动词+it+补语+to do句式。如:
We think it quite important for us to learn a foreign language well.
He feels it his duty to help the poor.
I find it difficult to learn English well.
作补语
动词+宾语+不定式(to do)
advise allow believe cause challenge compel declare encourage forbid force find hire induce instruct invite like order permit persuade remind request require select send suppose tell train urge
eg:
Father will not allow us to play on the street.
父亲不让我们在街上玩耍。
We believe him to be guilty.
我们相信他是有罪的。
to + be 的不定式结构,作补语的动词。
Acknowledge, believe, consider, think, declare(声称), discover, fancy(设想), feel, find, guess, judge, imagine, know, prove, see(理解), show, suppose, take(以为), understand
eg:
We consider Tom to be one of the best students in our class.
我们认为汤姆是班上最好的学生之一。
to be +形容词
Seem, appear, be said, be supposed, be believed, be thought, be known, be reported, hope, wish, desire, want, plan, expect, mean…
eg:
The book is believed to be uninteresting.
人们认为这本书没什么意思。
there be+不定式
believe,expect,intend,like,love,mean,prefer,want,wish,undrstand
eg:
We didn't expect there to be so many people there.我们没料到会有那么多人在哪里。
有些动词需用as 短语做补语,如regard,think believe,take,consider.
eg:
We regard Tom as our best teacher. 我们认为汤姆是我们最好的老师。
Mary took him as her father . 玛丽把他当作自己的父亲。
秃头不定式作补语
秃头不定式, 即不带“to”的不定式,其语法功能一般在句子中作宾语的补语(宾语补足语)。用秃头不定式作宾语补足语的常用动词如下:
口诀:“五看、三使役“,“两听、一感”要记住,若是“宾补”变“主补”,主补“to”字不能无。动词let属例外,其宾补/主补“to”均无。说明:
五看-----see/watch/notice/observe/look at;三使役-----have/make/let;两听-----hear/listen to;一感-----feel。
eg:
I often see him go to school on foot.(秃头不定式作宾语补足语) He is often seen to go to school on foot.(不定式作主语补足语,要带“to”) Let him try again.---- He is let try again.(let的主补与宾补均用秃头不定式)
Find 特殊用法
Find 后可用分词做宾补,或先加形式宾语,再加形容词,最后加带to 的动词不定式。find后也可带一个从句。此类动词还有get,have。
eg:
I found him lying on the ground.
I found it important to learn.
I found that to learn English is important.

英语什么时候用不定式什么时候用动名词
简单的来说,不定式的简单式由to+动词原形 构成,表示动作和主要动词同时发生,比如I'm glad to see you.
不定式的进行时由to+be+现在分词 构成,表示在主要动词发生时,不定词的动作一直在进行中.
不定式的完成时由to+have+过去分词构成,表示不定式的动作发生在主要动词之前

英语什么情况下会用到不定式
动词不定式概述
一 不定式的体
1. 不定式的一般式(to do)表示不定式的.动作将要发生或与谓语动作同时发生.
2 不定式的进行体(to be doing)表示不定式的动作正在发生.
不定式的完成体(to have done)表示不定式的动作在谓语动作之前发生.
二 不定式的逻辑主语
1 不定式的逻辑主语常不出现在句中.
2 句子的主语,宾语有时是不定式的逻辑主语.
3 不定式前"for+名词/代词"结构中的名词或代词也可以用来表示不定式的;逻辑主语.
4 在"It+be+形容词+of+名词/代词+to do"结构中,名词或代词为不定式的逻辑主语.该结构中的形容词通常用来表示人的品质.例如:kind, good, nice, bad, cruel, honest, bold, thoughtful, right, wrong, wise, clever, silly, foolish, careless, rude等.
例如:It's very kind of you to cal to tell me about the conference.
三 不定式的否定式
不定式否定式由not/never +to do构成
四 不定式的句法功能
1 不定式做主语
1)To say something is one thing; to do it is another.
2)It is not a good idea to build houses along the lines where two of the earth's plates join together.
注:充当主语的不定式即可置于句首,位于谓语动词之前,也可作为句子的真正主语置于句末,用作形式主语.
2 不定式作表语
3)Her uncle seems to be acting rather strangely towards her these days.
4)The purpose of the fence is to keep out a type of wild dog called a "Dingo".
5)One suggested answer is for farmers to limit the number of their cattle.
注:充当表语的不定式一般位于be ,seem等系动词后.
3 不定式作宾语
6)Shylock agreed to lend Antonio money on one condition.
注:充当宾语的不定式位于及物动词后.常用不定式作宾语的动词有:agree, plan, determine, dare, refuse, hope, wish, expect, promise, choose, pretend, decide, manage, intend, offer, afford, demand.
7)The dusty air makes it difficult to get a clear picture of space.
注:充当宾语的不定式如果有自己的表语,则可用代替只个不定式作为形式宾语,而作为真正宾语的不定式则放在表语之后.以it作为形式宾语的这种结构常用在think, feel, find, make, consider等动词之后.
big and strong.
4 不定式作宾语补足语
8)The powder made from fish, blood and bones will make the cabbage plants grow big and strong.
9)Portia told Bassanio to go to his friend at once.
注:在下列动词后作宾语补足语的不定式通常不带to.这些动词是observe, notice, see, hear, watch, have, feel, make, let.但上述动词转换为被动语态时,其后的不定式须带to.例如:The cabbage plants will be made to grow
动词不定式(todo)是初中英语课的一个重点,也是中考要考查的一个项目。动词不定式属于非谓语动词的一种形式,很多同学经常把它和谓语动词混在一起,掌握起来有困难。下面我们对动词不定式的用法做简单归纳,帮助同学们记忆:
一、动词不定式在句子中不能充当谓语,没有人称和数的变化。
二、动词不定式是由“to+动词原形”构成(有时可以不带to)。动词不定式的否定形式是“not+动词不定式”(not不与助动词连用)。
三、动词不定式短语具有名词、形容词和副词等的功能,可在句中用做多种句子成分。
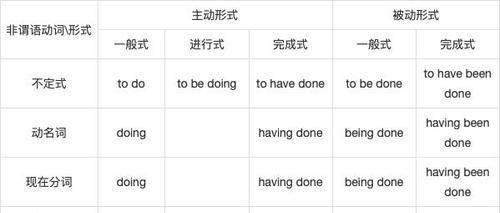
不定式什么时候用主动表被动
1.当遇上有将来味道的词时,用to do表示将来,例如:I wish to be sent to work in the country.在这句话当中,wish有将来的味道,因此我们用不定式,但i和sent是被动关系,所以我们用动词不定式的被动式。
2.某些词后面只能接不定式,例如seem、appear等表示不确定的词,例如,I might also seem to do things in a rather odd order.我可能似乎也做一些事,而不是在一个奇数阶。seem 、appear后只能接不定式,此处用to do表示将来。
3.在一些既能用to do,又能用doing的词中,我们用to do表示将来,例如:Remember to close the door,please在这句话中close表示的动作发生在remember之后,用to do表示将来。
4.某些词后可以接doing表示动作发生在谓语动词之后,例如She is considering changing her job. 她在考虑换个工作。这句话中,changing发生在considering之后,但却用changing表示将来。
5.常用于疑问词+不定式结构中,如what to do,how to do it,等。用在what to do结构中作定语,修饰what,与what是动宾关系,用在how to do it结构中需带自己的宾语,例如i know exactly what to do.我知道该怎么办,i know exactly how to do it.我知道怎么做它。
6.用在with的复合结构中,表示将来,即with+宾语+宾语补足语,这就是with的复合结构,若是不定式作宾补,就变成with sb. to do 有将来含义,如,: I can't go out with all these dishes to wash.就用了with的复合结构。
7.不定式作定语时,常用来修饰被序数词,最高级,no,any,all等限定的中心词,或者也可以用一个定语从句,例如,He was the best man to do the job. She was the first woman to win the gold medal in the Olympic Games.

以上就是关于不定式什么时候用不定式 ,在什么情况下用动词不定式呢的全部内容,以及不定式什么时候用不定式 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

