本文目录
如何判断用什么时态
如何判断使用英语动词的时态
要熟练、正确地运用动词的时态,首先要理解动词各种时态的意义、用法及其构成,然后再研究答题技巧。一般来说,判断动词的时态可以从以下四个方面入手:
一、注意时间状语的提示
所谓动词的时态指的是英语用于表现在不同的时间所发生的动作的动词形式,因此,动词特定的时态常常与特定的时间状语联系在一起。如:
at
this
time
tomorrow
_______
over
the
atlantic.
a.
we’re
going
to
flying
b.
we’ll
be
flying
c.
we’ll
fly
d.
we’re
to
fly
题中的时间状语at
this
time
tomorrow
表示的是时间点,而表示在某个瞬间发生的动作是进行时的基本用法,故选b。
二、注意句型与动词时态之间的对应关系。
在英语中,不少句型与一些动词在时态的运用方面都存在着特定的对应关系,在很多情况下正确地判断句子中动词时态的运用就是一件轻而易举的事情了。如:
let’s
keep
to
the
point
or
we
______
any
decisions.
a.
will
never
reach
b.
have
never
reached
c.
never
reach
d.
never
reached
在句型“祈使句+and/or
+
陈述句”中,陈述句的谓语要用“will+动词原形”,故选a。
三、注意某些动词与时态的对应关系。
在英语里有些动词与时态有着特定的对应关系,即有些动词只能用于某种或某些时态,而不能用于另一种或另一些时态。如果我们注意到某些动词与时态的这些对应关系,也能准确地判断动词的时态。如:
--can
i
help
you,
sir?
--yes,
i
bought
this
radio
here
yesterday,
but
it
______.
a.
didn’t
work
b.
won’t
work
c.
can’t
work
d.
doesn’t
work
work一词表示机器不能正常运转、运行的意思时,用一般现在时的否定式,不用其他时态,故选d。而open,
close,
lock
等词表示门、窗等不能正常开、关、锁的意思时,则要用将来时的否定形式,即won’t
open/close/lock等,这是它们是以主动的形式表示被动的意义,等于can’t
be
opened/closed/locked等。
四、注意上下文的提示。
在绝大多数的情况下,动词的时态是由上下文决定的,这就要求我们一方面要熟记各种时态的适用范围,另一方面要求我们注意上下文的提示。如:
--is
this
raincoat
yours?
--no,
mine
_______
there
behind
the
door.
a.
is
hanging
b.
has
hung
c.
hangs
d.
hung
根据上下文的提示,hang表示的是目前的状态,故选a。
判断时态的方法及相关例句
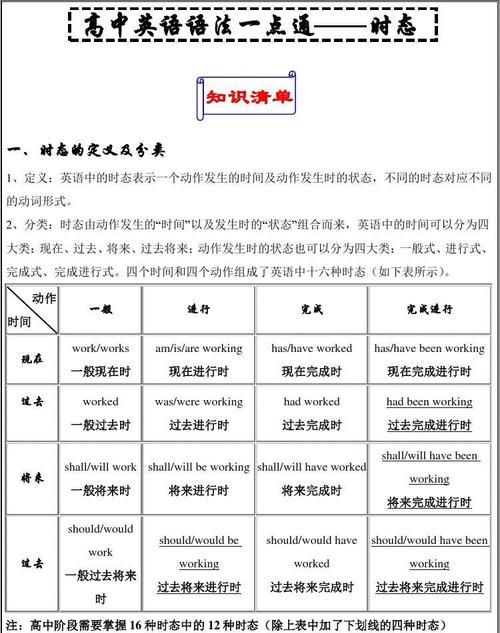
一、根据时间状语与时态的对应关系 动词特定的时态常常与特定的时间状语联系在一起,如由this time yesterday可知用过去进行时;由so far, in the past three years, till now可知要用完成时,等等。
1、句中含有yesterday; last year(last + 具体时间); two days ago(一段时间 + ago); just now; this morning; in 2008(in + 过去的年代); the other day; over the weekend等时间状语时,谓语动词用一般过去时;
2、句中含有tomorrow; next week(next +具体时间); in two hours(in +一段时间); (how) soon; from now on; 10 years from now(一段时间+from now); in the future; in 2012(in +将来的年代); by (the end of) next month(by+将来时间); for the weekend; this afternoon; this evening; tonight; this weekend等时间状语时,谓语动词用一般将来时;
3、句中既有yesterday等过去时间状语,又有一个具体时间点(at 5:00; this time; at that time)时,谓语动词用过去进行时;
4、句中含有recently; in the last/past two years(in the last/past+一段时间); over the years(over the+一段时间); since 2005(since+具体时间或从句); for two years(for+一段时间,句中无其它时间状语); before(单独用于句尾)等时间状语时,谓语动词用现在完成时;
5、by (the end of) last year(by+过去时间); two days before(一段时间+before); for和since说明的时间同时用于句中;by the time + 从句(过去时态)等时间状语时,谓语动词用过去完成时;
6、简单句中如不含上述时间状语或有含说话时间在内的表示现在时间关系的词语时(如now; today; these days等词)解析:由时间状语at this time tomorrow可知用将来进行时,故选B。
二、固定句型与动词时态间的对应关系 在英语中,不少句型与一些动词在时态的运用方面都存在着特定的对应关系,
1.在“祈使句+and/or+陈述句”句型中,陈述句中用will表示的一般将来时;
2.在This/如That/It is t he second time that…句型中用现在完成时,若is改为was,就用过去完成时;
3.在no soon er…than…和hardly…when…句型中,前面常用过去完成时,when/than后的句子用一般过去时;
4.was/were about to do…when…或was/were doing…when…或was/were on the point of doing…when…句型中,when分句的谓语动词用一般过时;
5.在一个含有时间状语从句的主从复合句中,如果主从句的谓语动词都是过去发生的动作,一般来说,表示短暂性动作的动词用一般过去时,表示持续性动作的动词用过去进行时;等等。
Let’s keep to the point or we _______ any decisions.
A. will never reach B. have never reached C. never reach D. never reached
解析:这是“祈使句+or +陈述句”句型,陈述句的谓语要用“will+动词原形”,故选A。
三、根据某些动词与时态的对应关系 在英语里有些动词与时态有着特定的对应关系,如see(看见),hear(听见),find(找到) 等都不可用于进行时态;work表示机器不能正常运行、运转时,常用一般现在时的否定式;open, close, lock等词表示门、窗等不能正常关、开、锁的意思时,常用won’t open /close /lock等,这时它们是以主动形式表示被动意义。
—Can I help you, sir? —Yes. I bought this radio here yesterday, but it _____.
A.didn’t work B. won’t work C. can’t work D. doesn’t work 解析:此处的work是指radio不能正常运行,应用一般现在时的否定式,故选D。
四、根据上下语境来确定时态 在绝大多数情况下,动词的时态是由上下文来决定的,这就要求我们一方面要熟记各种时态的适用范围,另一方面要求我们注意上下文的提示。
— Is this raincoat yours? — No, mine ______ there behind the door.
A.is hanging B. has hung C. hangs D. hung
解析:根据上下文的提示,hang表示的是目前的状态,故选A。
五、主从句时态的一致性原则:主从复合句可根据其时态一致性原则,通过主从句中任意一个句子的时态确定另外一个句子的时态;含有时间状语从句的主从句还可通过其引导词所表示的不同时间关系,确定主句和从句的时态。

英语中如何判断句子的时态和语态
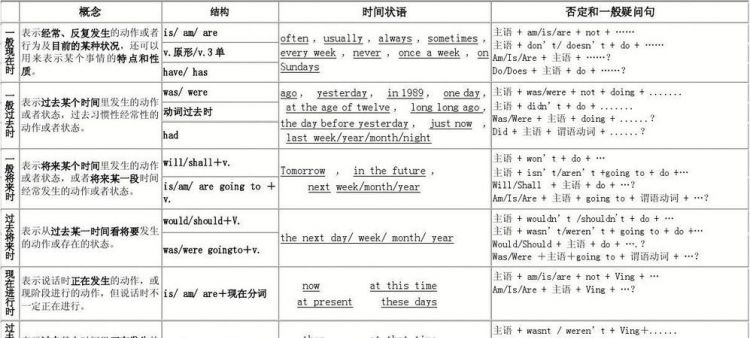
一般情况下看时间状语
一、一般现在时 表示一般状态、习惯动作、客观规律和永恒真理
二、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动;或表感情色彩,加强浯气.
三、现在完成时 表目前已完成的动作,强调对现在的影响.时间是算到你说话的时候为止,而且现在完成时有一些标志性的时间状语: 1.for+时间段;I have learned English for ten years. 2.常见的副词:lately;recently, just,up to now, till now, so far, these days, in the past few years/months/weeks/days 3.注意:for+时间段;since+时间点 They have lived in Beijing for five years. They have lived in Beijing since l995. 4.This is the first time that I have watched stars through a telescope. 第几次做某事,后面跟现在完成时.
四、一般过去时 表在过去某个特定时间发生且完成的动作,或过去习惯性动作,不强调对现在的影响,只说明过去.常跟明确的过去时间连用,如:yesterday;last week;in 1945,at that time;once;during the war;before;a few days ago;when,注意: 1、used to+动词原形,表过去经常但现在已不再维持的习惯动作. He used to smoke. 2、be/become/get used to+动名词doing,表习惯于 He has got used to getting up early. He used to smoke a lot. 3、They have lived in Beijing for five years. 用现在完成时表示到目前是5年. He lived in Japan for five years as a middle-school student. 用一般过去时则表示这个时间段和现在无关,只表示他过去在日本住了5年.
五、过去进行时 表示过去某个时间点或某段时间内正在发生的动作. The boy was doing his homework when his father came back from work. He was taking a leisurely walk by the lake when he heard someone shouted for help. 六、过去完成时 表示过去某个时间之前已经完成的动作,句中有明显的参照动作或时间,before,after,by,up till There had been 25 parks in our city up till 2000. By the end of last term we had finished the book. They finished earlier than we had expected.
一 ,一般现在时的用法
1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用.时间状语: every…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday.例如: I leave home for school at 7 every morning.
2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实.例如: The earth moves around the sun. 3 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性.例如:I don't want so much. 我不要那么多. Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行.
二, 一般过去时的用法
1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态.例如:时间状语有:yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982等.例如: Where did you go just now?
2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作.例如: When I was a child, I often played football in the street. 我是个孩子的时候,常在马路上踢足球.
三, 一般将来时 将来某一时刻将要发生的动作或状态I will come to see you tomorrow.
2)be going to do a. 主语的意图,即将做某事.例如:What are you going to do tomorrow? b. 计划,安排要发生的事.例如:The play is going to be produced next month.这出戏下月开播.c. 有迹象要发生的事.例如:Look at the dark clouds, there is going to be a storm. 看那乌云,快要下雨了.
3)be +不定式表将来,按计划或正式安排将发生的事. We are to discuss the report next Saturday.
4)be about to do,意为马上做某事.例如: He is about to leave for Beijing. 注意:be about to do 不能与tomorrow, next week 等表示明确将来时的时间状语连用.
四 , 现在进行时现在进行时的基本用法: a. 表示现在(指说话人说话时)正在发生的事情.We are waiting for you. b. 习惯进行:表示长期的或重复性的动作, Mr. Green is writing another novel. 他在写另一部小说.(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态.) c. 表示渐变,这样的动词有:get, grow, become, turn, run, go, begin等. It's getting warmer and warmer. 天越来越热了. d. 与always, constantly, forever 等词连用,表示反复发生的动作或持续存在的状态,往往带有说话人的主观色彩.You are always changing your mind. 你老是改变主意
五, 过去进行时
1)概念:表示过去某时正在进行的状态或动作.
2)常用的时间状语有this morning, the whole morning, all day yesterday, from nine to ten last evening, when, while等.My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself. It was raining when they left the station.
六,将来进行时
1) 概念:表示将来某时进行的状态或动作,或按预测将来会发生的事情.She'll be coming soon.
2)常用的时间状语有soon, tomorrow, this evening,on Sunday, by this time,tomorrow, in two days, tomorrow evening等.例如:By this time tomorrow, I'll be lying on the beach.
七,在完成时 用来表示之前已发生或完成的动作或状态,其结果的影响现在还存在;也可表示持续到现在的动作或状态.其构成:have(has)+过去分词.
现在完成时例句Tom has finished his home work and he is watching TV now.(完成作业是过去的动作,但对现在造成了影响,用现在完成时)He has lived here for 5 years.(居住的动作从5年前一直持续到现在,用现在完成时.)现在完成时时间状语:ever,many times,recently,just,yet,already,before等.八 过去完成时结构 主语+had+过去分词 表示过去某一动作或时刻之前完成的动作或状态,即过去的过去.时间状语:by,before,until,when例句 When Jack arrived,he learned Mary had been away for almost an hour.(Mary 离开在Jack到达这个过去的动作之前发生,用过去完成时)
-----------
引导时间状语的句子通常附有时间名词,若无,必须经过上下文的推敲来得知是否改用时间状语,其引导词通常有when,while,before,after等.时间状语只是属于复合句的一种,不属于动词时态.但往往动词时态会运用于时间状语中.动词时态一共有16中,每一种都有可能用于时间状语
怎样判断英语用什么时态
不知道你问什么语言,姑且当英语吧。
第一, 要注意句子中的时间状语,这是最重要的判断时态的标志。如果是 tomorrow, 通常是将来时,如果是 yesterday, last week, 通常是过去时。如果是 right now, now, 通常是将来时。 但是,什么都有例外,比如有时虽然是将来时的时间状语,但是用现在进行时表示,就是进行时表示将来时,要注意。
第二,要注意在间接引语中,比如she said, he told us, 后面的时态通常往后面退一个,比如, he is leaving for Shanghai tomorrow. He said he was leaving for Shanghai tomorrow.
第三,有很多情况没有明显的时间状语,比如现在完成时,但是基本每一种时态都有自己的特点,掌握好了这个特点你的问题就会迎刃而解。
good luck
以上就是关于判断时态的方法 ,如何判断用什么时态的全部内容,以及判断时态的方法 的相关内容,希望能够帮到您。

