本文目录
不定代词的句子举例
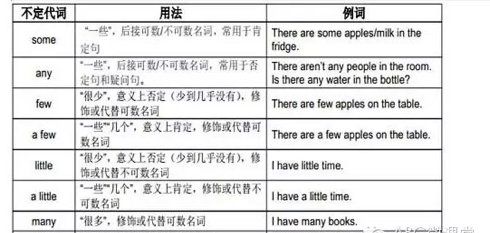
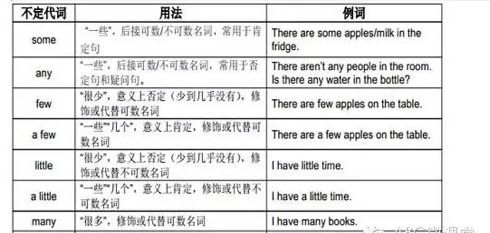
1.some 一些,某些,某个
不定代词some可以代替名词和形容词,常用在肯定句中作主语(也可以在以would,may,can,could疑问词开头的句子做主语)、宾语、定语等。作定语时,它可以修饰可数名词(单、复数皆可)和不可数名词。例如:
some are doctors,some are nurses.有些人是医生,有些人是护士。(作主语)
2.any一些,任何
不定代词any可以代替名词和形容词,常用在否定句或疑问句中作主语、宾语、定语等。作定语时,它可以修饰可数名词(多为复数)和不可数名词。例如:
there isn’t any ink in my pen.我的钢笔没有墨水。(作定语)
不定代词any有时也可以用在肯定句中,表示任何的。例如:
you may come at any time;i’ll be home the whole day.你任何时候来都行,我整天都将呆在家里 。
不定代词any也可以用作副词,做状语,表示程度。例如:
is he any better today?他今天好一点了吗?
3.all 全体,所有(指三者以上,包括三者)
不定代词all在句中可以作主语、宾语、表语、定语或同位语。它可以代表或修饰可数名词和不可数名词。代表或修饰可数名词时,指两个以上的人或物。作先行词时,引导词用that。例如:
All were present at the meeting.全都到会了。(作主语,代表可数名词)
4.both 全部,都
不定代词both指两个人或事物。和all一样,可以用作主语、宾语、定语或同位语。例如:
we invited both to come to our farm.我们邀请两个人都来我们的农场?(作宾语)
5.none 无人或无
不定代词none的含义和all物相反,和no one,not any同义,但其用法相当于名词,在句子中一般作主语或宾语。它代替不可数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式;代替可数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单、复数皆可。例如:
none of the problems is /are easy to solve.这些问题没有一个是容易解决的。(作主语, 代替可数名词)
6.either 两者之中的任何一个,这个或那个。
不定代词 either 可以作主语、宾语和定语。例如:
either of them will agree to this arrangment.他们两人中会有人同意这样的安排的。(作主语)
7.neither 两者都不
不定代词 neither 是 either 的否定形式,可以作主语、宾语和定语。例如:
neither is interesting.两个都没有趣。(作主语)
8.each 每个,各自的
不定代词each指每一个人或事物的个别情况,甚至指这些个别情况各不相同。它在句中可以作主语、宾语、定语和同位语。例如:
she gave the children two apples each.她给了每个小孩两个苹果。(作the children的同位语。)
9.every 每个,每一的,一切的
不定代词every有全体的意思,和all的意义相近,但只能作定语。
I believe either method will work.(作定语) 10.neither 两个之中一个也不是不定代词neither是either的否定形式,可以作主语、宾语和定语.例如: Neither is interesting.(作主语) -Did you see Mary and Jack? -No,I saw neither of them.(作宾语) I think neither book is worth reading.(作定语) 注:a.不定代词neither表示两个都不,所以汉语的我俩都没去那儿译成英语为Neither of us went there.而不能译成 Both of us did not go there.后者意为我俩没都去那儿. b.肯定形式的动词+neither=否定形式的动词+either.例如: I like neither of them.=I dont like either of them. 11.other 其他的,另外的不定代词other相当于名词或形容词,可以在句中作主语、宾语、定语等.相当于名词时,有复数形式 others,还有所有格形式 others 和others.不定代词 other之前常用冠词 the.例如: He has two daughters .One is a teacher,the other is a nurse.(作主语) Some will go swimming,others will go shopping.(作主语) I have two pictures of the Great Wall here.You have seen one.Now Ill show you the other .(作宾语) There are other ways of helping him out of difficulty.(作定语) 12.another 另一个,又一个another是由an和other合并构成,因此,它只能代替或修饰可数的单数名词,前面不再用冠词.不定代词another可以在句中作主语、宾语、表语和定语.例如: One is blind,another is deaf,and a third is lame.(作主语) This shirt is too small for me.Please show me another .(作宾语) She is a fool,and her husband is another.(作表语) Would you like another cup of milk?(作定语) You will have to stay here for another five days.(作定语,five days形式上是复数,但意义上是单数,可以和another连用) 13.one 1)不定代词one指不定人称,表示人,译为人,一个人等.它有反身代词oneself和所有格形式ones. 2)不定代词one也可以用来代替前面出现过的可数名词,以免重复.它有复数形式ones,可以与冠词连用,可以有自己的定语. 不定代词one可以在句中作主语或宾语;ones只能作定语.例如: One has to do ones best.(one 作主语,ones作定语.) Please give me the book,the one on the desk.(one作宾语)
14.none of 没有一个
作主语时谓语动词可单可双
15.(a)few (a)little(几乎没有)有一些
(a)few+可数 复数 few (指几乎没有,含否定意味)+可数
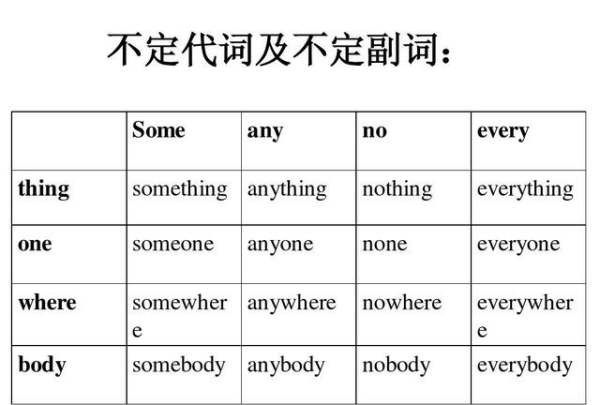
(a)little+不可数 little(指几乎没有,含否定意味)+不可数 1.some, any, every, no都能和one, body, thing一起构成代词,这些代词叫复合不定代词。它们基本含义为:
指
人 somebody
someone 某人
anybody 、anyone :任何人
everybody 、everyone:每人
nobody 、no one :没人
指物 Something某物某事 anything任何事物 everything一切 nothing没东西
2. 一般情况下,some构成的复合不定代词,其作用和some相同,用于肯定句;any构成的复合不定代词用于否定句或疑问句;no构成的复合不定代词表示否定含义,用于否定句。如:
① I have something to tell you. 我有事要告诉你。
② He didn’t say anything at the meeting yesterday. 昨天在会上他没发言。
③ Everybody likes swimming. 每个人都喜欢游泳。
④ There is nothing wrong with your ears.
你耳朵没毛病。
3. something可用于提建议或请求的问句中,以及希望说话对方作出肯定回答的问句中。如:
Would you like something to eat? 你要吃点东西吗?
4. 复合不定代词在句子中作主语时,谓语动词一般用单数形式。如:
Nobody knows his name. 没有人知道他的名字。
5. 不定代词的定语要后置。如:
Is there anything important in today’s newspaper? 今天的报纸上有什么重要新闻吗?
一般的,不定代词(包括复合不定代词)在句子中,通常用第三人称单数形式
6。复合不定代词的否定。
1、“not every-”表示的是部分否定,意为“并非都,不都”。例如:
Not everything will go well. 并非一切都会那么顺利。
The teacher didn’t call everyone’s name. 老师并没有点所有人的名。
2、“not any-”和no-均表示全否定。例如:
He listened, but heard nothing.他听了听,但什么也没听到。
= He listened, but didn’t hear anything.
You haven’t called anyone/anybody up, have you? 你没给谁打过电话,是吗?
= You have called no one/nobody up, have you?
1.不定式是英语动词的一种形式。它在许多情况下可省略to,它不同于汉语动词,汉语动词只有一种形式。如:我看书。她看书。但英语要说“看”必须根据主语的人称,动作发生的时间等确定其形式。如:1)I read a book. 2)She reads a book.1)句中的“read”
是一般现在时第一人称的动词定式。2)句中的“reads”是一般现在时第三人称单数的动词定式。
I want to read a book./She wants to read a book.
我想要看书。她想要看书。其中的“看”不易确定其形式。因为动作还未发生,因此称不定式。通俗的说,就是“不一定是什么形式”
2.不定代词是不指明代替任何特定名词或形容词的代词,英语中不定代词有:some(something,somebody,someone),any(anything,anybody,anyone), no(nothing,nobody,no one), every(everything,everybody,everyone),all,each,both,much,many,(a)little,(a)few,other(s),another,none,one,either, neither等。
1) 陈述部分的主语是I,疑问部分要用 aren't I.
I'm as tall as your sister,aren't I?
2) 陈述部分的谓语是wish,疑问部分要用may +主语。
I wish to have a word with you, may I?
3) 陈述部分用 no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词时,疑问部分用肯定含义。
The Swede made no answer, did he / she?
Some plants never blown (开花), do they ?
4) 含有ought to 的反意疑问句,陈述部分是肯定的,疑问部分用shouldn't / oughtn't +主语。
He ought to know what to do, oughtn't he? / shouldn't he?
5) 陈述部分有have to +v. (had to + v.),疑问部分常用don't +主语(didn't +主语)。
We have to get there at eight tomorrow, don't we?
6) 陈述部分的谓语是used to 时,疑问部分用didn't +主语或 usedn't +主语。
He used to take pictures there, didn't he? / usedn't he?
7) 陈述部分有had better + v. 疑问句部分用hadn't you?
You'd better read it by yourself, hadn't you?
8) 陈述部分有would rather +v.,疑问部分多用 wouldn't +主语。
He would rather read it ten times than recite it, wouldn't he?
9) 陈述部分有You'd like to +v. 疑问部分用wouldn't +主语。
You'd like to go with me, wouldn't you?
10) 陈述部分有must 的疑问句,疑问部分根据实际情况而定。
He must be a doctor, isn't he?
You must have studied English for three years, haven't you? / didn't you?
He must have finished it yesterday, didn't he?
11)感叹句中,疑问部分用be +主语。
What colours, aren't they?
What a smell, isn't it?
12) 陈述部分由neither… nor, either… or 连接的并列主语时,疑问部分根据其实际逻辑意义而定。
Neither you nor I am engineer, are we?
13) 陈述部分主语是指示代词或不定代词everything, that, nothing, this, 疑问部分主语用it。
Everything is ready, isn't it?
14) 陈述部分为主语从句或并列复合句,疑问部分有三种情况:
a. 并列复合句疑问部分,谓语动词根据邻近从句的谓语而定。
Mr. Smith had been to Beijing for several times, he should have been in China now, shouldn't he?
b. 带有定语从句,宾语从句的主从复合句,疑问部分谓语根据主句的谓语而定:
He is not the man who gave us a talk, is he?
He said he wanted to visit Japan, didn't he?
c. 上述部分主句谓语是think, believe, expect, suppose, imagine等引导的定语从句,疑问部分与宾语从句相对应构成反意疑问句。
I don't think he is bright, is he?
We believe she can do it better, can't she?
15) 陈述部分主语是不定代词everybody, anyone, somebody, nobody, no one等,疑问部分常用复数they,有时也用单数he。
This is our new headmaster, isn’t it?
Those are Japanese, aren’t they?
One should be ready to help others, shouldn’t one?
One can’t be too careful, can you?
Each of the students has a dictionary, hasn’t he?
Each of the students passed the examination, didn’t they?
None of his money is left, is it?
None of his friends are interested, are they?
None of his friends has come, has he?
Something will have to be done about the price, won’t it?
Everybody is kind to you, aren’t they?
No one left here yesterday, did they?
Someone turned that radio down, don’t they?
Neither side could win, could they?
Everything that he says is false, isn’t it?
I am older than you, aren’t I / ain’t I?
I am working now, ain’t I / am I not?
I wish to see the movie now, may I?
I wish I were you, may I?
16) 带情态动词dare或need的反意疑问句,疑问部分常用 need (dare ) +主语。
We need not do it again, need we ?
He dare not say so, dare you?
当dare, need 为实义动词时,疑问部分用助动词do + 主语。
She doesn't dare to go home alone, does she?
17) 省去主语的祈使句的反意疑问句,疑问部分用will you。
Don't do that again, will you?
Go with me, will you / won't you ?
注意: Let's 开头的祈使句,后用shall we?
Let us 开头的祈使句,后用will you?
Let's go and listen to the music, shall we?
Let us wait for you in the reading-room, will you ?
18) 陈述部分是there be结构的,疑问部分用there省略主语代词。
There is something wrong with your watch, isn't there?
There will not be any trouble, will there?
19)否定前缀不能视为否定词,其反意疑问句仍用否定形式。
It is impossible, isn't it?
He is not unkind to his classmates, is he?
20) must在表推测时,根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句。
He must be there now, isn't he?
It must be going to rain tomorrow, won't it?
快速记忆表
陈述部分的谓语 疑问部分
I aren't I
Wish may +主语
no,nothing,nobody,never,
few, seldom, hardly, 肯定含义
rarely, little等否定
含义的词
ought to(肯定的) shouldn't/ oughtn't +主语
have to+v.(had to+v.) don't +主语(didn't +主语)
used to didn't +主语或 usedn't +主语
had better + v. hadn't you
would rather + v. wouldn't +主语
you'd like to + v. wouldn't +主语
must 根据实际情况而定
感叹句中 be +主语
Neither…nor,
either…or 连接的根 据其实际逻辑意义而定
并列主语
指示代词或不定代词
everything,that, 主语用it
nothing,this
并列复合句 谓语根据邻近从句的谓语而定
定语从句,宾语从句的
主从复合句 根据主句的谓语而定
think,believe,expect,
suppose,imagine等引导 与宾语从句相对应的从句
everybody,anyone,
somebody,nobody,no one 复数they,单数he
情态动词dare或need need (dare ) +主语
dare, need 为实义动词do +主语
省去主语的祈使句will you?
Let's 开头的祈使句Shall we?
Let us 开头的祈使句Will you?
there be 相应的谓语动词+there(省略主语代词)
否定前缀不能视为否定词 仍用否定形式
不定代词做主语谓语动词用单数
must表推测 根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句
英语中不定代词有哪些及其翻译
不定代词有哪些不定代词在英语中的用法归纳不定代词的种类不定代词指的是all,each,every,both,either,neither,none,little,few,many,much,other,another,some,any,no,以及由some,any,no,every构成的复合代词。

1.some与any。some用于肯定句中,any用于否定句、疑问句和条件句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的句子中,通常要用some而不用any。如:Willyoulendmesomemoney?可以借些钱给我吗?Whydon’tyoubringsomeflowers?为什么不带些花来呢?
2.指两者和三者的不定代词。有些不定代词用于指两者(如both,either,neither),有的不定代词用于指三者(如all,any,none,every),具体使用时要根据一定的上下文正确选用。如:Heisblindinbotheyes.他双目失明。Weretheyallcollegestudents?他们都是大学生吗?注:each可用于两者、三者或三者以上,而every只用于三者或三者以上,因此用于两者时只能用each,不能用every。如:Therearetreesoneachsideoftheroad.路的两边都有树。
3.(a)few与(a)little。few和afew后接复数名词,而little和alittle后接不可数名词。其中不带不定冠词的few和little表示数量很少或几乎没有,强调“少”,含有否定意义;而带有不定冠词的afew和alittle则表示数量虽然少但毕竟还有,强调“有”,含有肯定意义。如:Heknewfewofthem.他们中间他认识的人很少。Hesoldonlyafewofthepapers.他只卖出了几份报纸。Heknewlittleaboutit.他对此知道得很少。Thereisstillalittleleft.还剩一点点。
4.all,every,each的用法。从强调重点上看:all强调整体地考虑总体,every强调考虑总体中的所有成员(与all很接近),each则强调逐个逐个地考虑总体;从用法上看:all和each既可单独使用,也可后接名词,还可后接of短语;而every后必须接名词,既不能单独使用也不能后接of短语;从含义上看,each指两者或两者以上的“每个”,every指三者或三者以上“每个”,因此指两者时只能用each。不定代词在英语中的用法归纳:little和few都可以作代词和限定词little用来指不可数的事物或修饰不可数的事物;而few则用来指可数的事物(人)或修饰可数的事物(人)。ManypeoplereadMarcoPolo'sbook,butfewbelievewhathesaid.很多人读过马可波罗的书,但很少有人相信他所说的话。
Fewpastimesbringafamilyclosertogetherthangatheringaroundandlisteningtomotherorfatherreadagoodstory.(孩子们)围在一起听父亲或母亲读美丽的故事很少有别的娱乐活动比这更能使家人们的心灵接近了。little和few表示说话人否定的意思,而alittle和afew表示说话人肯定的意思,前者常常翻译为"很少、几乎没有",后者翻译为"一些"。但不能得出结论说alittle或afew就比little或few多。两者不存在孰多孰少的比较,只是表示说话人的语气不同。例如某人口袋里有10元钱,可以是little,也可以是alittle。例:It'simpossibleformetobuyaTVsetnow.Ihavelittlemoneyleft.我现在不可能买一台电视机,我几乎没有钱了。
不定代词的用法和例句
不定代词具有名词和形容词的性质,并有可数和不可数的区别,(1)one
some
与any的用法:
one泛指任何人One
should
wash
oneself
regularly;
还可以在形容词和that,this等词后替代刚才可能提过的可数名词
如:This
film
is
not
as
good
as
the
one
I
saw
yesterday.some和any通常作定语
some
用于数词前,表示大约,用于肯定句;any多用于疑问句,否定句.(2)each,every的用法
each强调个体
所代表的可以使两个以上,而every必须三个以上(3)none
和no的用法
no=not
any用于修饰可数和不可数的名词,none
代替不可数名词时,谓语动词用单数.代替可数名词做主语时,
谓语既可单数
又可复数.(4)many
much的用法
修饰可数名词
修饰不可数名词(5)few,
little
,a
little
,a
few(6)other
和another(7)all和
both(8)neither和either的用法***
补充一下,,不定代词可分为由body,
one
,thing
构成的合成代词,如:somebody,
anybody,
everybody,
nobody;
someone,
everyone
和
something,
everything,
nothing
八年级英语不定代词的用法
这些解释都很易懂,例句也简单。希望对你有所帮助!
一、不定代词概说
英语的不定代词有 all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no, (a) few, (a) little, both, enough, every 等,以及由 some, any, no 和 every 构成的合成代词(即somebody, anyone, nothing 等)。在这些不定代词中,多数都能作主语、宾语、表语或定语,但是代词 none 以及由 some, any, no 和 every 构成的合成代词只能作主语、宾语或表语,不能作定语,而 no 和 every 则只用作定语。
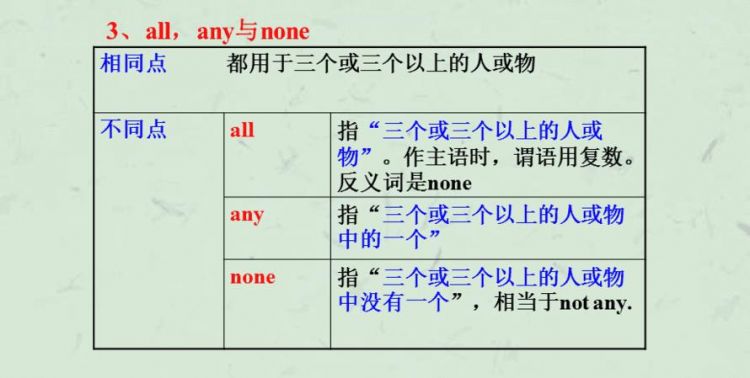
二、指两者和三者的不定代词
有些不定代词用于指两者(如both, either, neither),有的不定代词用于指三者(如all, any, none, every),注意不要弄混:
Both of my parents are doctors. 我的父母都是医生。
All of the students are interested in it. 所有的学生对此都很感兴趣。
There are trees on any side of the square. 广场的每一边都种有树。
He has two sons, neither of whom is rich. 他有两个儿子,都不富有。
He has three sons, none of whom is rich. 他有三个儿子,都不富有。
【说明】each 可用于两者、三者或三者以上,而 every 只用于三者或三者以上,因此用于两者时只能用 each,不能用 every。如不能说 There are trees on every side of the road.
三、复合不定代词的用法特点
复合不定代词包括 something, somebody, someone, anything, anybody, anyone, nothing, nobody, no one, everything, everybody, everyone 等。它们在句中可用作主语、宾语或表语,但不能用作定语。something, someone 等和 anything, anyone等的区别与 some 和 any 的区别一样,前者一般用于肯定句,后者一般用于否定句、疑问句或条件句(参见 any & some)。具体使用时应注意以下几点:
1. 复合不定代词受定语修饰时,定语应放在它们后面:
There is nothing wrong with the radio. 这收音机没有毛病。
Have you seen anyone [anybody] famous? 你见过名人吗?
2. 指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数 he, him, his (不一定指男性)。但在非正式文体中常用复数代词 they, them, their:
Everyone knows this, doesn’t he [don’t they]? 人人都知道这一点,不是吗?
If anybody [anyone] comes, ask him [them] to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
3. 指事物的复合不定代词若用作主语,谓语动词只能用单数,相应的人称代词也只能用 it,而不用 they:
Everything is ready, isn’t it? 一切都准备好了,是吗?
4. 不定代词 anyone, everyone 等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接of 短语。若是指物或后接 of 短语,可用 any one, every one (分开写):
any one of the boys (books) 孩子们(书)当中的任何一个(本)
every one of the students (schools) 每一个学生(一所学校)
四、不定代词any与not连用——是any not 还是 not any
按英语习惯,any 以及含有any的复合不定代词用于否定句时,它只能出现在否定词之后,而不能在否定词之前:
误:Any one doesn’t know how to do it.
正:No one knows how to do it. 任何人都不知道如何做它。
误:Anybody [Anyone] cannot do it.
正:Nobody [No one] can do it. 这事谁也干不了。
误:Anything cannot prevent me from going.
正:Nothing can prevent me from going. 什么也不能阻挡我去。
五、不定代词与部分否定
不定代词all, both, every 等与 not 连用时构成部分否定;若要表示完全否定,则需换用 none, neither, no one等。比较:
All of the students like the novel. 所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
Not all of the students like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
All of the students don’t like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
None of the students like the novel. 这些学生当中没有一个喜欢这本小说。
六、不定代词 all, both, each 等用作同位语
不定代词all, both, each 等若用作主语同位语,主语可以是名词或代词;若用作宾语等其他成分的同位语,则宾语等成分必须是人称代词,而不能是名词:
We have all read it. 我们都读过他。(all 修饰的主语是代词)
The villages have all been destroyed. 村庄都被毁了。(all 修饰的主语是名词)
They told us all to wait there. 他叫我们都在那儿等。(all 修饰的宾语是代词)
但不能说:They told the men all to wait there. (all 修饰的宾语是名词不是代词)
七、不定代词 so little 与 such little的区别
用 so little 还是 such little 取决于不定代词 little 的意思:若表示数量方面的“少”,则用 so little;若表示形状体积的“小”,则用 such little:
He has so little time for reading. 他读书的时间少得可怜。
I’ve never seen such little boxes. 我从未见过那样小的盒子。
八、不定代词 some 与 any 的用法区别
一般说来,不定代词 some 用于肯定句中,any 用于否定句和疑问句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的句子中,通常要用 some 而不用any:
Would you like some cake? 吃点蛋糕吗?
Why not buy some bread? 为什么不买些面包呢?
Shall I get some chalk for you? 要我帮你拿些粉笔来吗?
【说明】不定代词 any 有时也用于肯定句中,此时表示“任何”:
Any colour will do. 任何颜色都行。
Come any day you like. 随便哪天来都可以。
九、不定代词 many 与 much 的用法区别
不定代词 many 和 much 都表示“许多”,但 many 修饰或代替可数名词(复数),与 few(少数)相对;而 much 用来修饰或代替不可数名词(单数),与little(少量)相对。在口语中两者主要用于非肯定句中:
Did you see many people there? 你在那儿看见许多人了吗?
We don’t have much time. 我们没有许多时间。
在肯定句中,一般用 a lot of, lots of, plenty of 等代之。但在正式文体中有时也用于肯定句中;另外,若用作主语或主语的定语,或其前有 how, too, as, so, a good, a great 等修饰,也可用于肯定句中:
Many of us left early. 我们有许多人离开得很早。
Much work has been done. 许多工作都已经做了。
You’ve given me too much. 你已给我太多了。
Take as many (much) as you want. 你要多少拿多少。
I asked her a great many questions. 我问了她许多问题。
十、不定代词 few, a few 与 little, a little的用法区别
1. 不定代词 few 和 a few 后接可数名词的复数形式。few 表示数量很少或几乎没有,强调“少”,含有否定意义;a few 表示数量虽然少但毕竟还有,强调“有”,含有肯定意义:
It is very difficult, and few people understand it. 它很难,没有几个人能懂。
It is very difficult, but a few people understand it. 他虽难,但是有些人懂。
2. little 和 a little 之后接不可数名词,其区别跟 few 和 a few 之间的区别相似:
Unfortunately, I had little money on me. 很不巧,我身上没带什么钱。
Fortunately, I had a little money on me. 幸好我身上带着一点钱。
引自:***/Article/200802/103_3.html
以上就是关于不定代词代替名词例子 ,不定代词的句子举例的全部内容,以及不定代词代替名词例子 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。
